MAPK/ERK


The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is a highly conserved family of serine/threonine kinases that mediate a board range of cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, motility, migration, stress response, apoptosis and survival. The activation of MAPK involves signaling pathways consisting of MAPK kinase (i.e. MAPKKK or MEKK) that activates MAPK/ERK (i.e. MAPKK or MEK). A variety of extracellular signals such as mitogens, cytokines, growth factors, and environmental stressors stimulate a phosphorylation-dependent increase in the activity of MAPK.
Activated MAPKs transduce the phosphorylation and activation of MAPK-activated protein kinases (MAPKAPKs), e.g. RSK, MSK, or MNK family, and MK2/3/5. There are three main MAPK families, signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (Erk1/2 or p44/42), the c-Jun N-terminal kinases 1-3 (JNK1-3)/ stress activated protein kinases (SAPK1A, 1B, 1C), the p38 isoforms (p38α, β, γ, and δ). ERK signaling is involved in cell division, migration and survival. p38 MAPK and JNK/SAPK pathways are activated by cellular stress. The p38 MAPK pathway regulates cell motility, transcription, and chromatin remodeling. JNK/SAPK signaling affects apoptosis and inflammation. Dysregulation of MAPK pathway results in tumorgenesis and other pathological conditions.
-
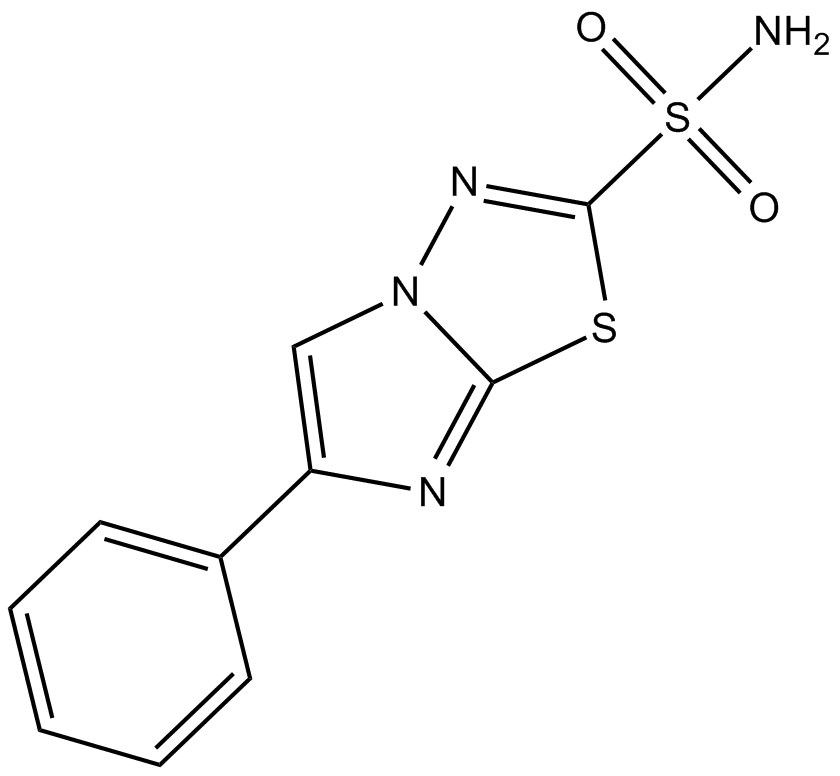 B9010 AEG 3482Target: JNKSummary: inhibitor of Jun kinase (JNK)-dependent apoptosis
B9010 AEG 3482Target: JNKSummary: inhibitor of Jun kinase (JNK)-dependent apoptosis -
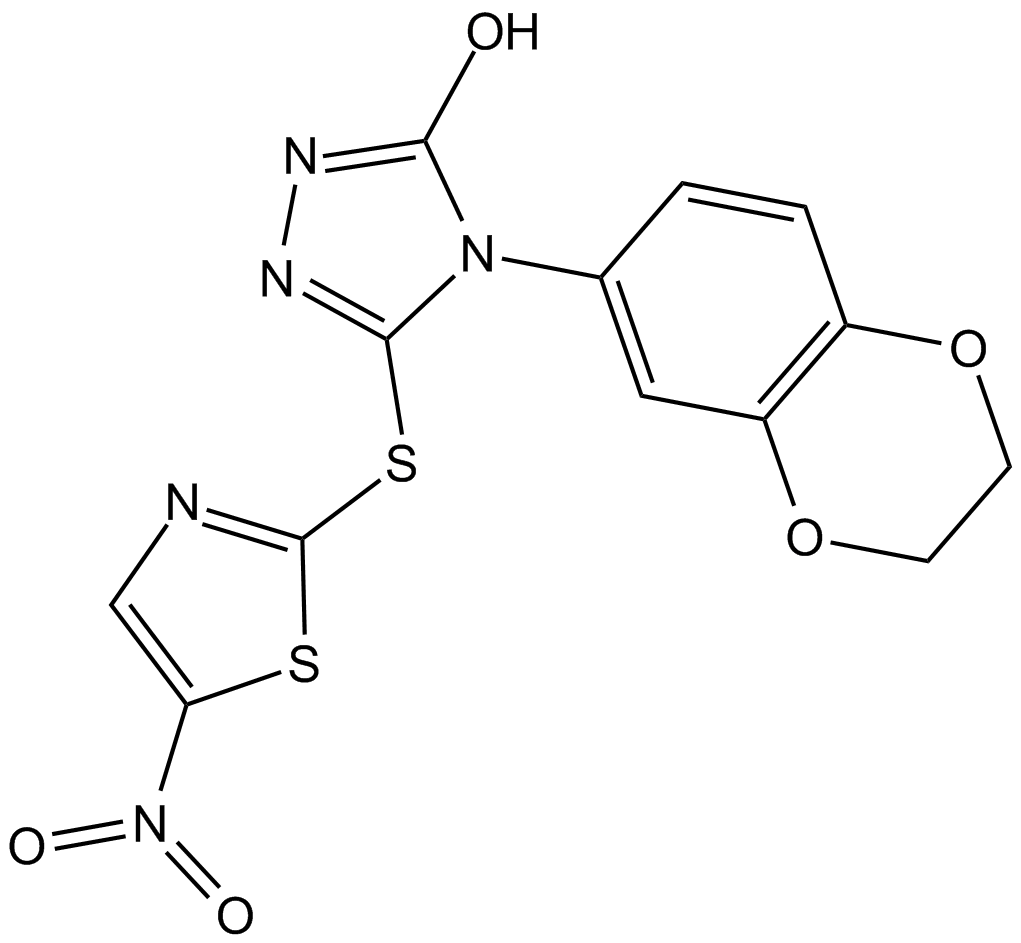 B9011 BI 78D3Summary: Competitive JNK inhibitor
B9011 BI 78D3Summary: Competitive JNK inhibitor -
 B9012 BRD 7389Summary: P90 RSK inhibitor
B9012 BRD 7389Summary: P90 RSK inhibitor -
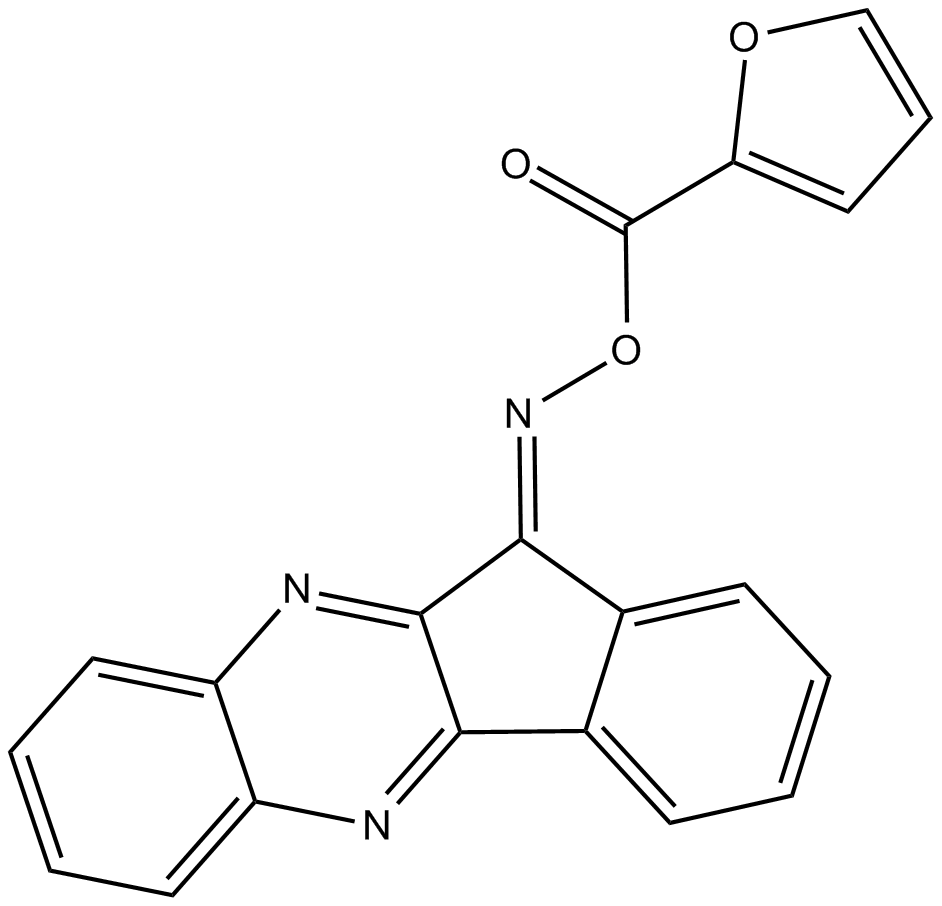 B9015 IQ 3Summary: Selective JNK3 inhibitor
B9015 IQ 3Summary: Selective JNK3 inhibitor -
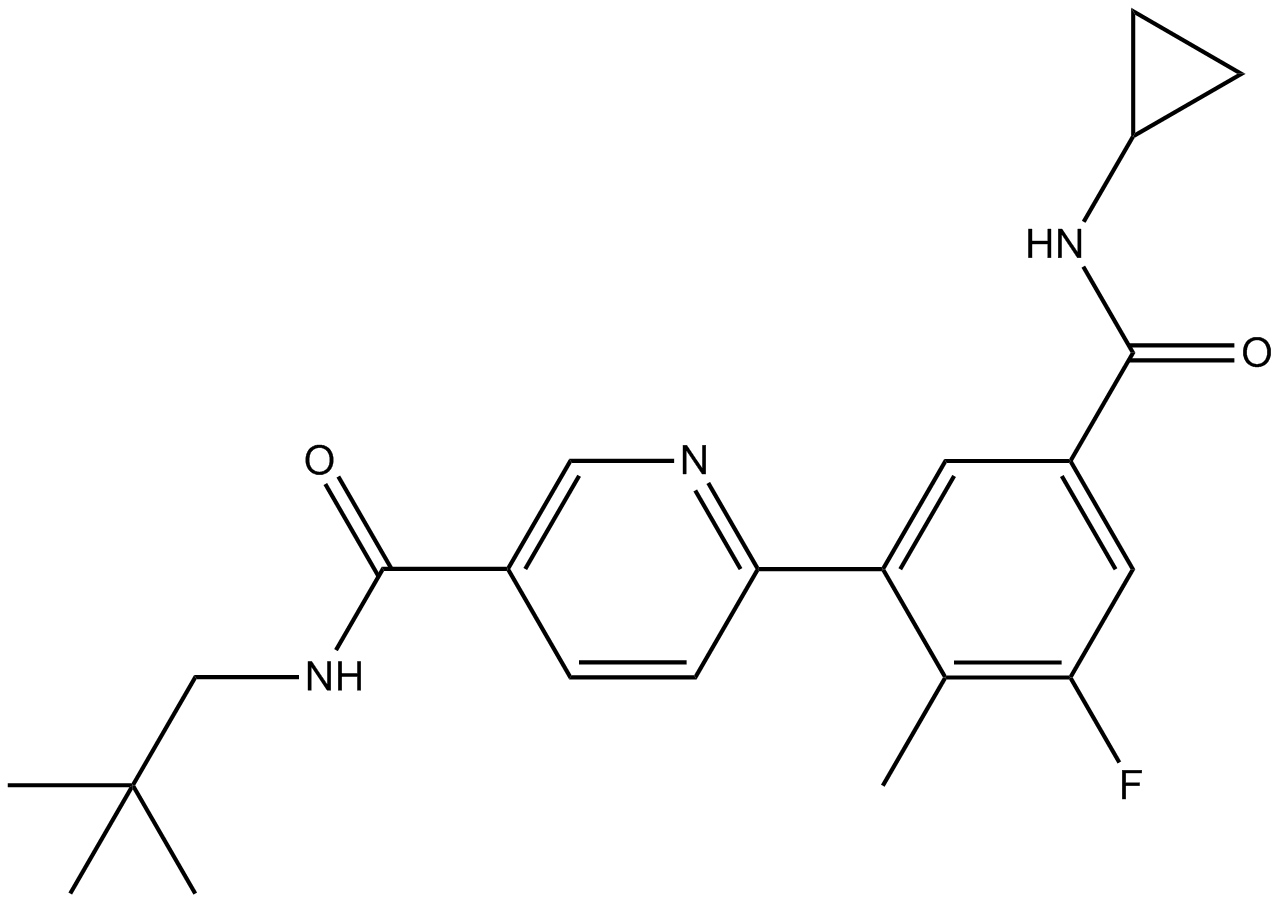 B4620 Losmapimod1 CitationSummary: p38 MAPK inhibitor, orally active
B4620 Losmapimod1 CitationSummary: p38 MAPK inhibitor, orally active -
 B4727 B-Raf IN 1Summary: B-Raf inhibitor
B4727 B-Raf IN 1Summary: B-Raf inhibitor -
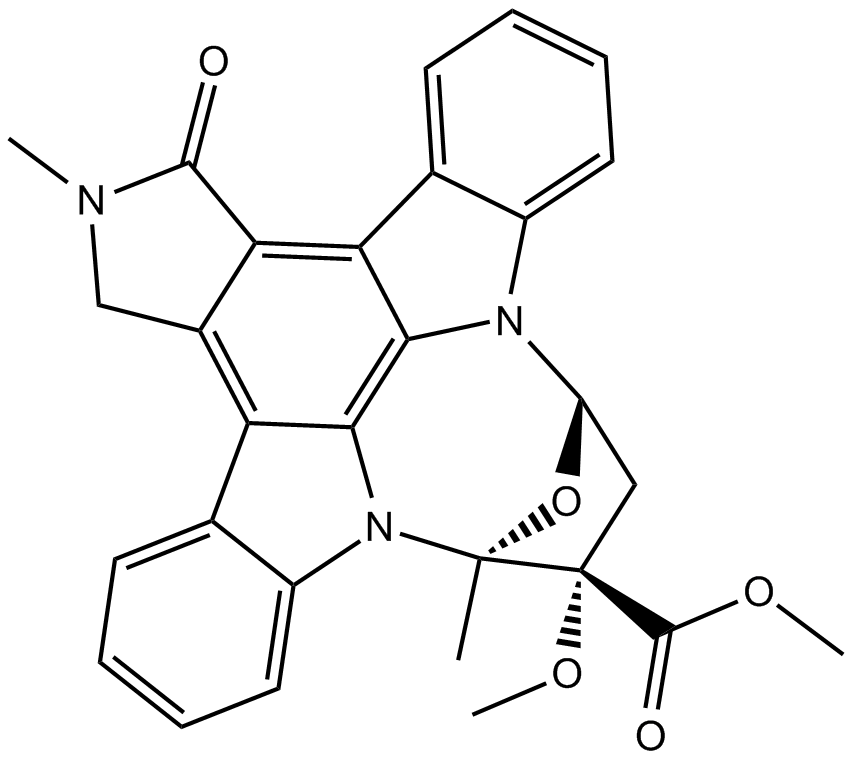 B6673 KT 5823Summary: protein kinase G inhibitor
B6673 KT 5823Summary: protein kinase G inhibitor -
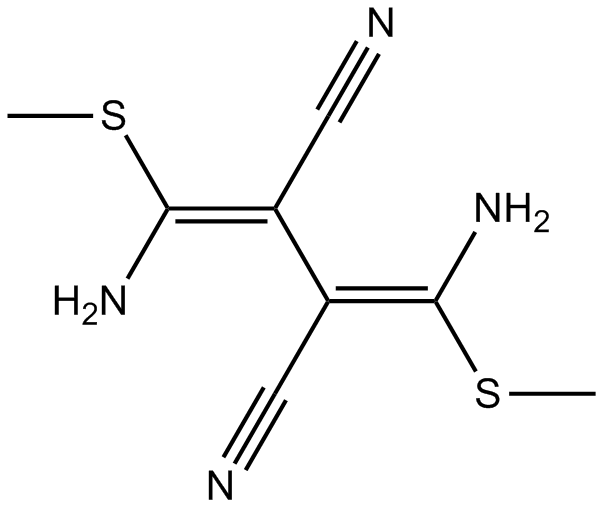 B6882 U0124Summary: Inactive analog of U0126(MEK-1/2 inhibitor), used as a negative control
B6882 U0124Summary: Inactive analog of U0126(MEK-1/2 inhibitor), used as a negative control -
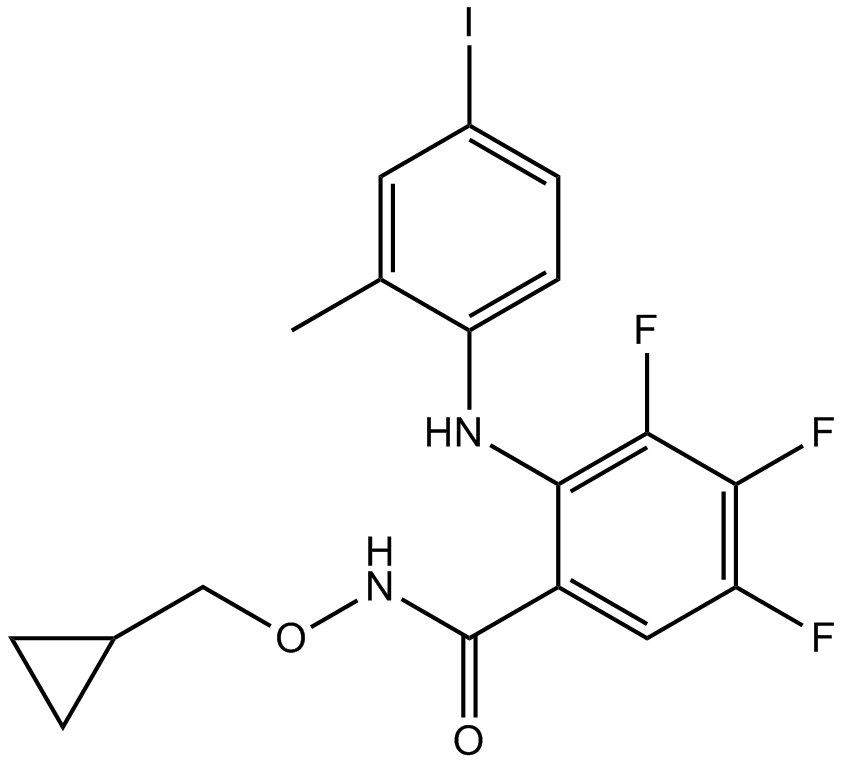 B7124 PD 198306Summary: MEK1/2 inhibitor
B7124 PD 198306Summary: MEK1/2 inhibitor -
 B7246 Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPSSummary: cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibitor
B7246 Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPSSummary: cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibitor


