GPCR/G protein
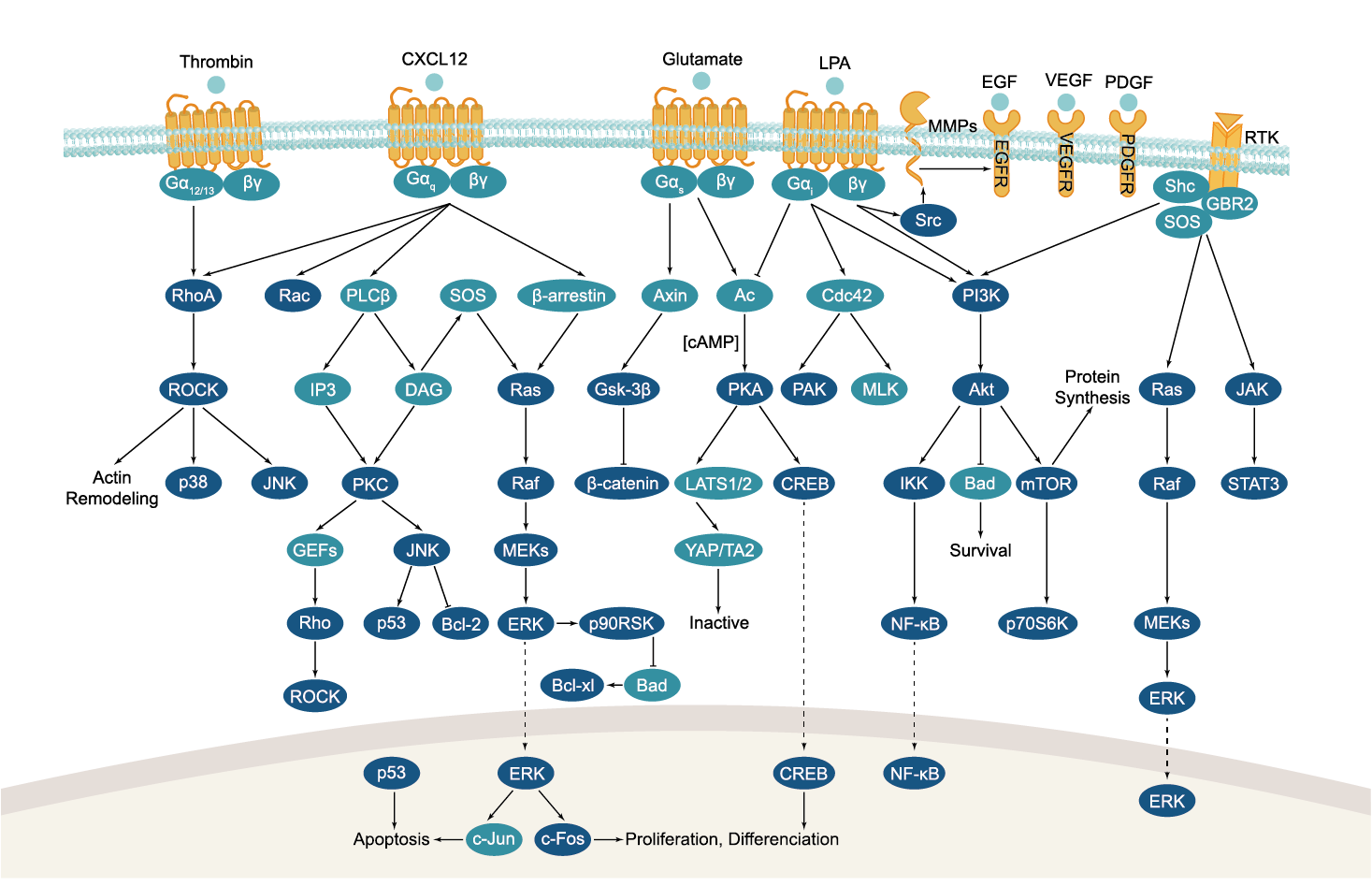

All GPCRs share a common seven trans-membrane structure. GPCRs are associated with heterotrimeric G-proteins which are GTP-binding proteins made of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. When a ligand binds to GPCR, it activates the attached G-protein, the GDP is replaced with GTP. The activated G-protein then dissociates into an alpha and a beta-gamma complex which activates downstream signaling pathways. These intracellular signaling pathways include cAMP/PKA, calcium/NFAT, phospholipase C, protein tyrosine kinases, MAP kinases, PI-3-kinase, nitric oxide/cGMP, Rho, and JAK/STAT.
GPCRs are one of the most important therapeutic targets for various diseases, over 30% of all modern medicinal drugs target this family. Aberrant GPCR functions are involved in pathological conditions such as neurological, immunological and hormonal disorders. A large number of GPCRs have been identified, but whose ligands are not known, are classified as orphan receptors.
-
 BA8984 SoquelitinibSummary: Soquelitinib (CPI-818) is a highly selective covalent inhibitor.
BA8984 SoquelitinibSummary: Soquelitinib (CPI-818) is a highly selective covalent inhibitor. -
 BA4021 LaflunimusSummary: Laflunimus (HR325) is an immunosuppressant and analog of Leflunomide active metabolite A771726.
BA4021 LaflunimusSummary: Laflunimus (HR325) is an immunosuppressant and analog of Leflunomide active metabolite A771726. -
 BA4132 KR-39038Summary: KR-39038 is an orally effective (G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5) inhibitor.
BA4132 KR-39038Summary: KR-39038 is an orally effective (G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5) inhibitor. -
 BA4280 N6,N6-DimethyladenosineSummary: N6,N6-Dimethyladenosine is a modified ribonucleoside.
BA4280 N6,N6-DimethyladenosineSummary: N6,N6-Dimethyladenosine is a modified ribonucleoside. -
 BA4296 5-Amino-5-deoxyadenosineSummary: 5'-Amino-5'-deoxyadenosine (NH2dAdo; Nsc238990) is a purine nucleoside analog.
BA4296 5-Amino-5-deoxyadenosineSummary: 5'-Amino-5'-deoxyadenosine (NH2dAdo; Nsc238990) is a purine nucleoside analog. -
 BA4409 NBI-42902Summary: NBI-42902 is an orally active potent functional and competitive antagonist of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor.
BA4409 NBI-42902Summary: NBI-42902 is an orally active potent functional and competitive antagonist of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor. -
 BA4450 HWL-088Summary: HWL-088 is a potent, orally active free fatty acid receptor 1 agonist (at 18.9 nM) with moderate activity (at 570.9 nM).
BA4450 HWL-088Summary: HWL-088 is a potent, orally active free fatty acid receptor 1 agonist (at 18.9 nM) with moderate activity (at 570.9 nM). -
 BA4464 RG-12525Summary: RG-12525 is a specific, competitive, orally available antagonist.
BA4464 RG-12525Summary: RG-12525 is a specific, competitive, orally available antagonist. -
 BA5012 TropisetronSummary: Tropisetron (SDZ-ICS-930freebase) is a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist.
BA5012 TropisetronSummary: Tropisetron (SDZ-ICS-930freebase) is a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. -
 BA5205 OLHHASummary: OLHHA is a dual receptor antagonist and agonist.
BA5205 OLHHASummary: OLHHA is a dual receptor antagonist and agonist.


