Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
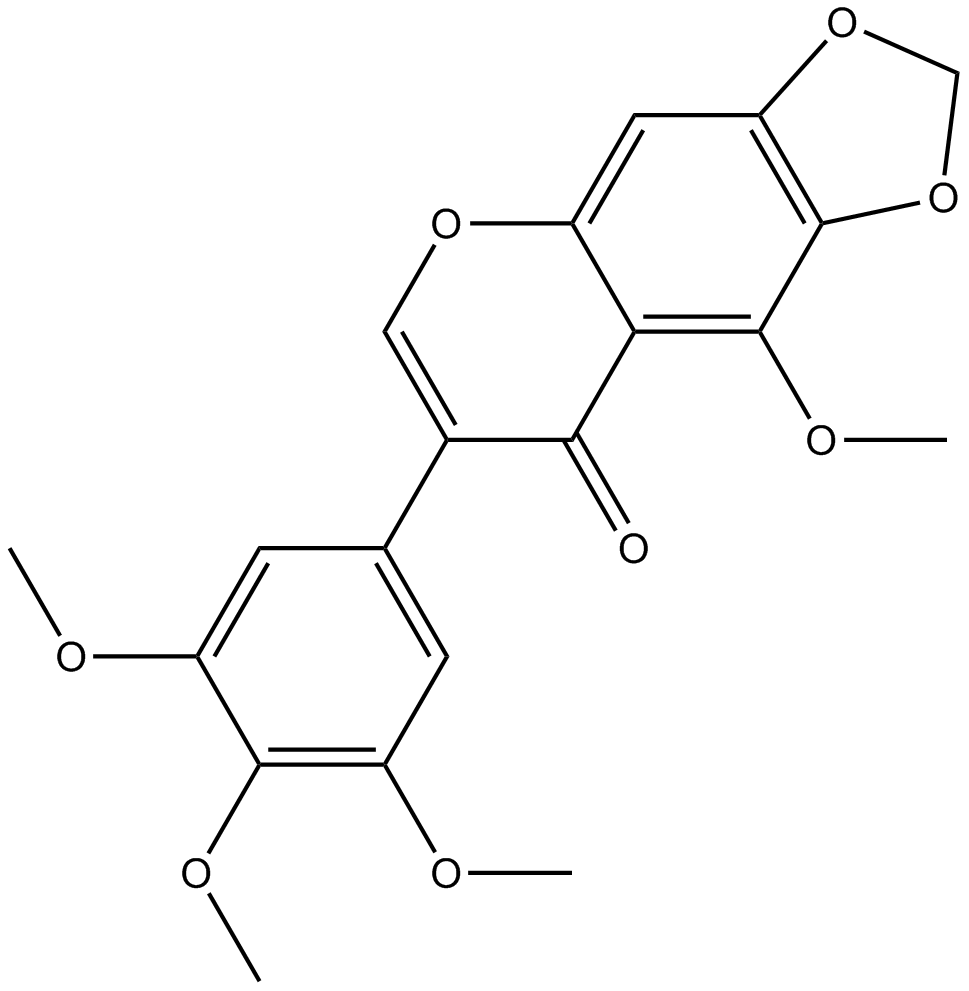 N1426 Irisflorentin
N1426 Irisflorentin -
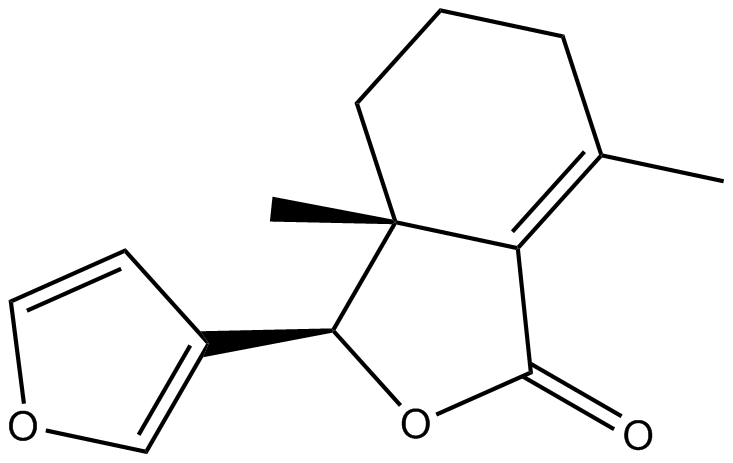 N1441 Fraxinellone
N1441 Fraxinellone -
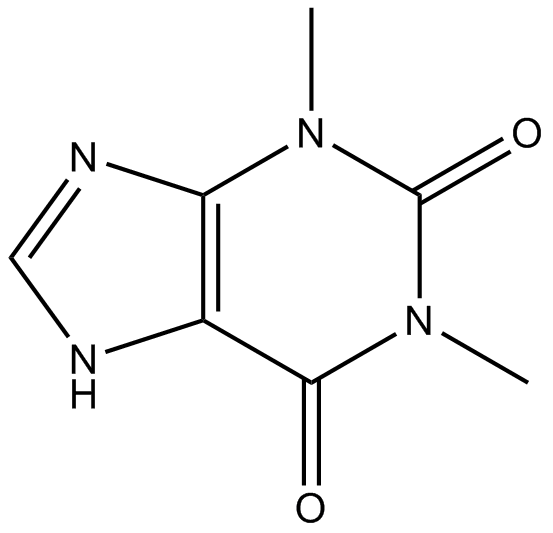 N1442 Theophylline
N1442 Theophylline -
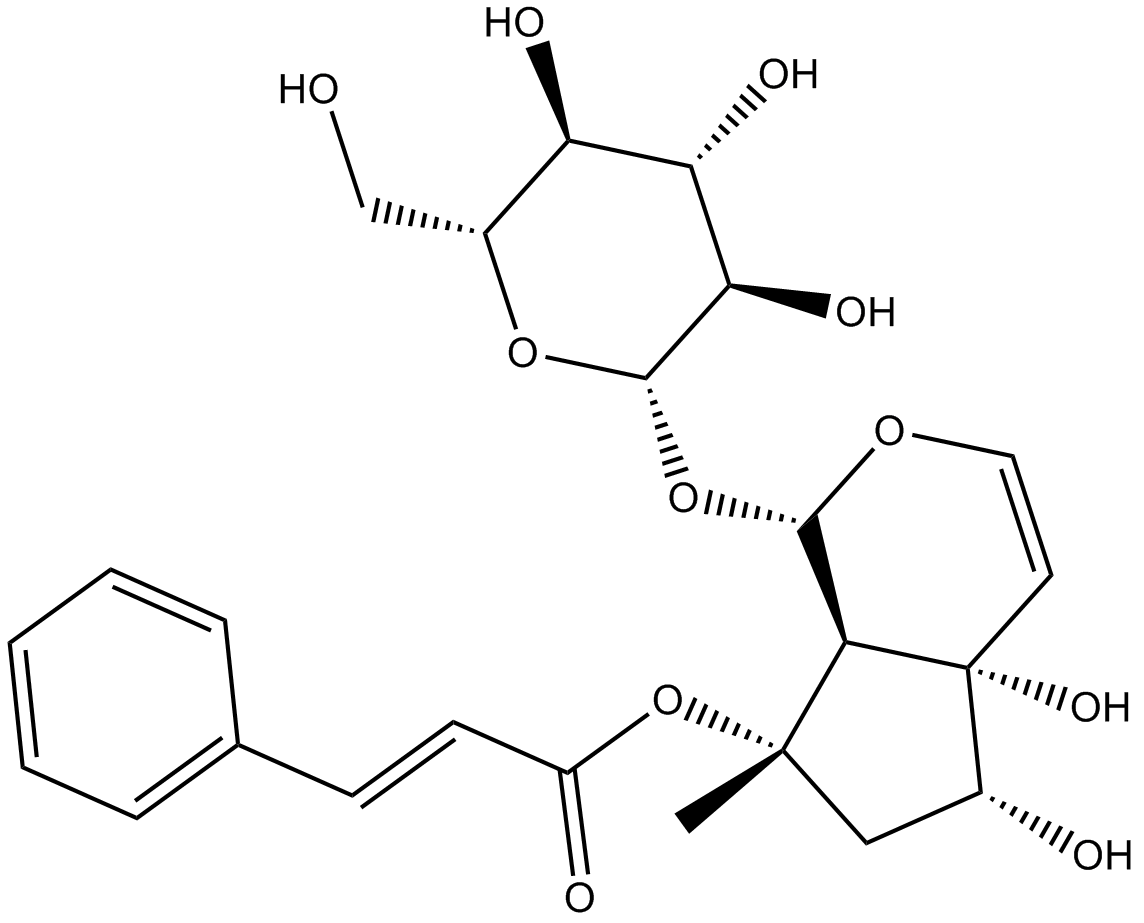 N1461 HarpagosideSummary: Anti-inflammatory natural product
N1461 HarpagosideSummary: Anti-inflammatory natural product -
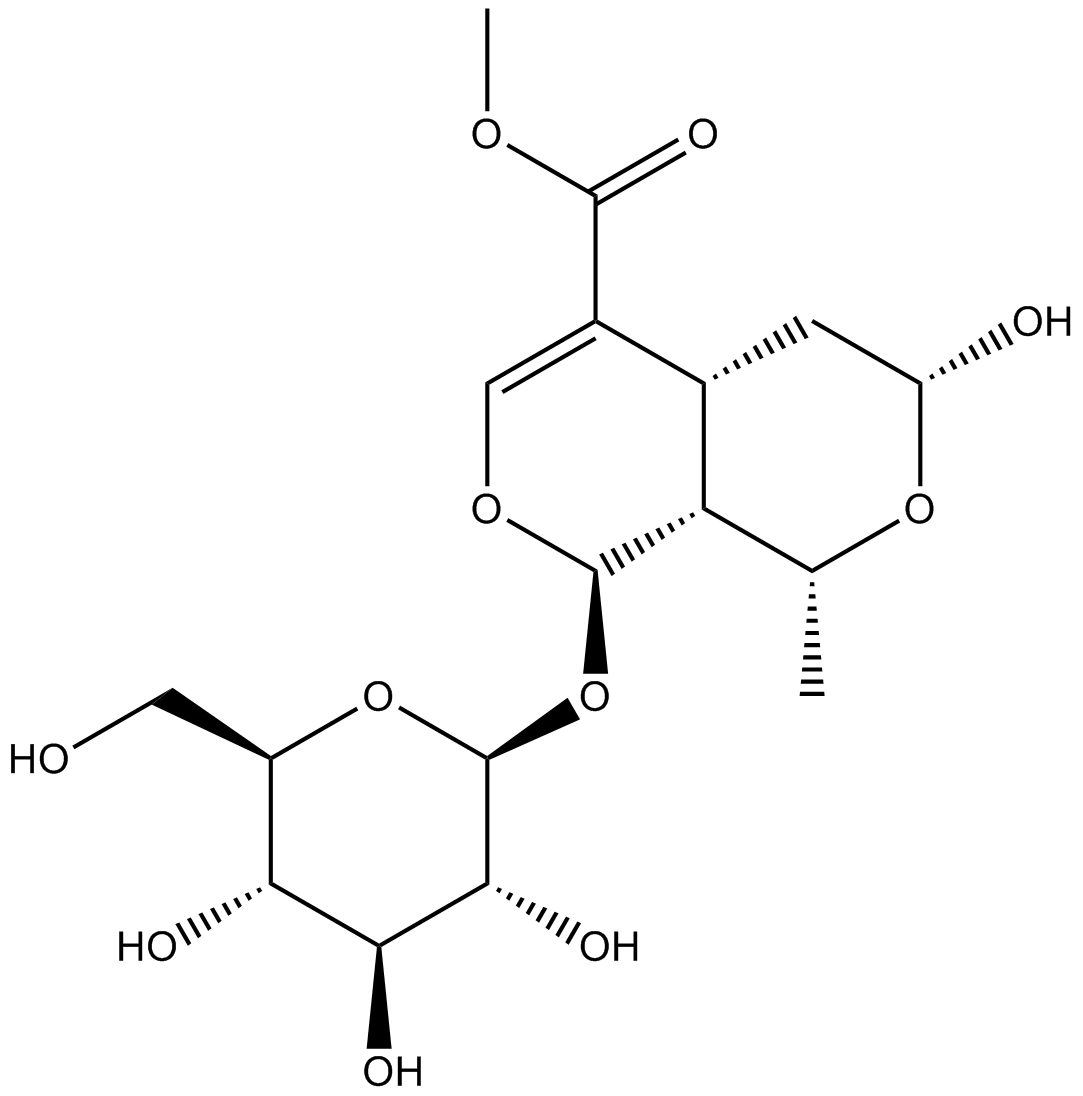 N1489 Morroniside
N1489 Morroniside -
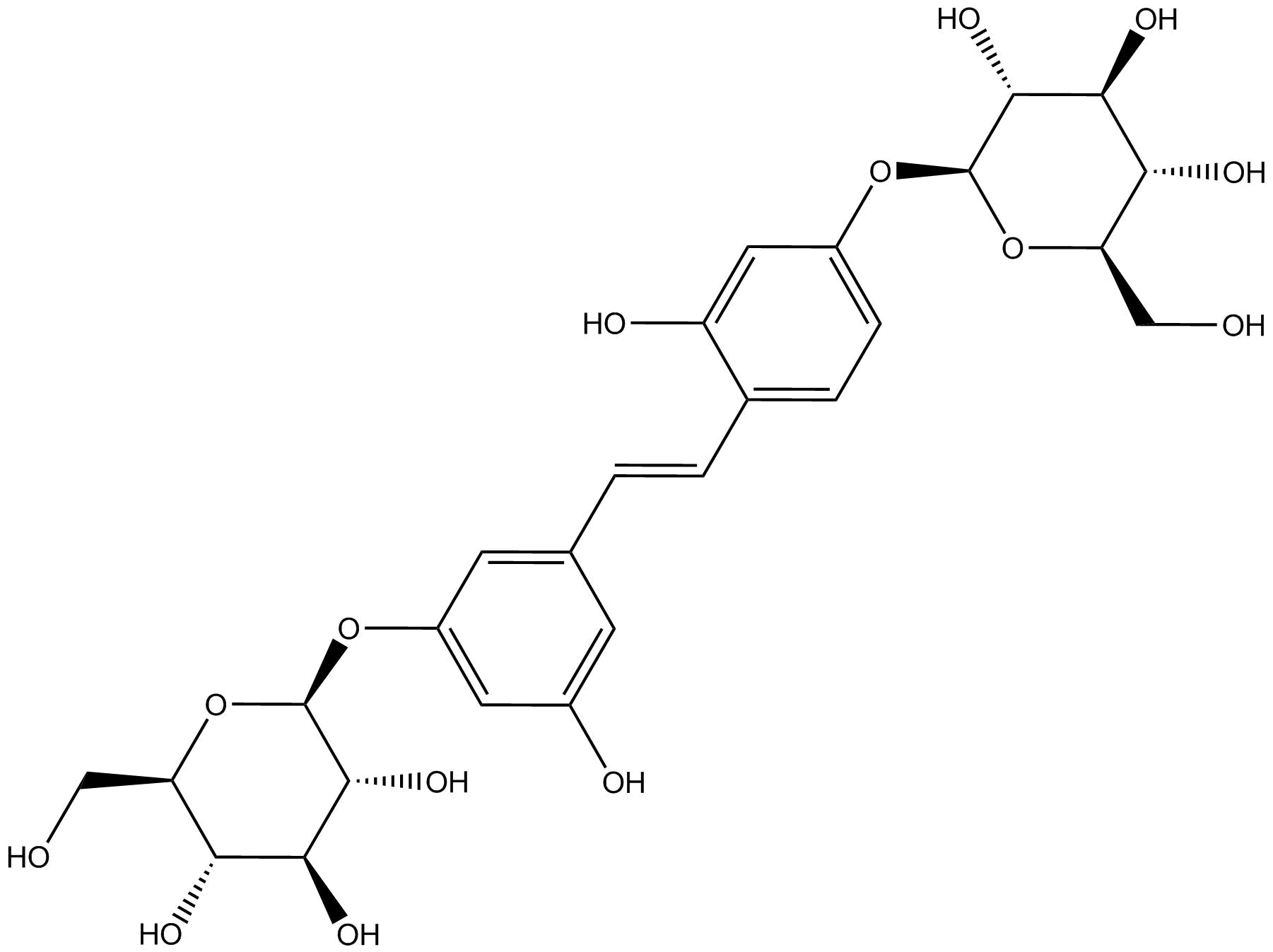 N1520 Mulberroside A
N1520 Mulberroside A -
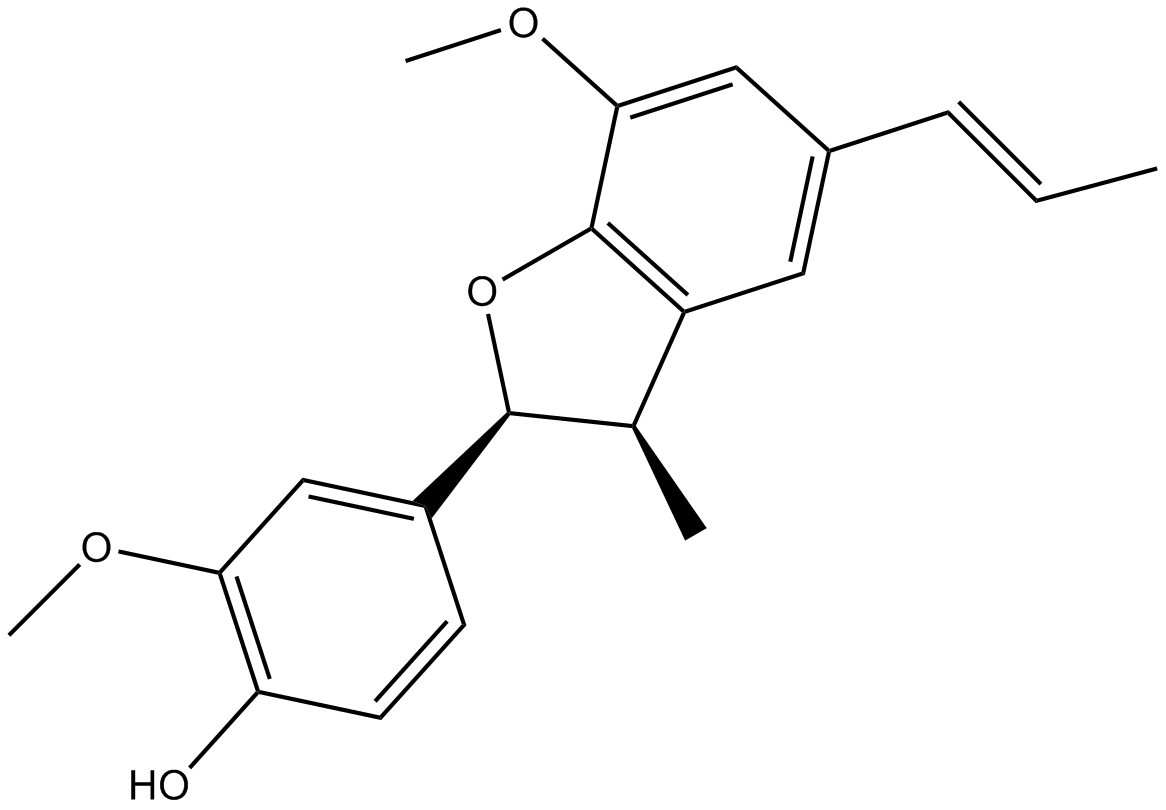 N1521 Dehydrodiisoeugenol
N1521 Dehydrodiisoeugenol -
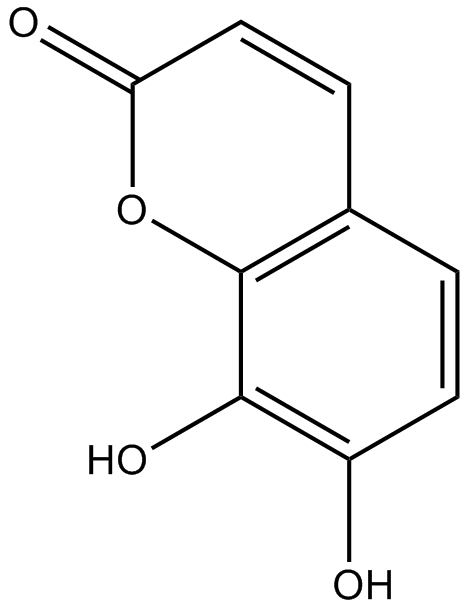 N1567 DaphnetinSummary: Protein kinases inhibitor for EGFR/PKA/PKC
N1567 DaphnetinSummary: Protein kinases inhibitor for EGFR/PKA/PKC -
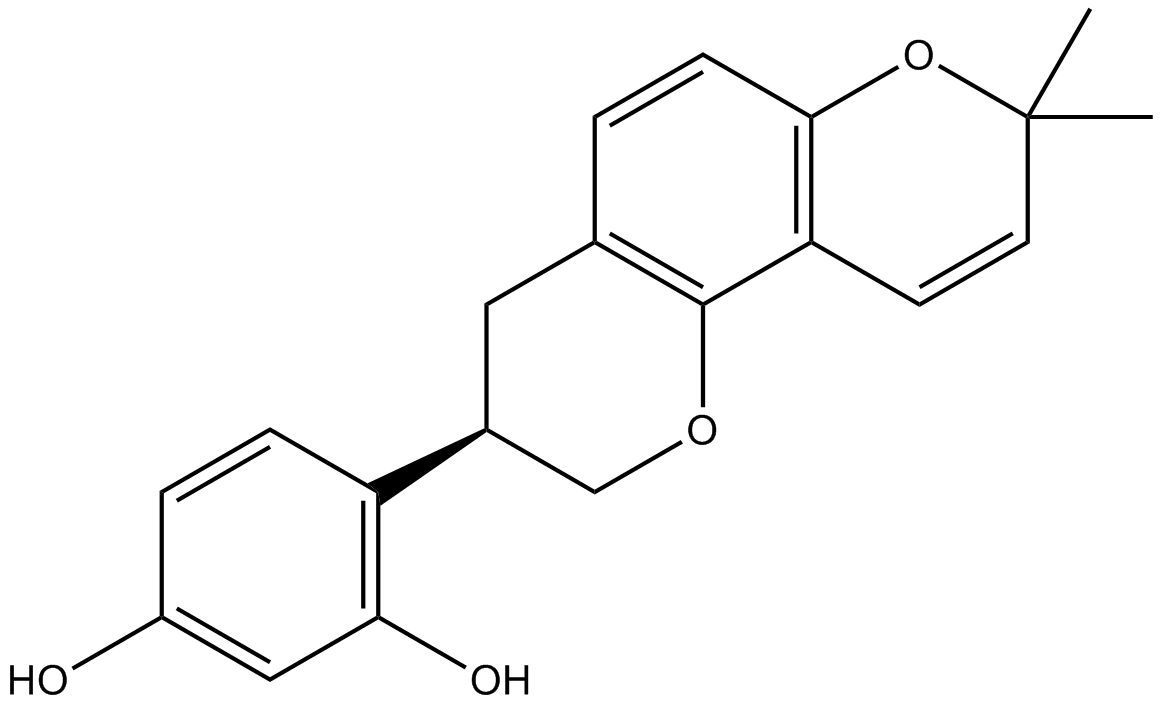 N1579 GlabridinSummary: Prenylated isoflavonoid with various bioactivities
N1579 GlabridinSummary: Prenylated isoflavonoid with various bioactivities -
 N1597 Protopanaxdiol
N1597 Protopanaxdiol


