Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
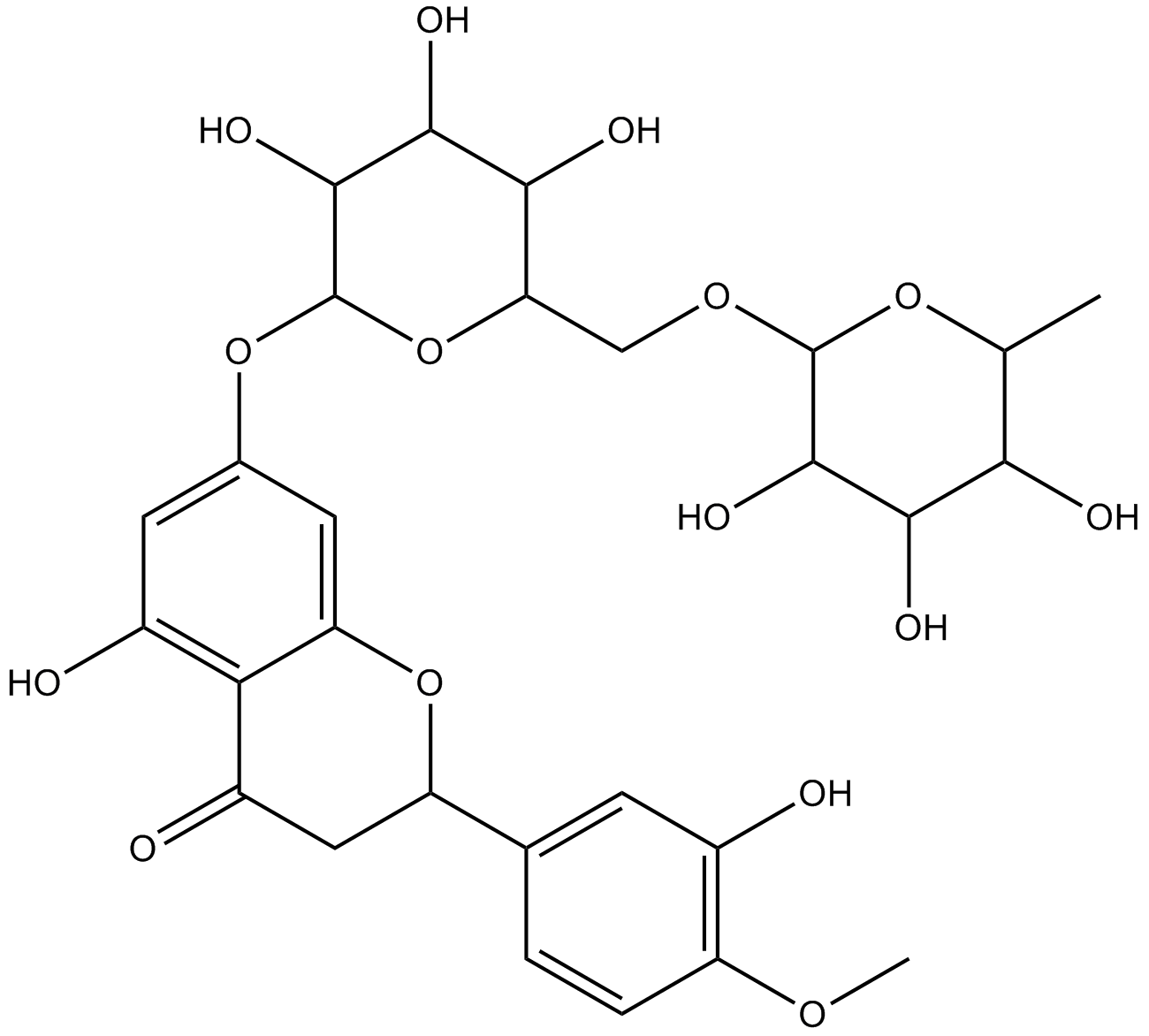 N1809 HesperidinSummary: Flavonoids from citrus species
N1809 HesperidinSummary: Flavonoids from citrus species -
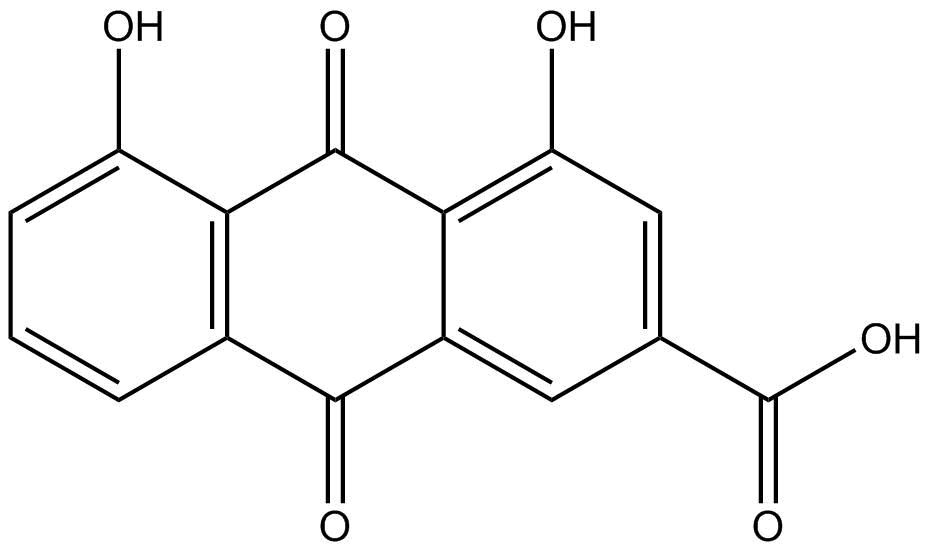 N1810 Rhein
N1810 Rhein -
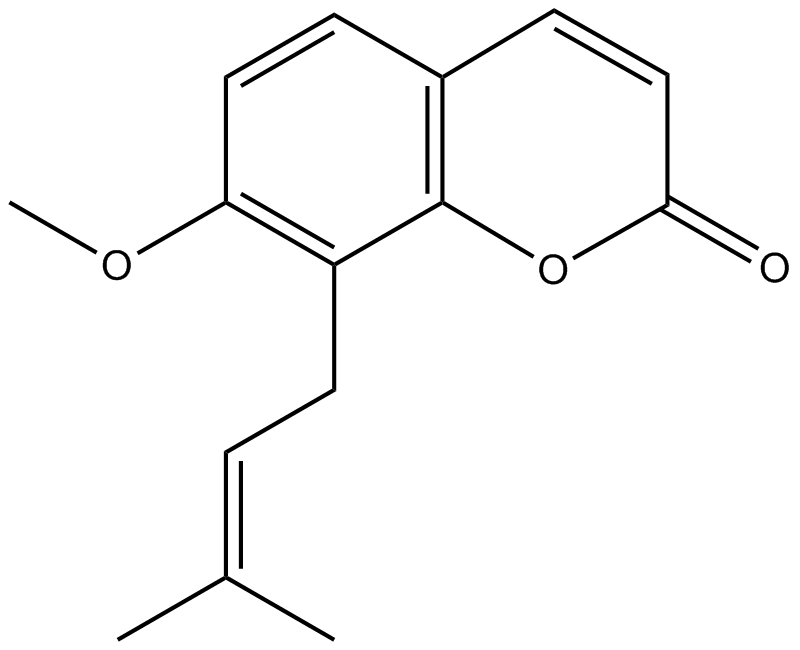 N1825 OstholeTarget: Histamine H1 ReceptorsSummary: Antitumor reagent
N1825 OstholeTarget: Histamine H1 ReceptorsSummary: Antitumor reagent -
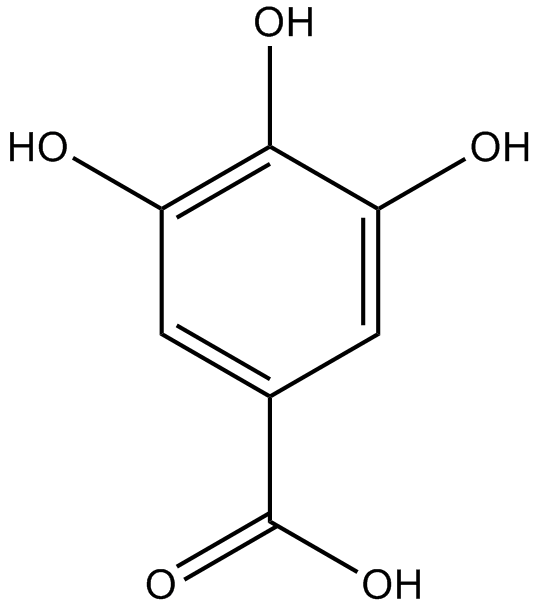 N1830 Gallic acidTarget: Antioxidants
N1830 Gallic acidTarget: Antioxidants -
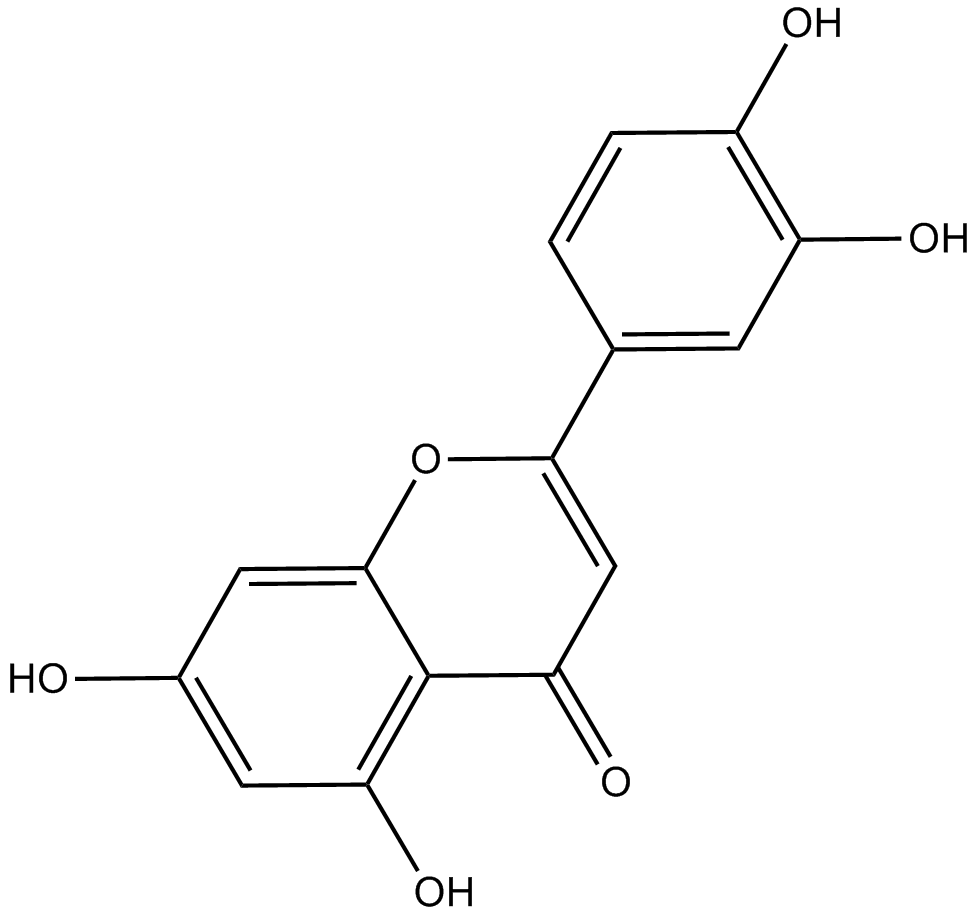 N1831 LuteolinTarget: AP-1|MMP|15-lipoxygenasesSummary: Antioxidant and free radical scavenger
N1831 LuteolinTarget: AP-1|MMP|15-lipoxygenasesSummary: Antioxidant and free radical scavenger -
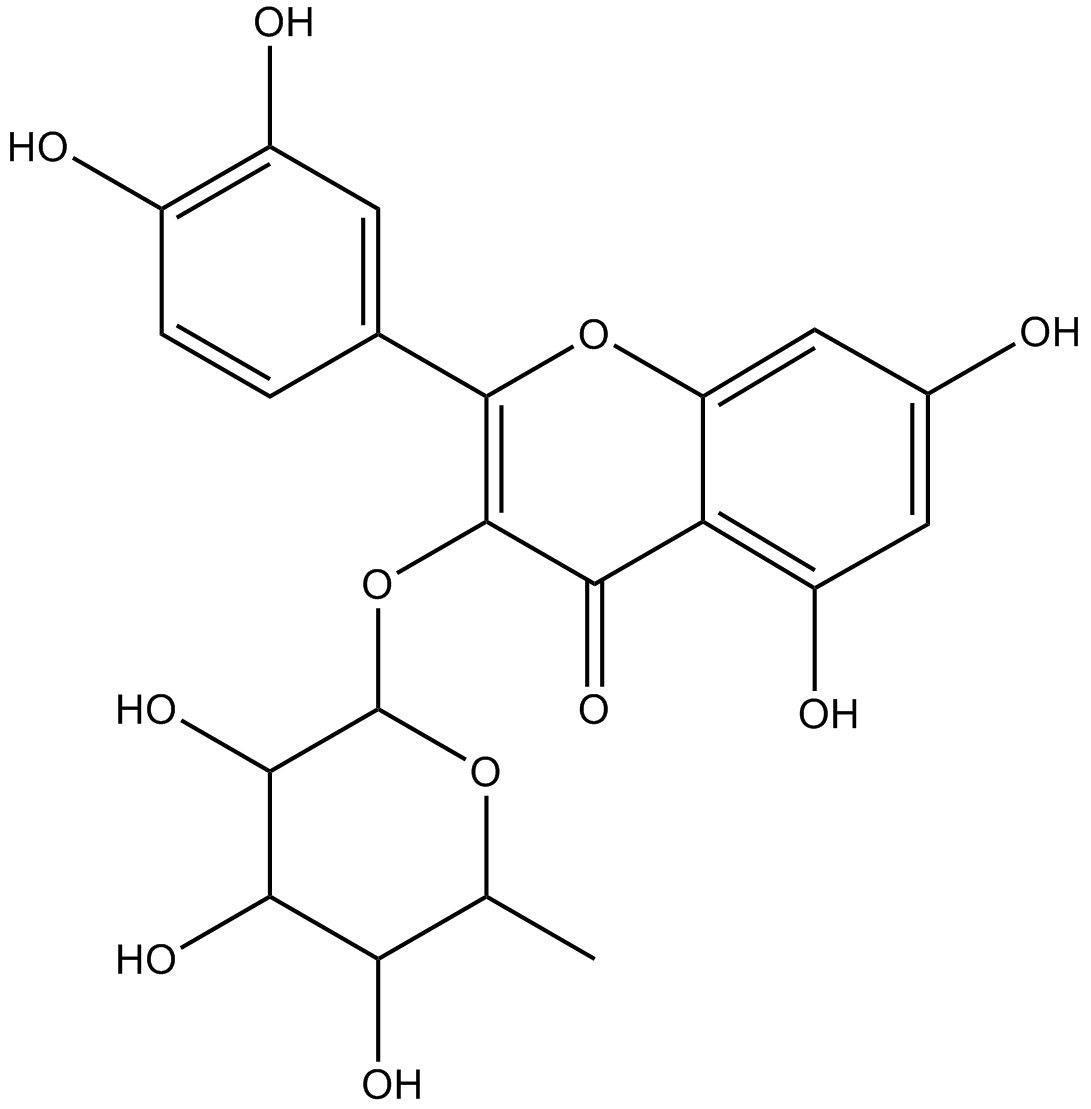 N1840 QuercitrinSummary: Natural flavonoid antioxidant
N1840 QuercitrinSummary: Natural flavonoid antioxidant -
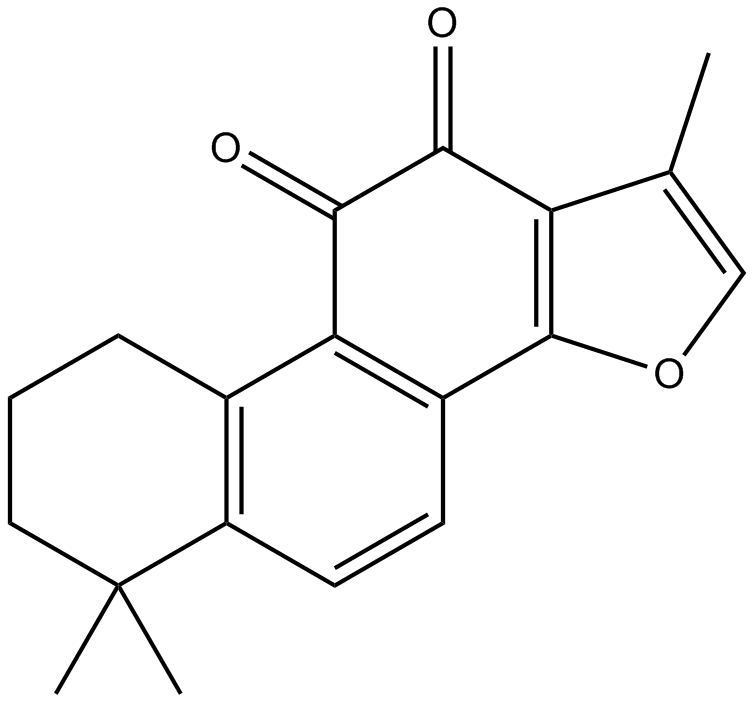 N1846 Tanshinone IIATarget: AP-1|MAGLSummary: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory reagent
N1846 Tanshinone IIATarget: AP-1|MAGLSummary: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory reagent -
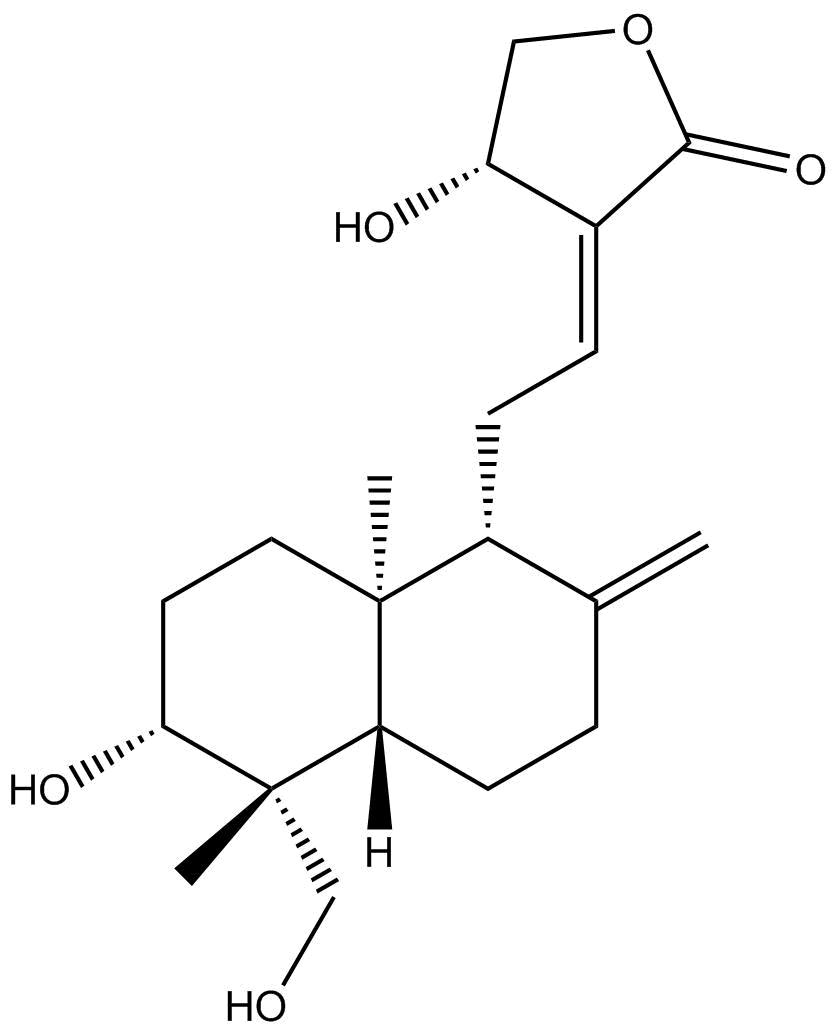 N1855 AndrographolideSummary: NF-κB signaling Inhibitor
N1855 AndrographolideSummary: NF-κB signaling Inhibitor -
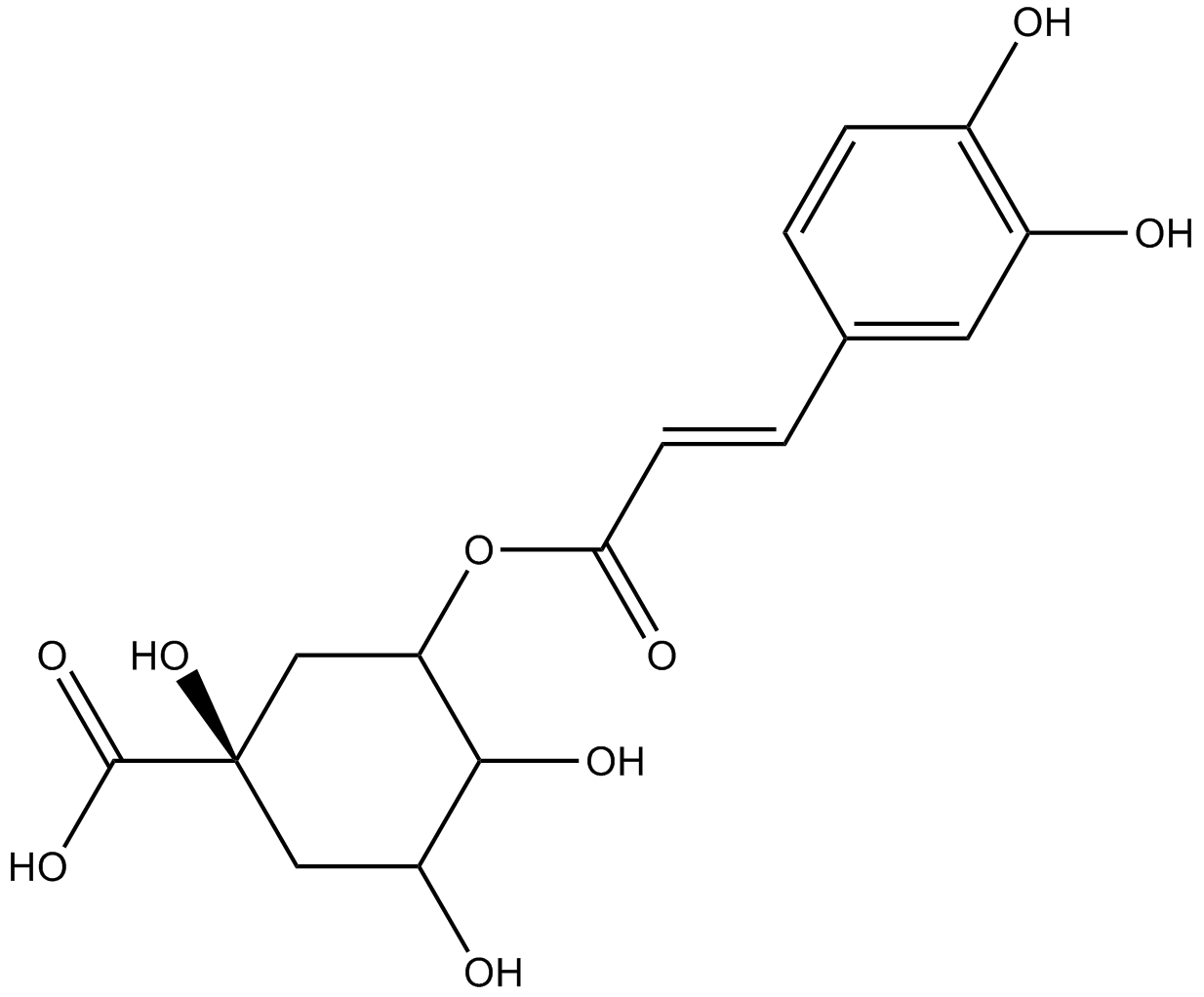 N1857 Neochlorogenic acid
N1857 Neochlorogenic acid -
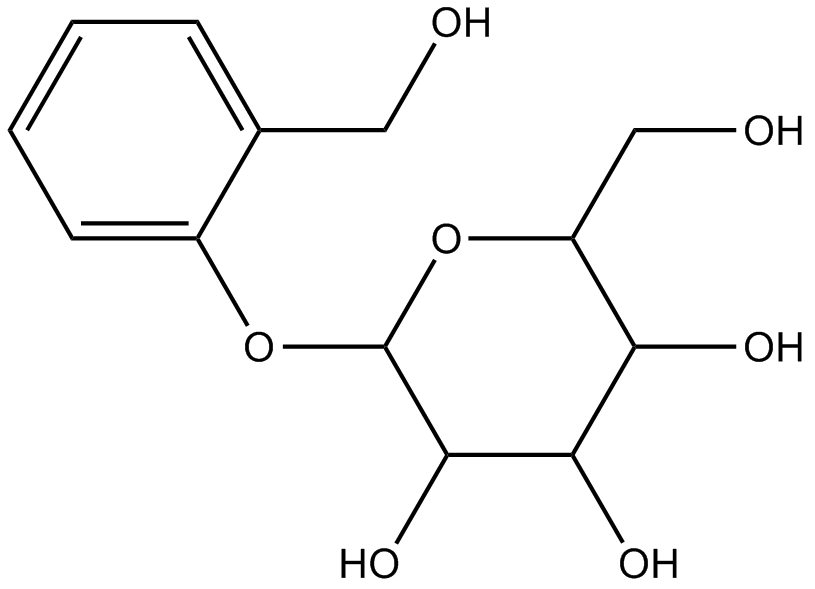 N1880 D-(-)-Salicin
N1880 D-(-)-Salicin


