Neuroscience
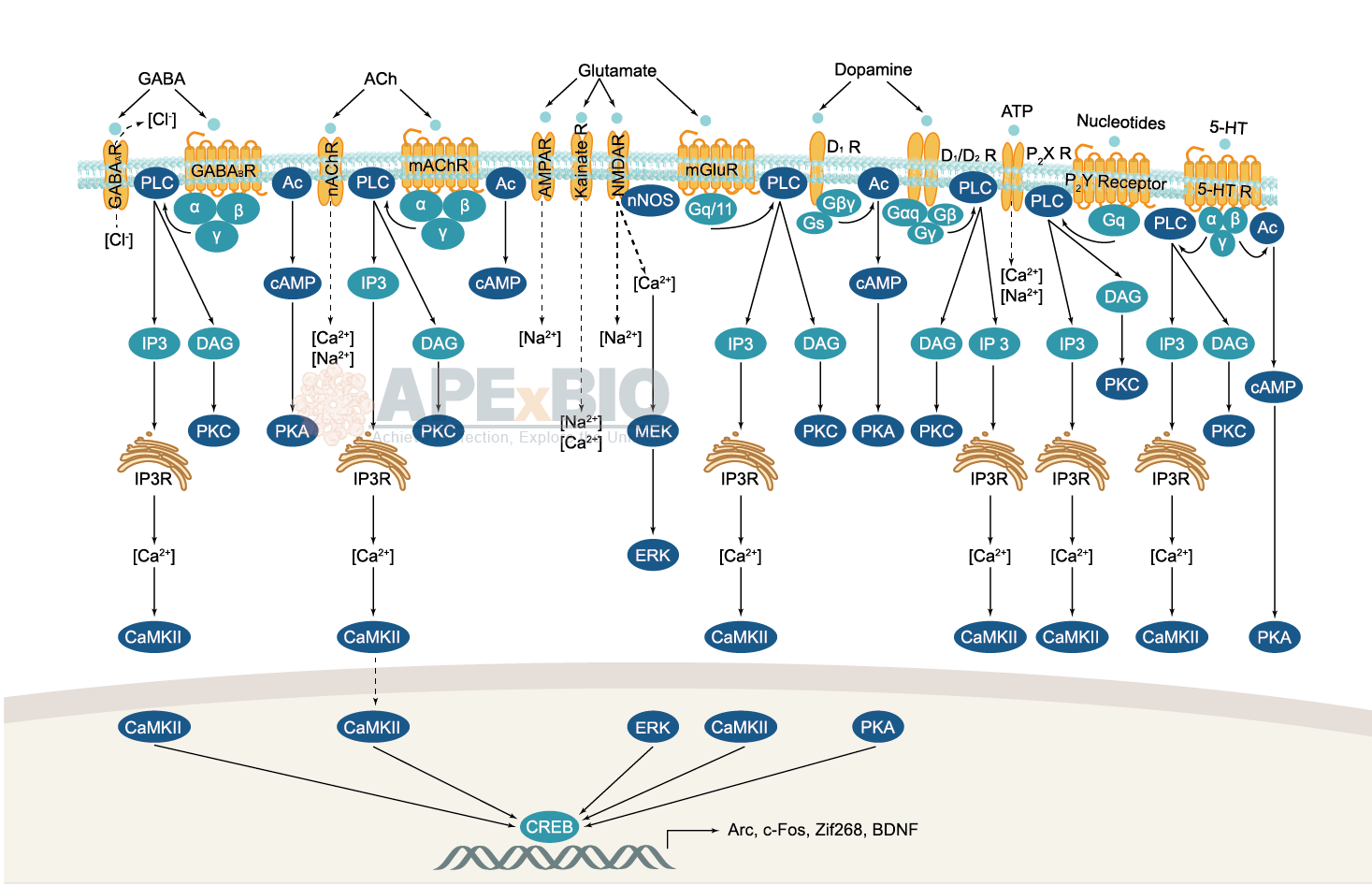

Neurons are the foundations of the sophisticated neural networks. Neurotransmitters such as dopamine, glutamate, and GABA, are crucial signaling molecules for the delivery of neuronal signals. Neurons synthesize/import neurotransmitters, and store them in presynaptic vesicles. A neuronal impulse is propagated by the vesicles released from presynaptic neurons.
Neurotransmitter receptors function via various G-protein coupled and G-protein independent mechanisms that activate downstream intracellular signaling pathways such as cAMP/PKA, PI3K/AKT, phospholipase A2, and phospholipase C pathways. For instance, dopamine receptors act through adenylate cyclase to activate PKA and other signaling molecules, thereby mediate gene expression through the actions of CREB and other transcription factors. Other neurotransmitters such as NMDAR or AMPAR are associated with ion channels that control flux of Ca2+ and Na+, thus propagating the action potential across the post-synaptic neuron.
Dysfunctions in GABAergic/glutamatergic/serotonergic/dopaminergic pathways result in a broad range of neurological disorders such as chronic pain, neurodegenerative diseases, and insomnia, as well as mental disorders including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, and addiction.
-
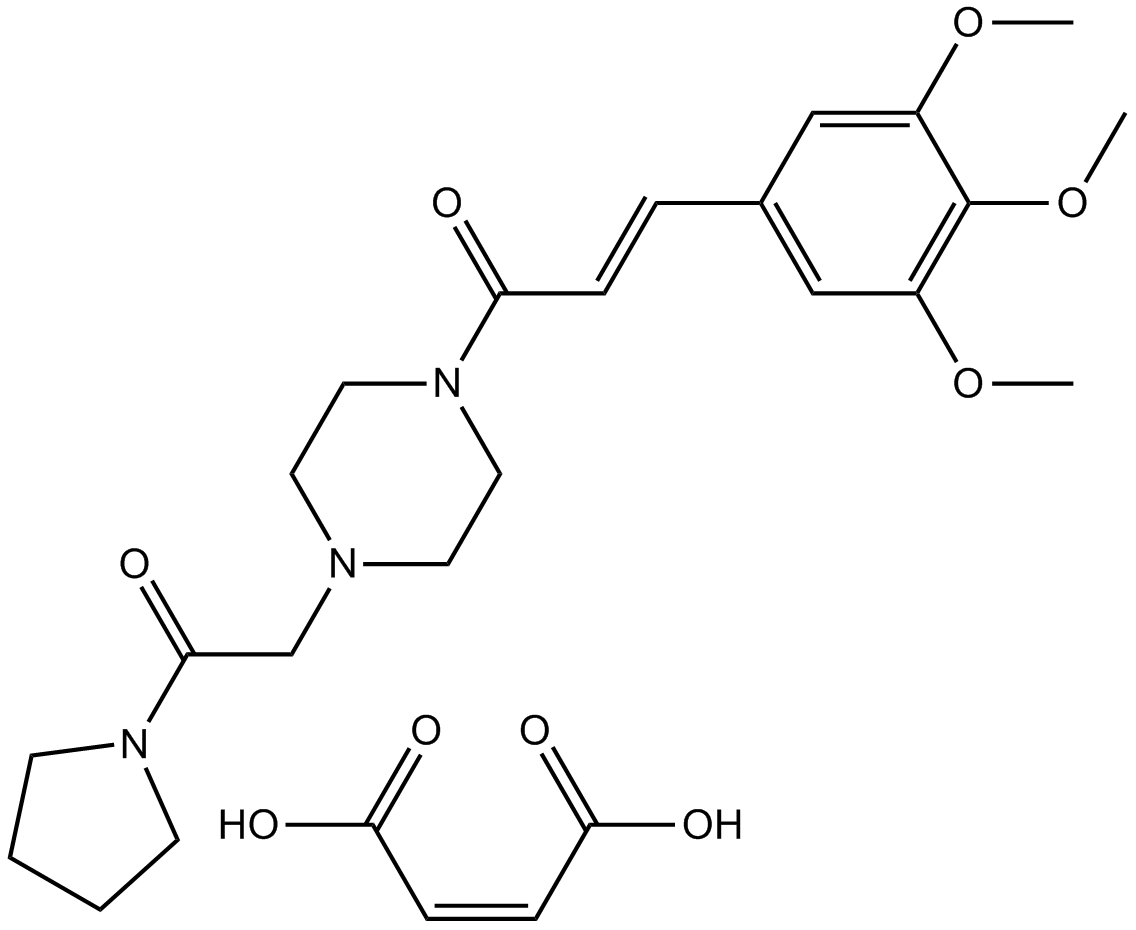 B1911 Cinepazide maleateSummary: Calcium channel inhibitor
B1911 Cinepazide maleateSummary: Calcium channel inhibitor -
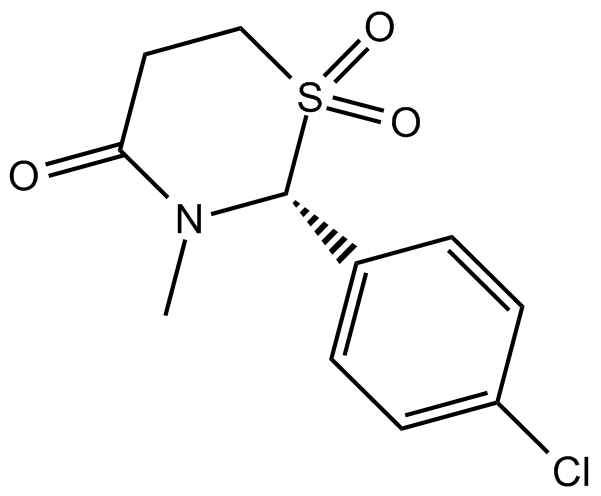 B1909 ChlormezanoneSummary: Anxiolytic and skeletal muscle relaxant
B1909 ChlormezanoneSummary: Anxiolytic and skeletal muscle relaxant -
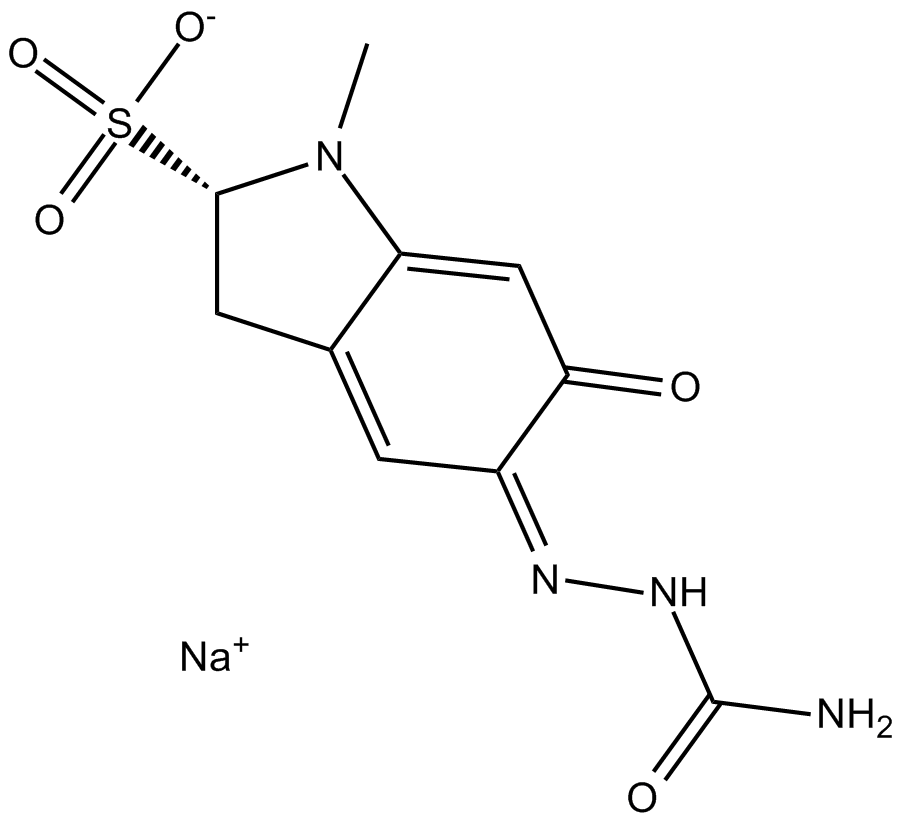 B1903 Carbazochrome sodium sulfonate (AC-17)Target: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)Summary: antihemorrhagic agent
B1903 Carbazochrome sodium sulfonate (AC-17)Target: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)Summary: antihemorrhagic agent -
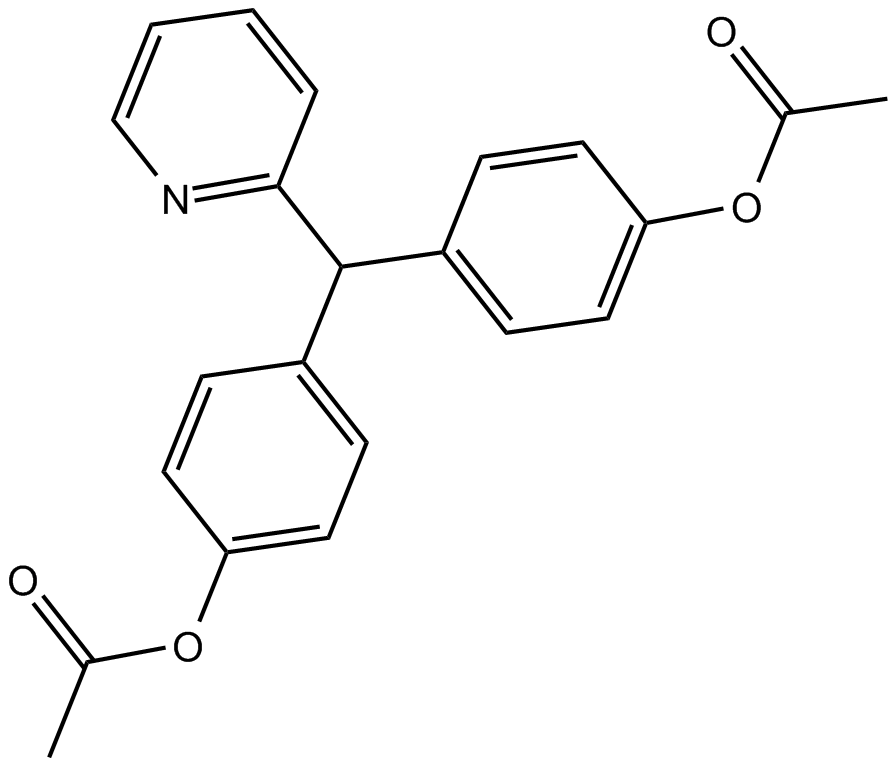 B1898 BisacodylSummary: stimulant laxative drug
B1898 BisacodylSummary: stimulant laxative drug -
 B1891 AzacyclonolSummary: tranquilizer,antipsychotic
B1891 AzacyclonolSummary: tranquilizer,antipsychotic -
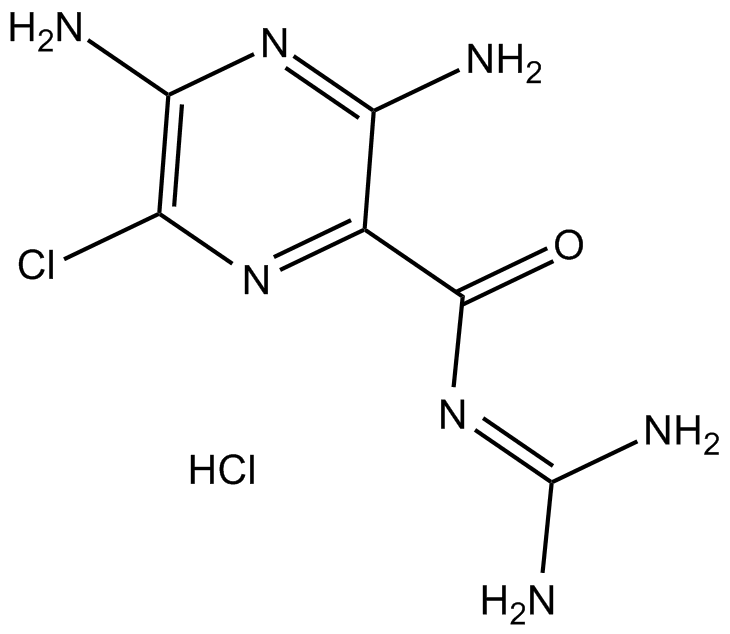 B1884 Amiloride HCl1 CitationSummary: epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) inhibitor, selective
B1884 Amiloride HCl1 CitationSummary: epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) inhibitor, selective -
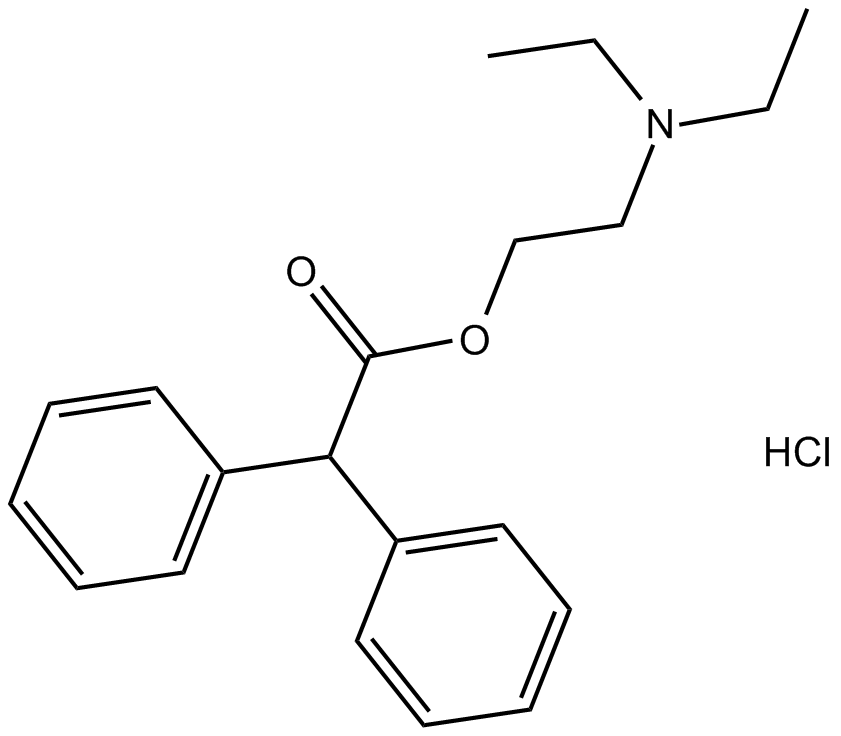 B1878 Adiphenine HClSummary: nicotinic receptor inhibitor
B1878 Adiphenine HClSummary: nicotinic receptor inhibitor -
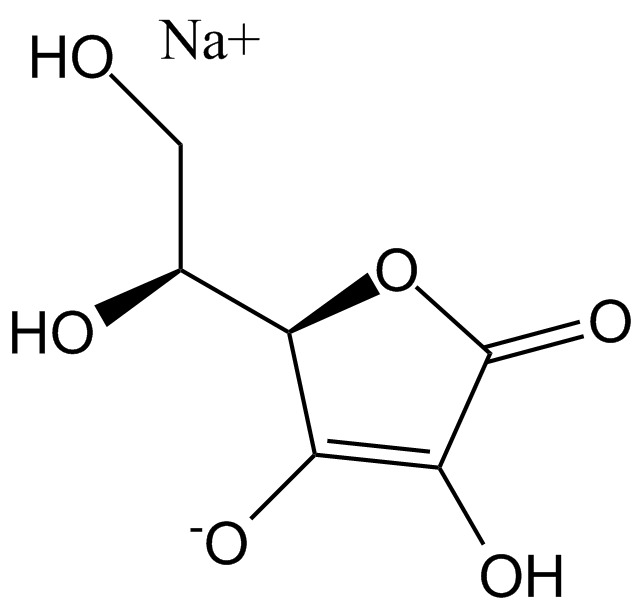 B1834 Sodium ascorbateSummary: mineral salts of ascorbic acid
B1834 Sodium ascorbateSummary: mineral salts of ascorbic acid -
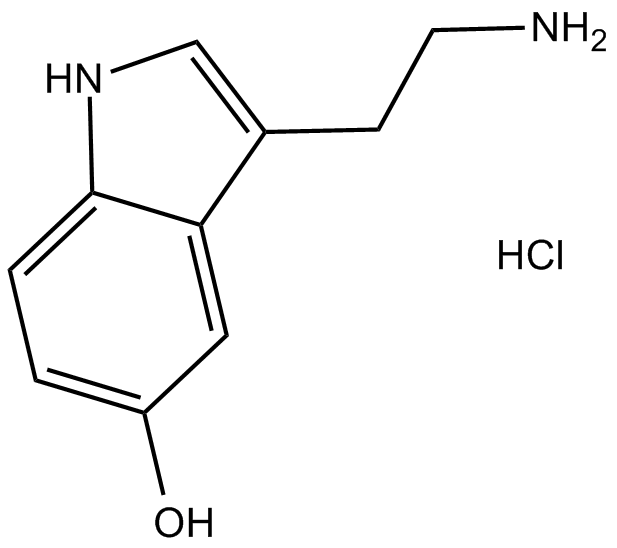 B1830 Serotonin HClSummary: Endogenous 5-HT receptor agonist
B1830 Serotonin HClSummary: Endogenous 5-HT receptor agonist -
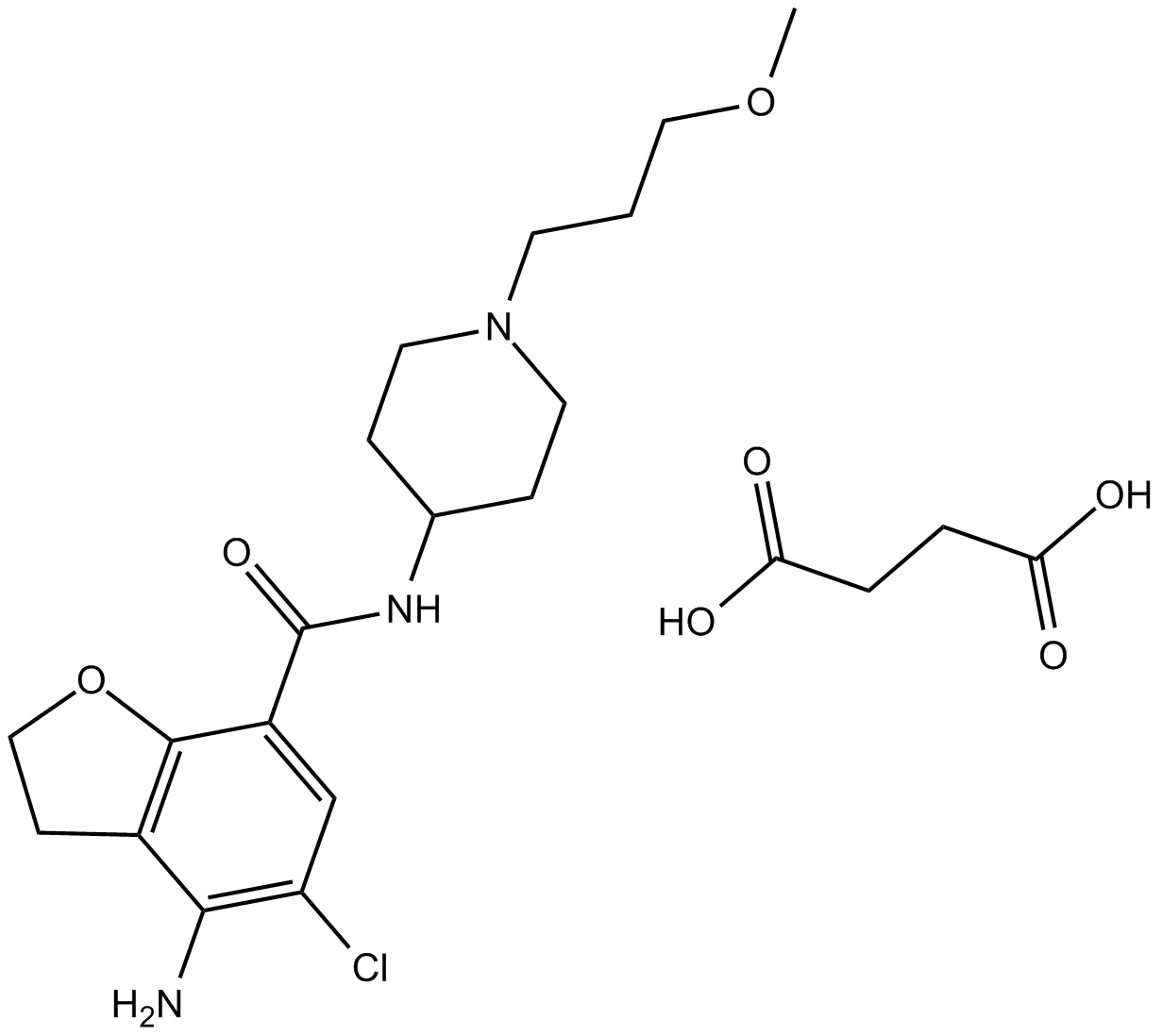 B1822 Prucalopride SuccinatSummary: Selective, high affinity 5-HT4 receptor agonist
B1822 Prucalopride SuccinatSummary: Selective, high affinity 5-HT4 receptor agonist


