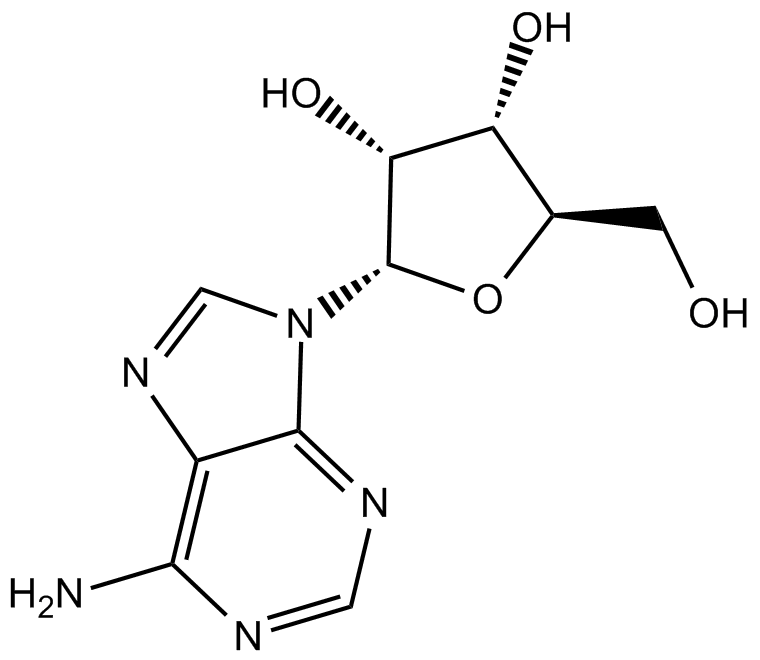
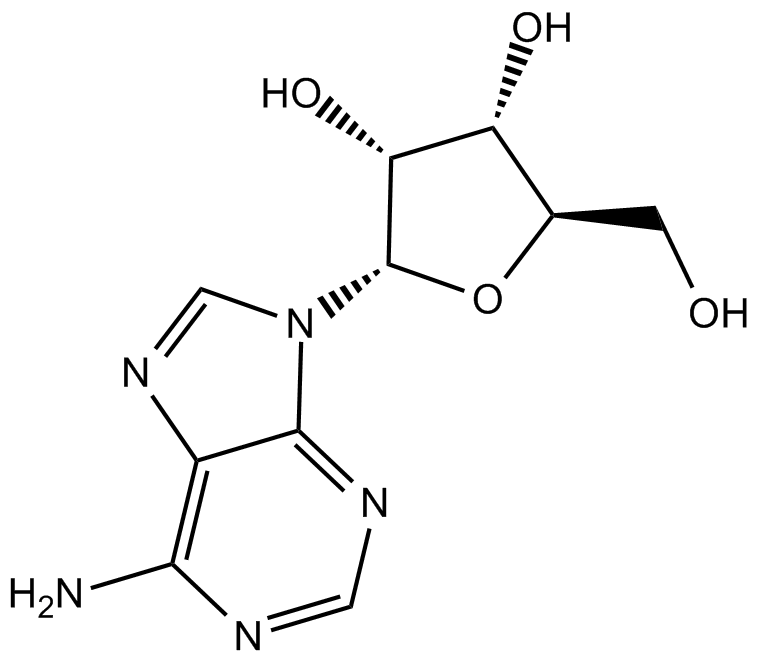
Adenosine
Adenosine (CAS 58-61-7) is a purine nucleoside consisting of adenine covalently linked to a ribose sugar via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Endogenously, adenosine modulates cellular signaling through activation of specific G protein-coupled adenosine receptors (A1, A2A, A2B, and A3), influencing diverse physiological processes such as neurotransmission, vasodilation, and immune responses. In biomedical research, adenosine is widely utilized to investigate purinergic signaling pathways, cardiac function, and the regulation of inflammatory and neuroprotective mechanisms, as well as serving as a pharmacological tool in receptor binding and functional assays.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 267.24 |
| Cas No. | 58-61-7 |
| Formula | C10H13N5O4 |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥12.75 mg/mL in DMSO with gentle warming |
| Chemical Name | (2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NC1=C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O3)C2=NC=N1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure