Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel


Membrane Transporters mediate the movement of ions and molecules via binding and moving the substance across the membrane. There are two main actions of transporter: facilitated diffusion (passive transport) and active transport. Membrane transporters which bind the hydrolysis of ATP to the transport of target molecules are referred to as ATPases. For instance, Na+,K+-ATPases or Na+,K+-pumps are responsible for the transport of Na+ out of and K+ into cells.
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
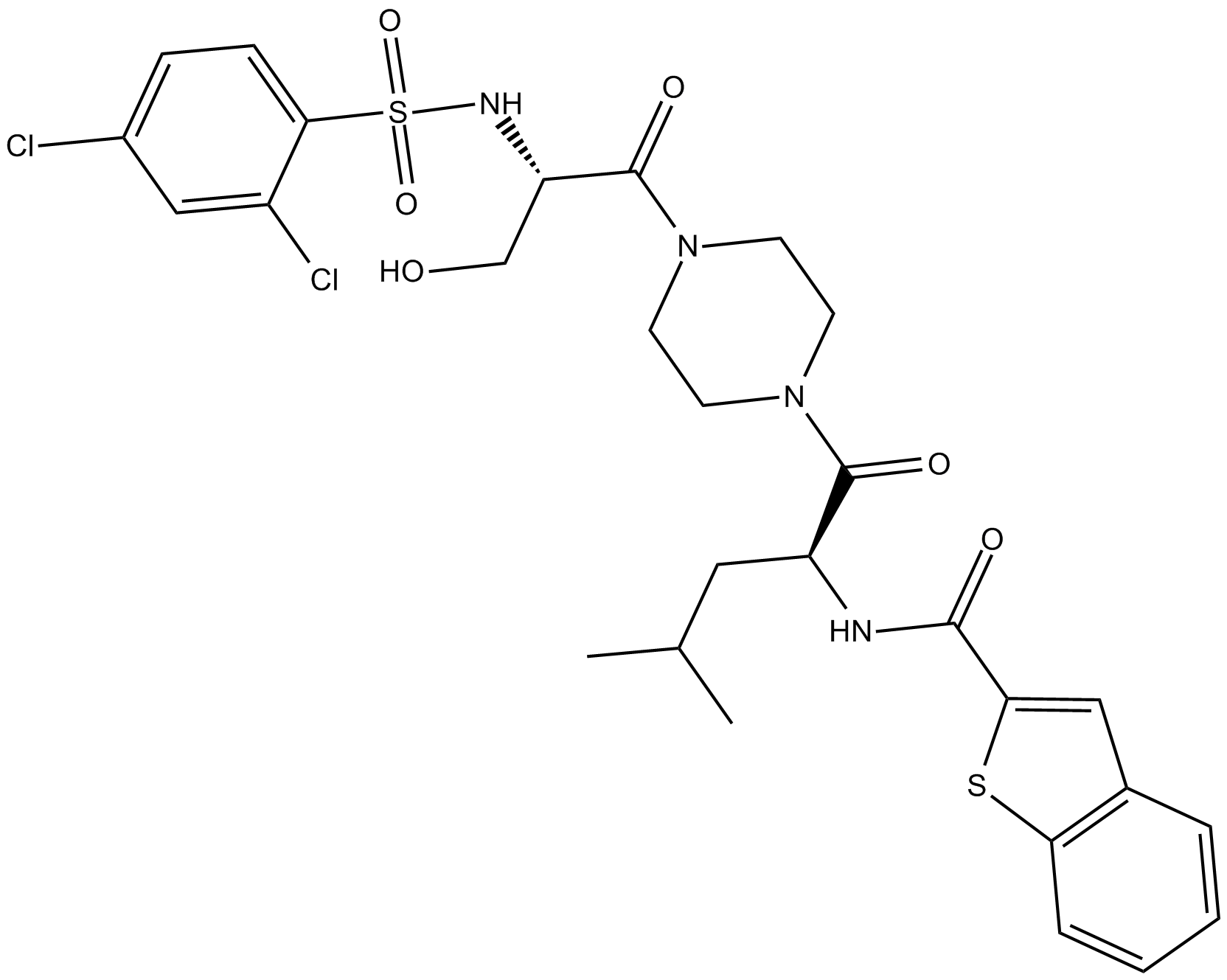 C5065 GSK1016790ASummary: TRPV4 agonist
C5065 GSK1016790ASummary: TRPV4 agonist -
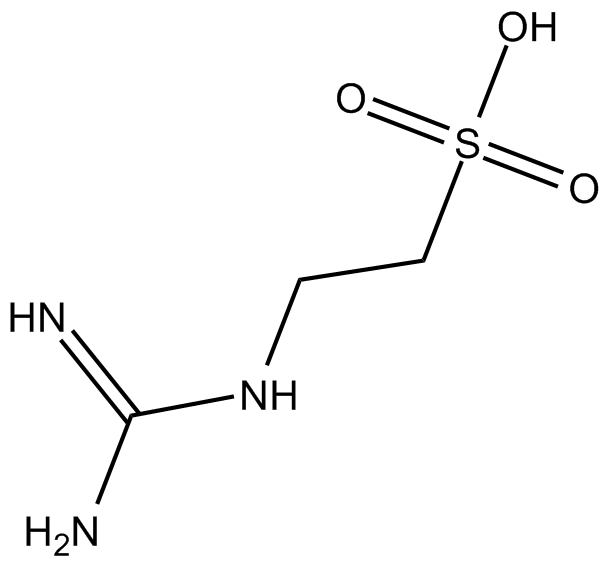 C5294 Guanidinoethyl sulfonateSummary: competitive glycine receptor antagonist
C5294 Guanidinoethyl sulfonateSummary: competitive glycine receptor antagonist -
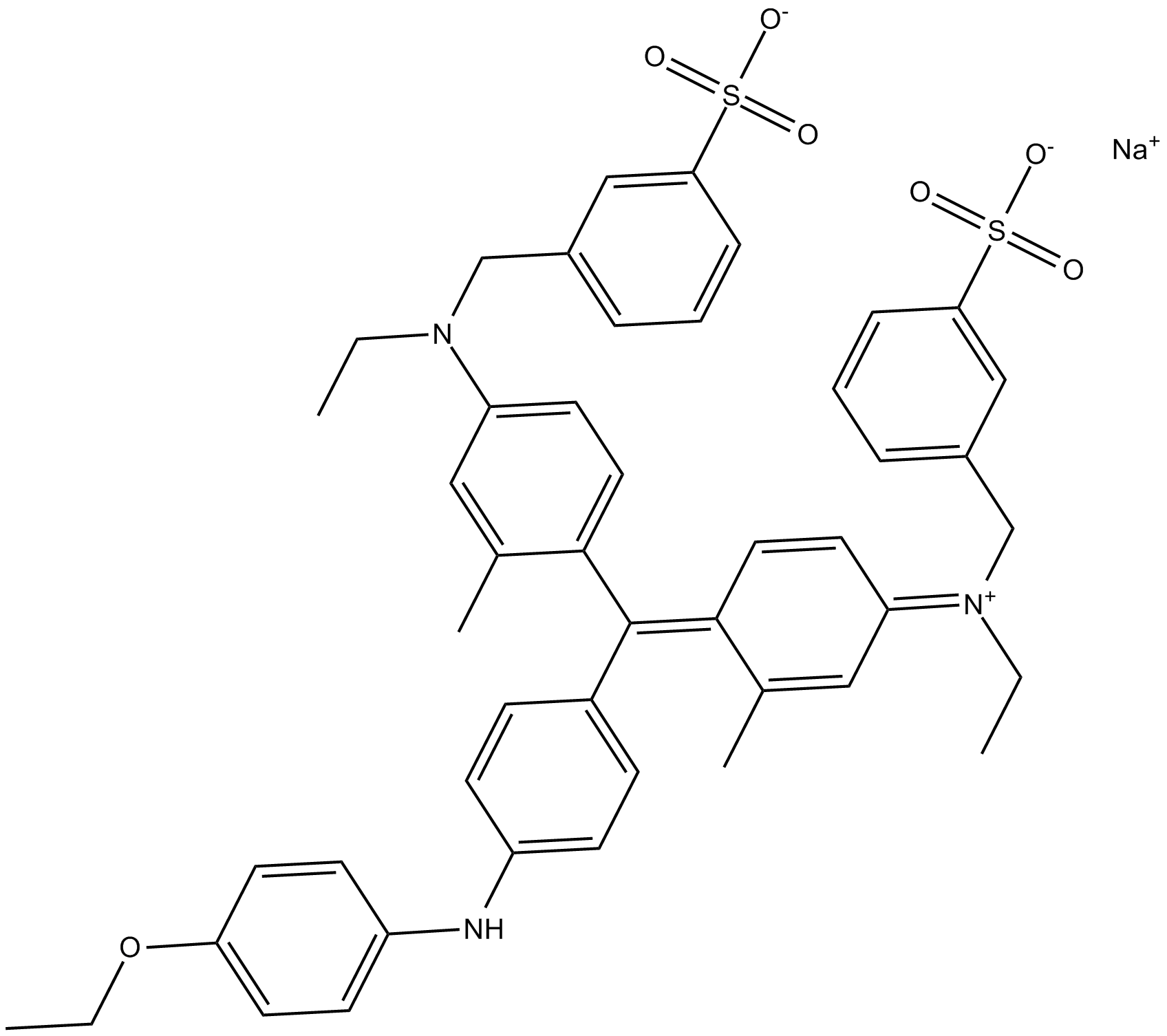 C5579 Brilliant Blue GSummary: used for protein staining in SDS-PAGE, Blue Native PAGE, and the Bradford Method; selective inhibitor of the P2X purinoceptor channel P2X7
C5579 Brilliant Blue GSummary: used for protein staining in SDS-PAGE, Blue Native PAGE, and the Bradford Method; selective inhibitor of the P2X purinoceptor channel P2X7 -
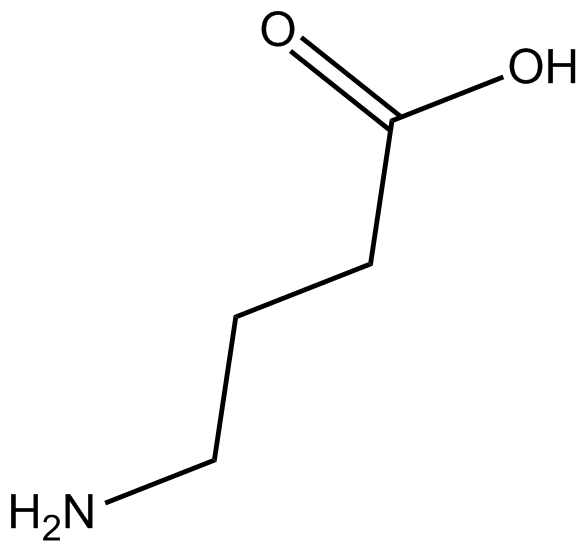 P10002 4-Aminobutyric acid
P10002 4-Aminobutyric acid -
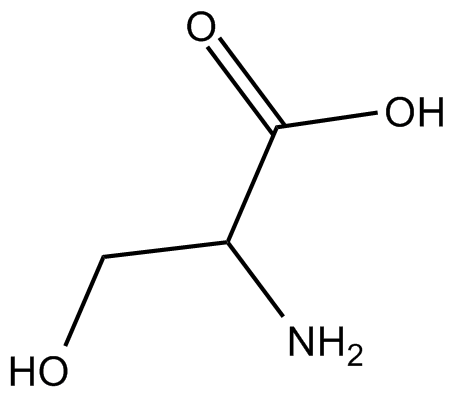 A6743 H-D-Ser-OHTarget: NMDA receptor
A6743 H-D-Ser-OHTarget: NMDA receptor -
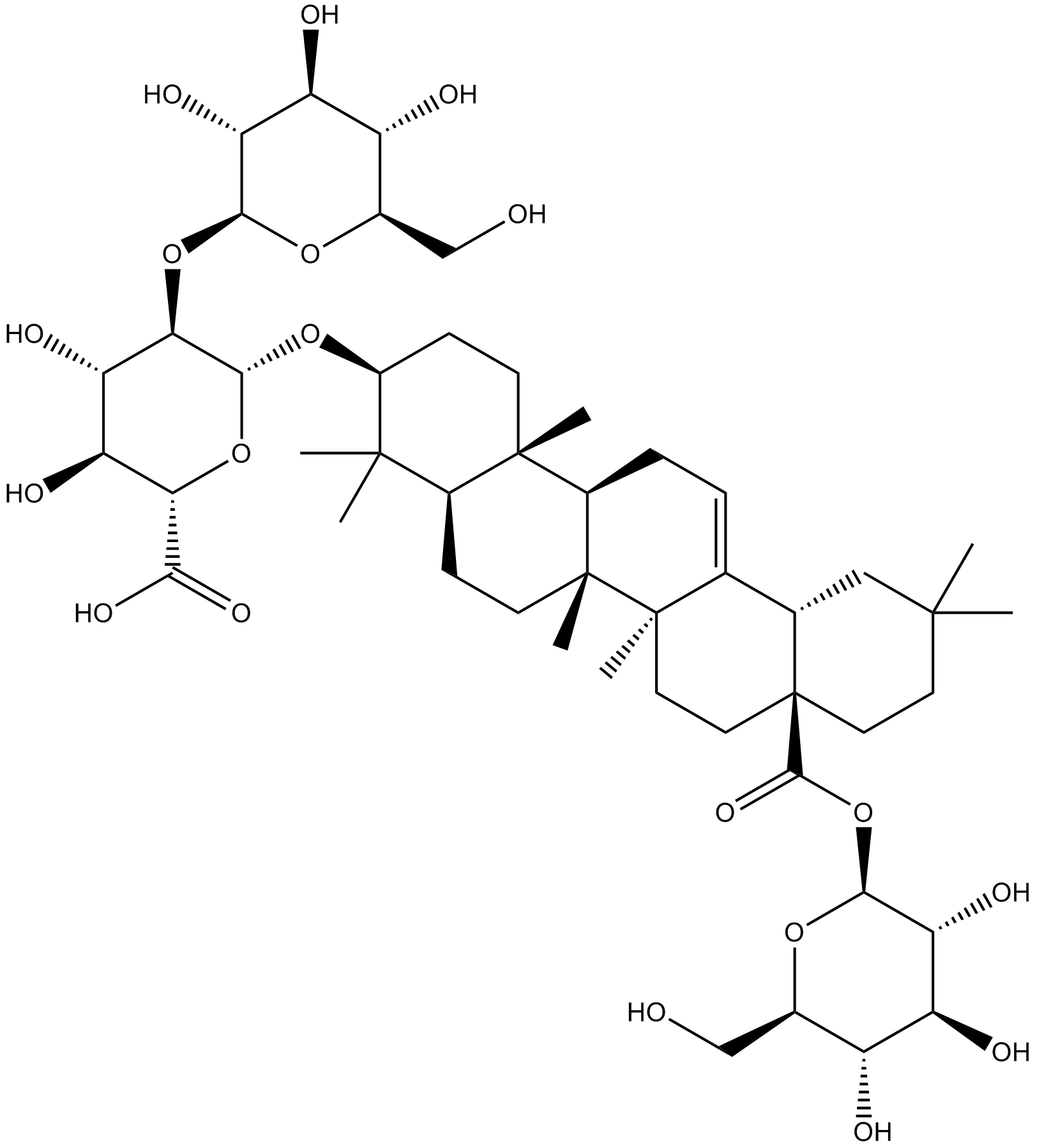
 N1375 SolamargineSummary: cytotoxic agent
N1375 SolamargineSummary: cytotoxic agent -
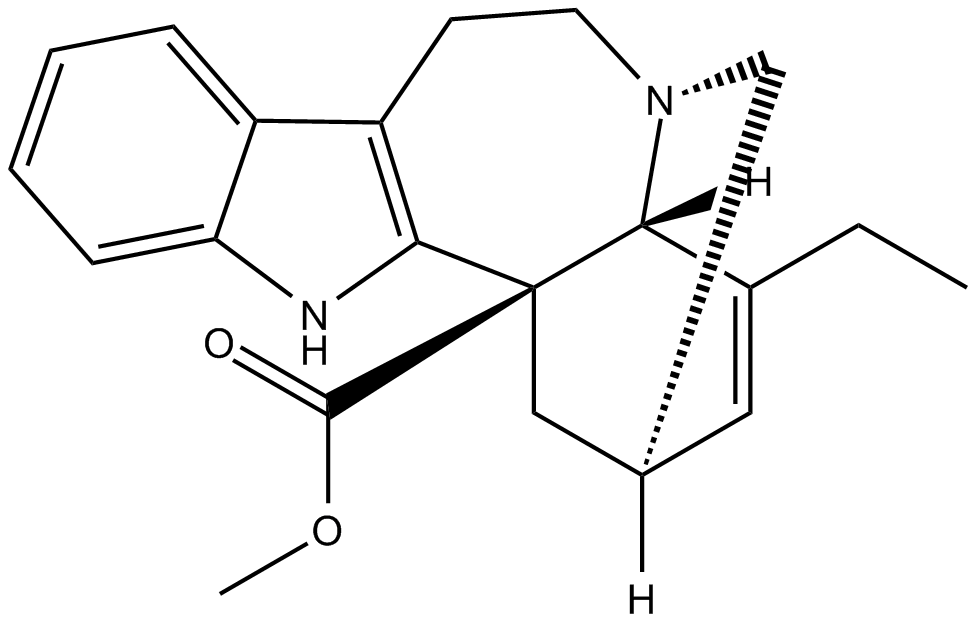 N1382 Catharanthine
N1382 Catharanthine -
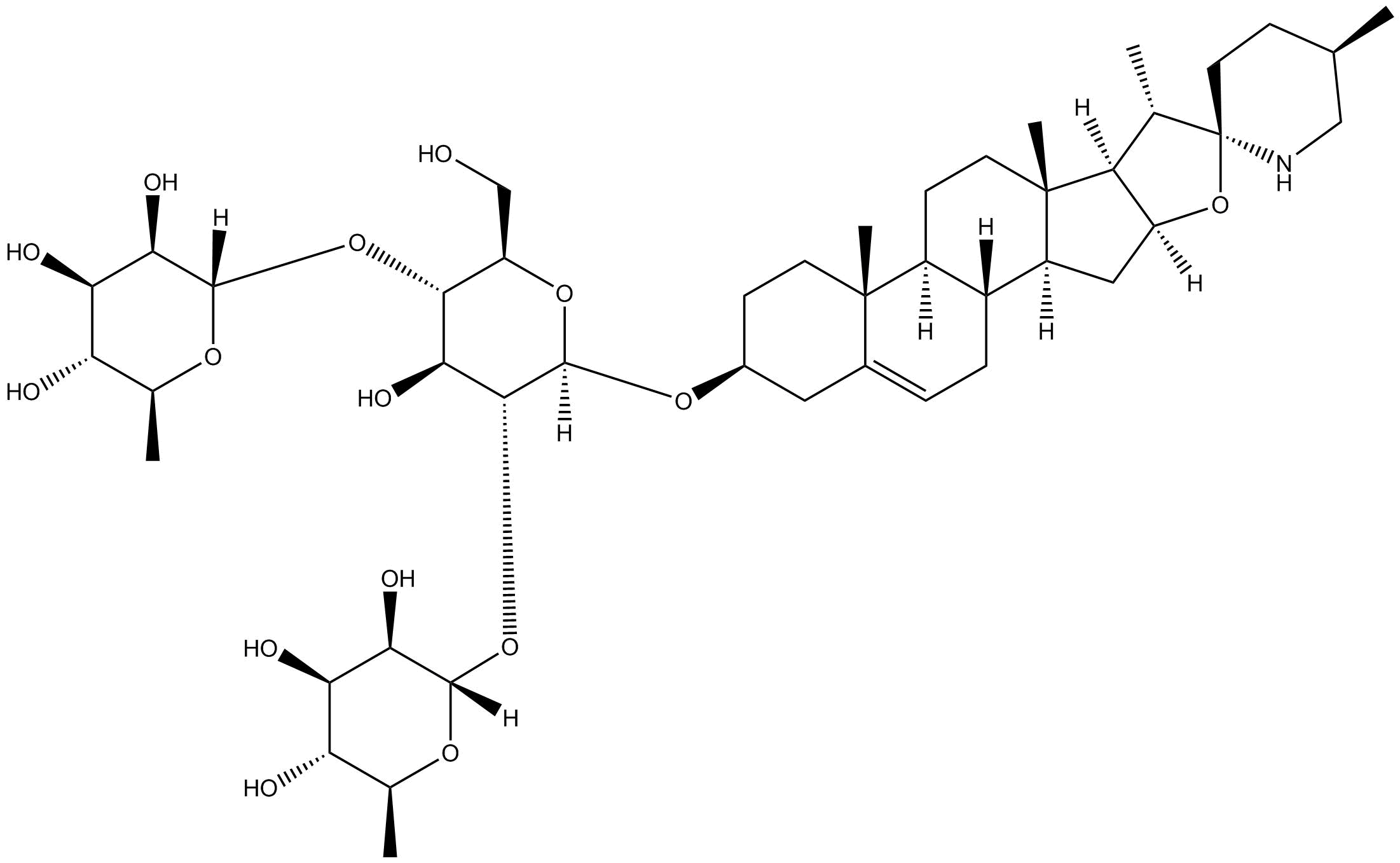
 N1401 Ginsenoside Ro
N1401 Ginsenoside Ro -
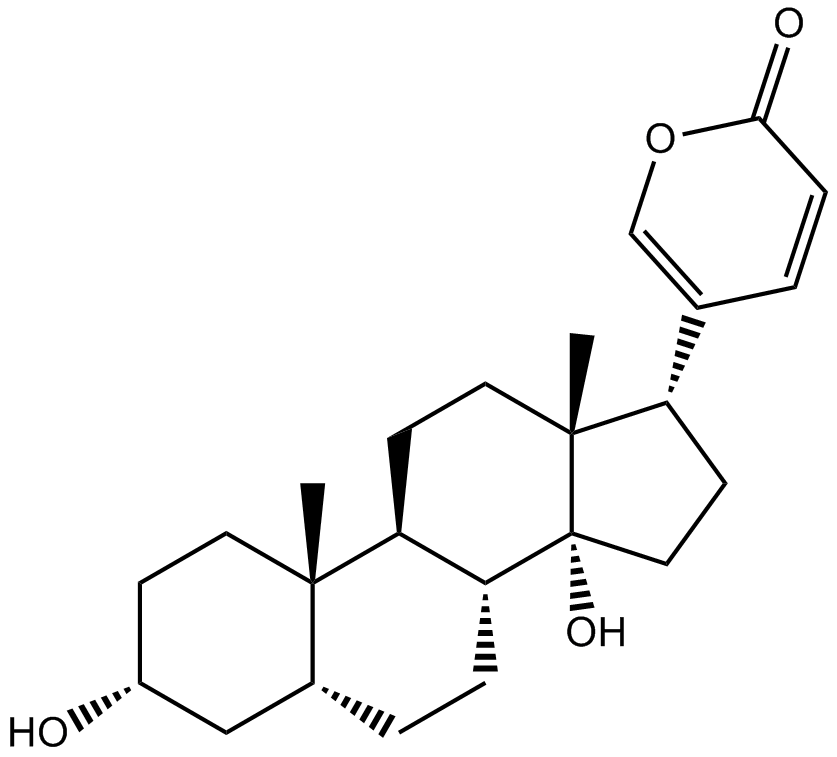 N1507 Bufalin3 CitationSummary: Cardiotonic steroid
N1507 Bufalin3 CitationSummary: Cardiotonic steroid -
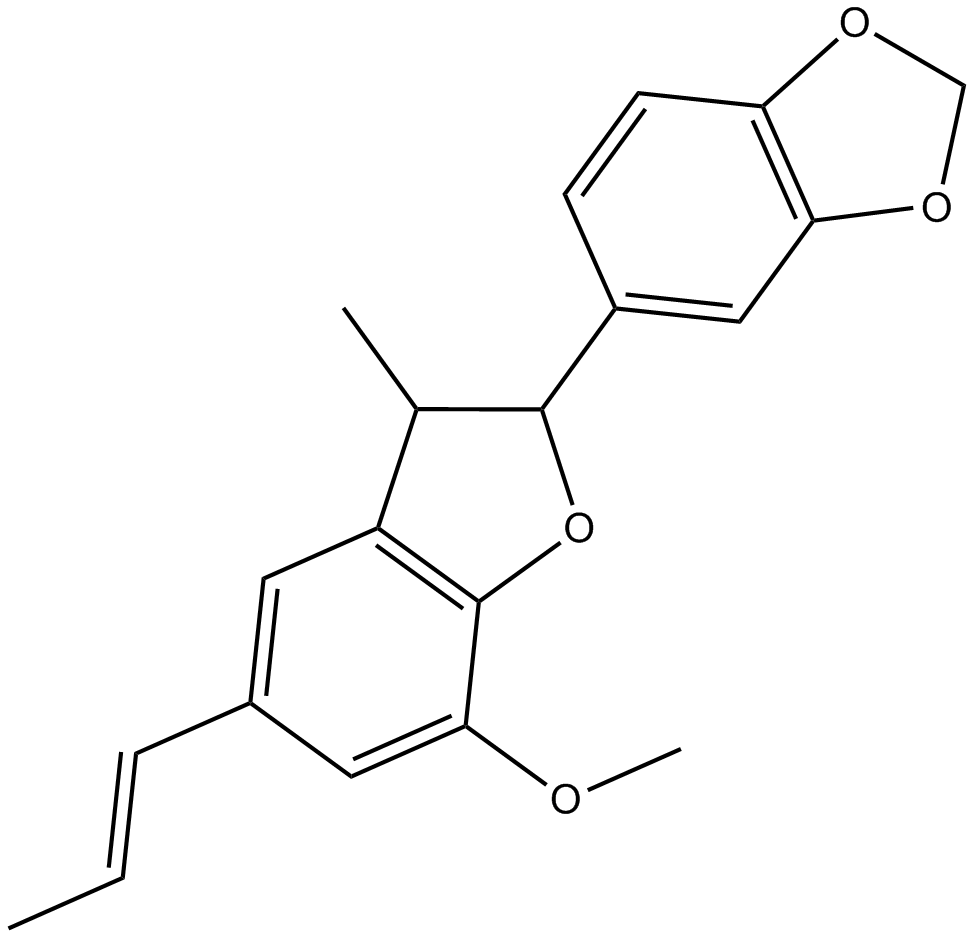 N1572 (-)-Licarin B
N1572 (-)-Licarin B


