Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
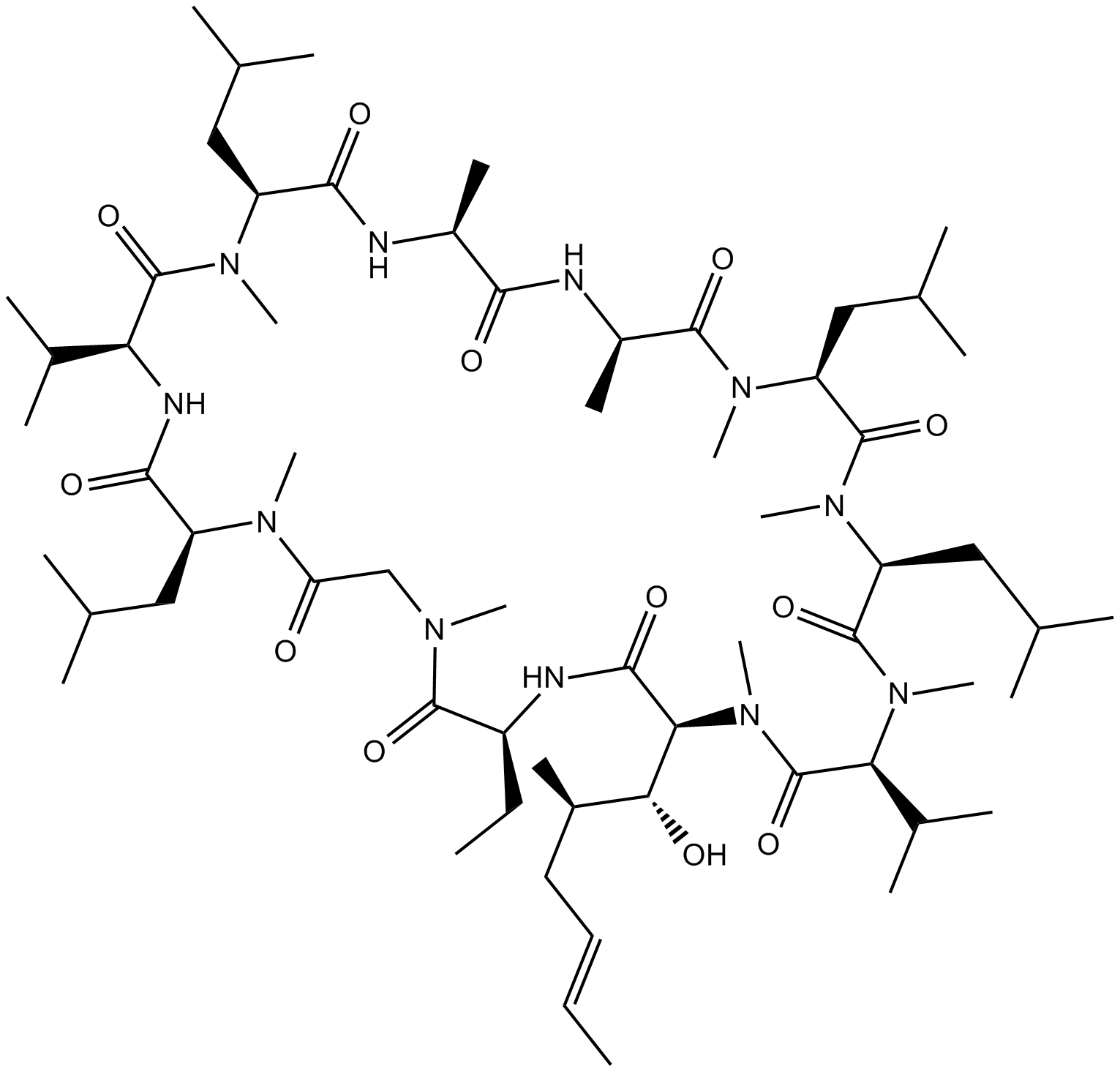 B1922 Cyclosporin A8 CitationSummary: immunosuppressive agent
B1922 Cyclosporin A8 CitationSummary: immunosuppressive agent -
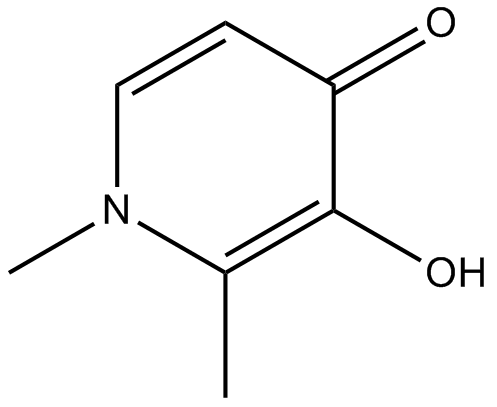 B1723 DeferiproneSummary: Chelating agent
B1723 DeferiproneSummary: Chelating agent -
 B1928 Diclofenac DiethylamineSummary: non-selective COX inhibitor
B1928 Diclofenac DiethylamineSummary: non-selective COX inhibitor -
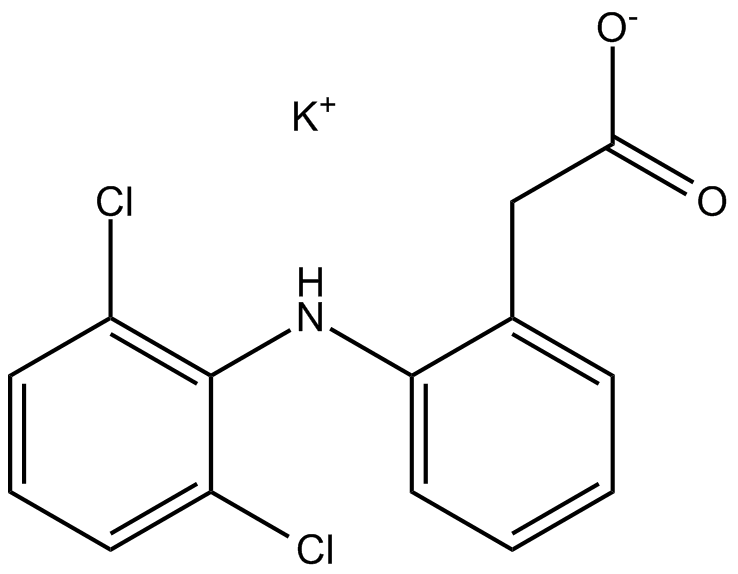 B1929 Diclofenac PotassiumSummary: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
B1929 Diclofenac PotassiumSummary: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug -
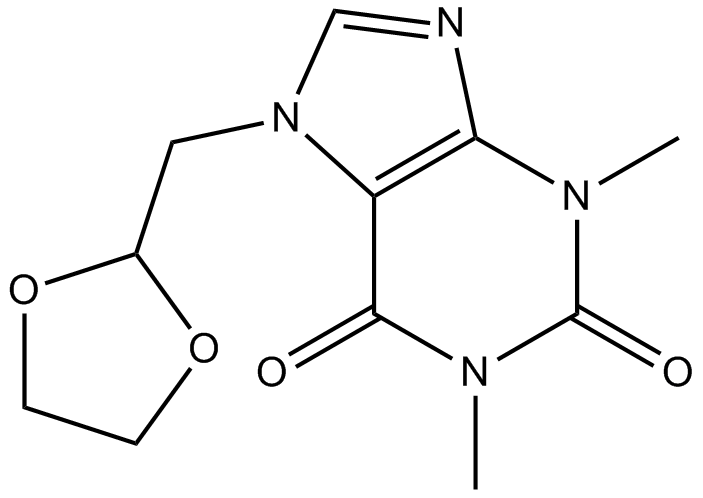 B1734 DoxofyllineSummary: PDE inhibitor
B1734 DoxofyllineSummary: PDE inhibitor -
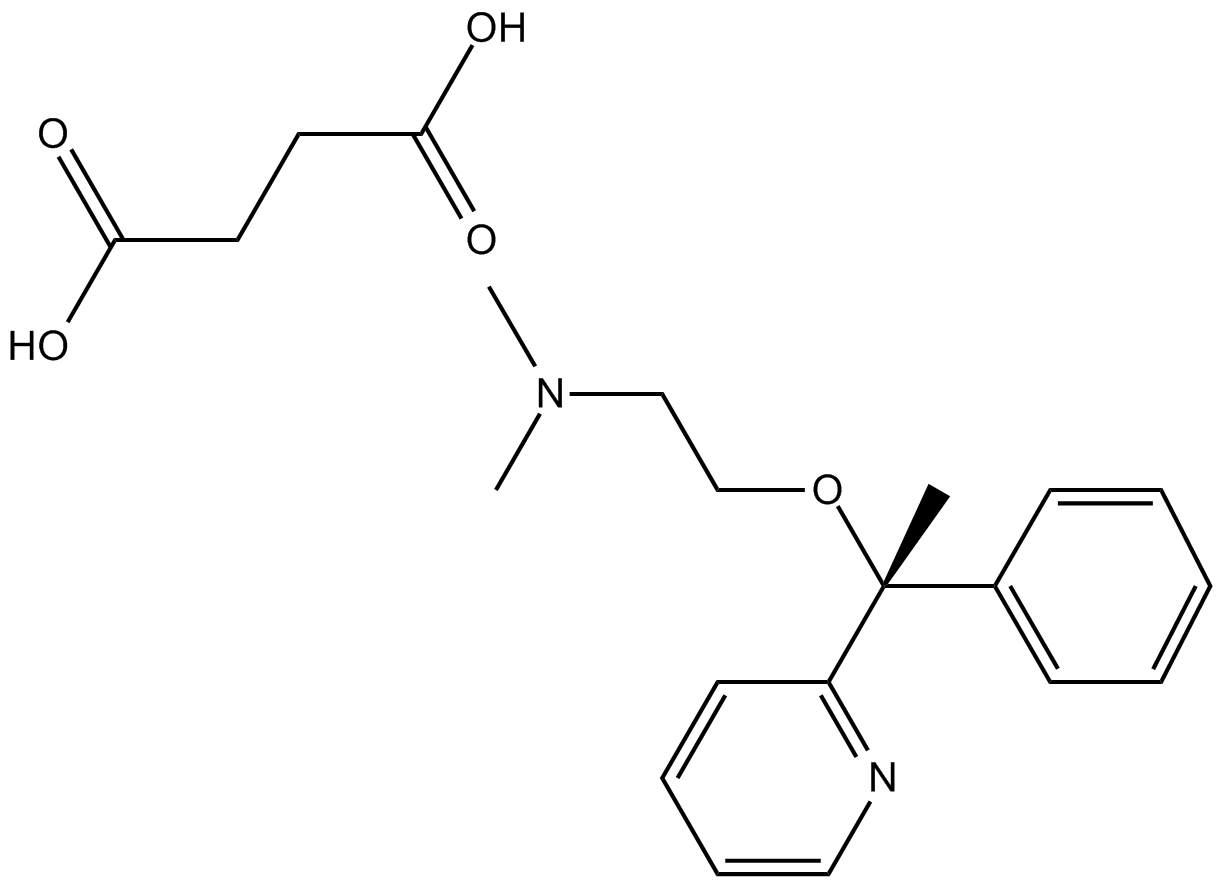 B1735 Doxylamine SuccinateSummary: Histamine receptor inhibitor
B1735 Doxylamine SuccinateSummary: Histamine receptor inhibitor -
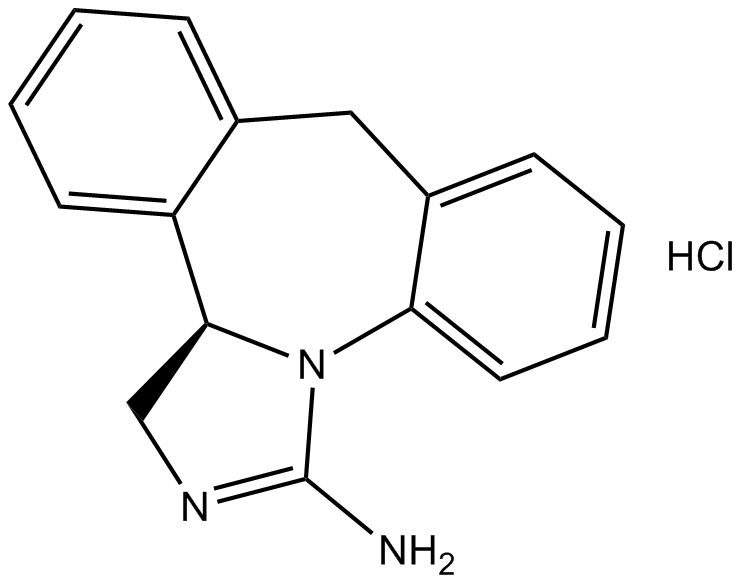 B1744 Epinastine HClTarget: Histamine H1 ReceptorsSummary: Histamine receptor antagonist
B1744 Epinastine HClTarget: Histamine H1 ReceptorsSummary: Histamine receptor antagonist -
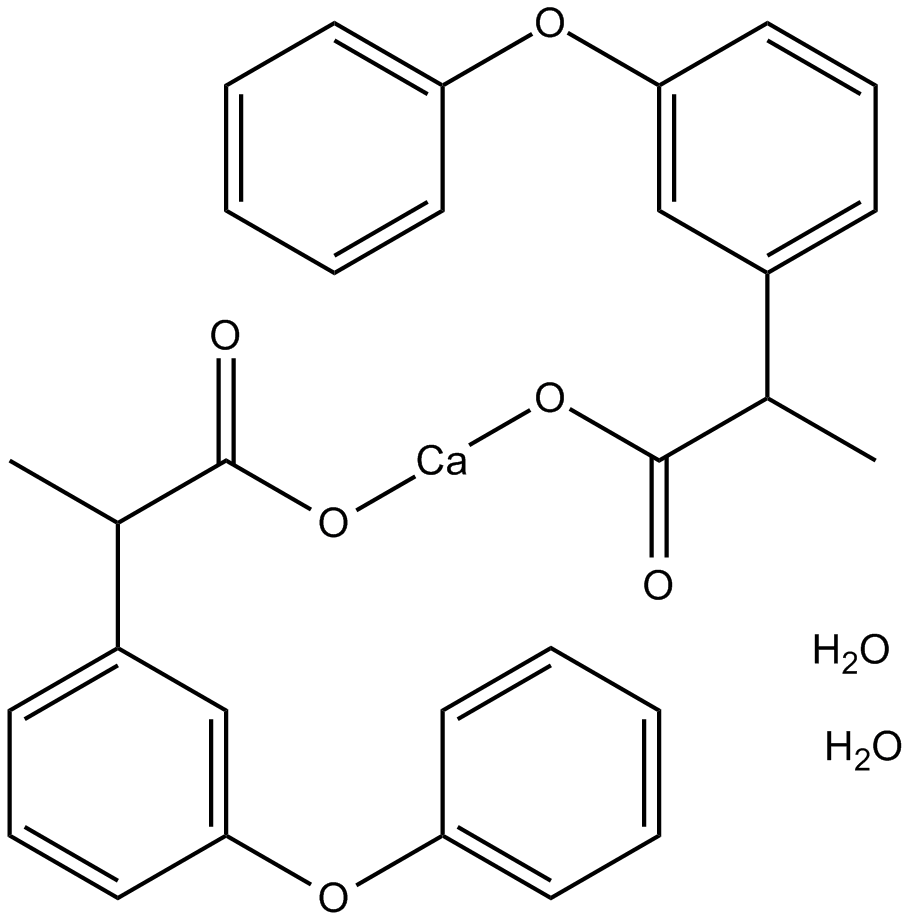 B1945 Fenoprofen calcium hydrateSummary: nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory antiarthritic agent
B1945 Fenoprofen calcium hydrateSummary: nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory antiarthritic agent -
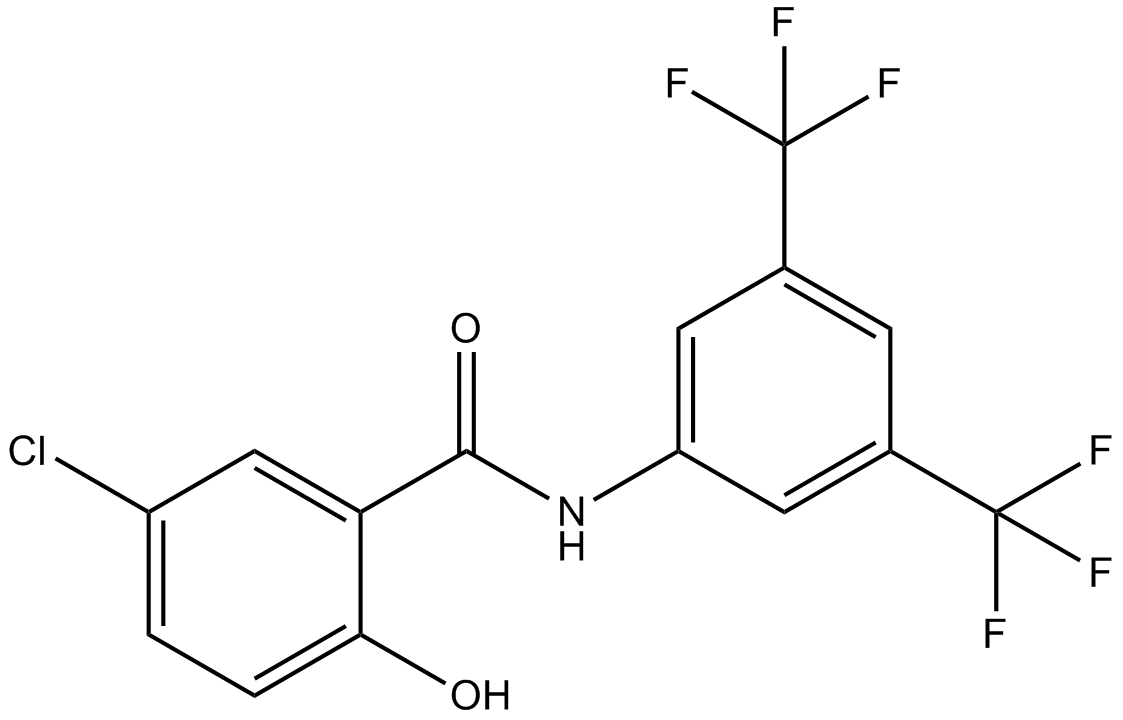 B1587 IMD 03541 CitationSummary: IKKβ inhibitor
B1587 IMD 03541 CitationSummary: IKKβ inhibitor -
 B1646 ML130 (Nodinitib-1)Target: NOD1Summary: Potent and selective inhibitor of NOD1
B1646 ML130 (Nodinitib-1)Target: NOD1Summary: Potent and selective inhibitor of NOD1


