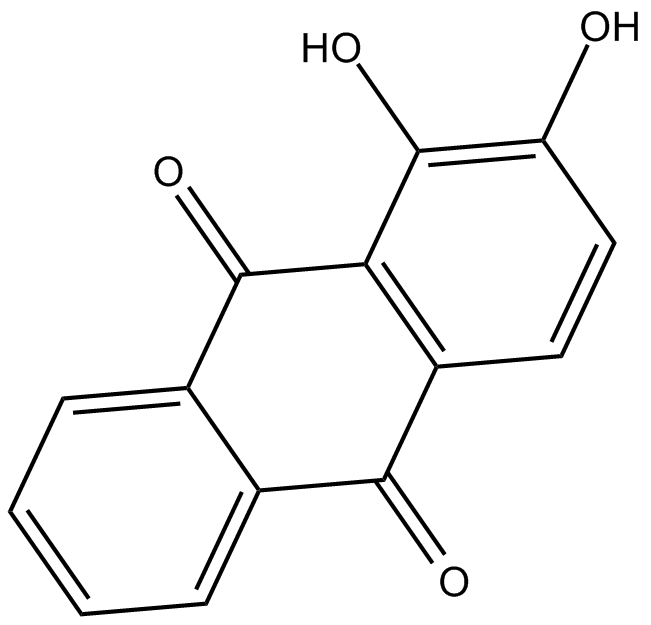
Alizarin
Alizarin (CAS 72-48-0) is a natural compound derived from the roots of plants of the Rubia genus. It has been traditionally used as a red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Particularly, in biological experiments, it is used to stain bacteria, human adipose-derived stem cells, multipotent adult progenitor cells, skin, hair, and keratin fibers. In addition, alizarin is an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 isoforms CYP1A1, CYP1A2, and CYP1B1 (IC50s = 6.2, 10, and 2.7 µM, respectively). Alizarin acts as an antioxidant against iodophenol-derived phenoxyl radicals, superoxide anion radicals, and lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes. It also reduces hepatic content of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and serum levels of alanine aminotransferase in poisoned rats. In cancer research, alizarin suppresses tumor expansion through inhibition of ERK-pathway related phosphorylation and induction of cell cycle arrest in S phase. In in vitro studies, Alizarin demonstrates antiproliferative activity in prostate cancer, breast cancer, and bone sarcoma cell lines.
References:
[1] Fotia C, Avnet S, Granchi D, Baldini N. The natural compound Alizarin as an osteotropic drug for the treatment of bone tumors. J Orthop Res. 2012 Sep;30(9):1486-92.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 240.21 |
| Cas No. | 72-48-0 |
| Formula | C14H8O4 |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥8.12 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 1,2-dihydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Oc(c(O)c1C(c2c3cccc2)=O)ccc1C3=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure