Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
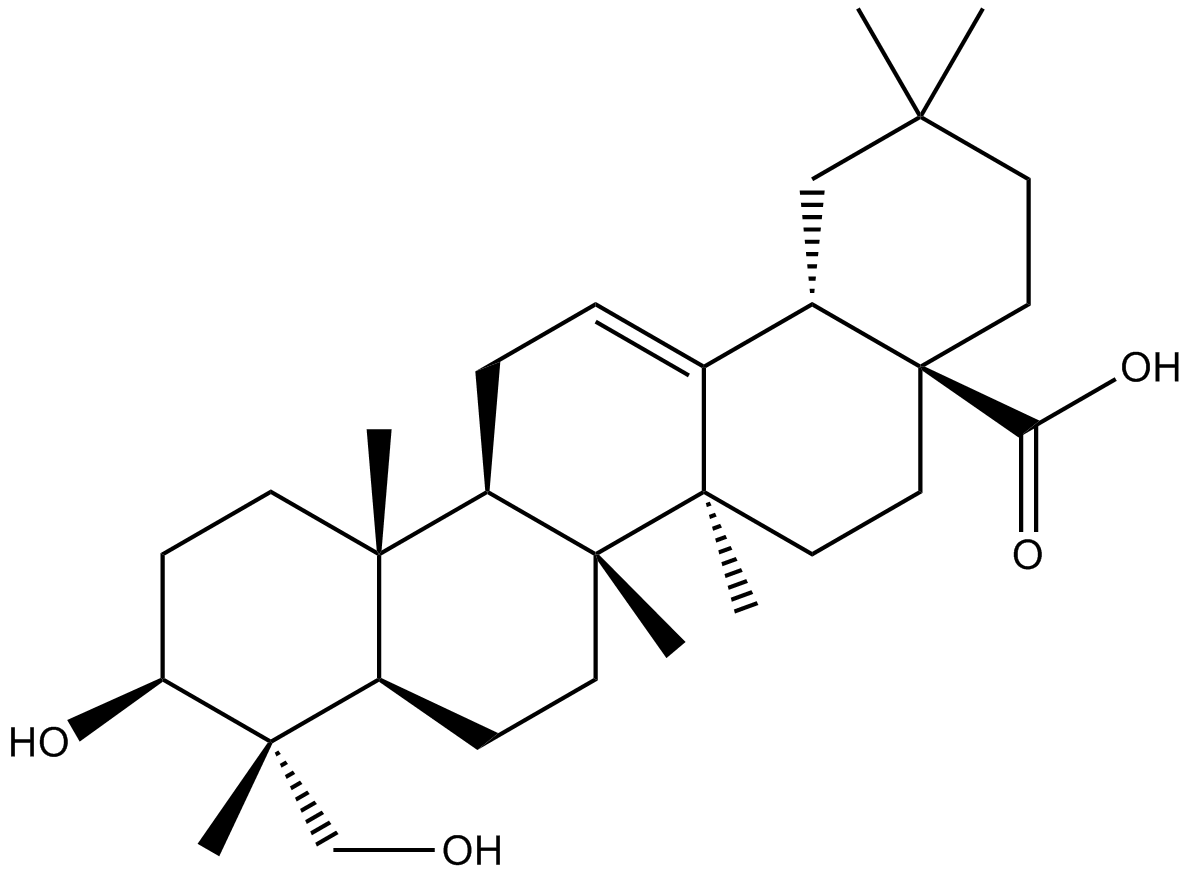 N1306 Hederagenin
N1306 Hederagenin -
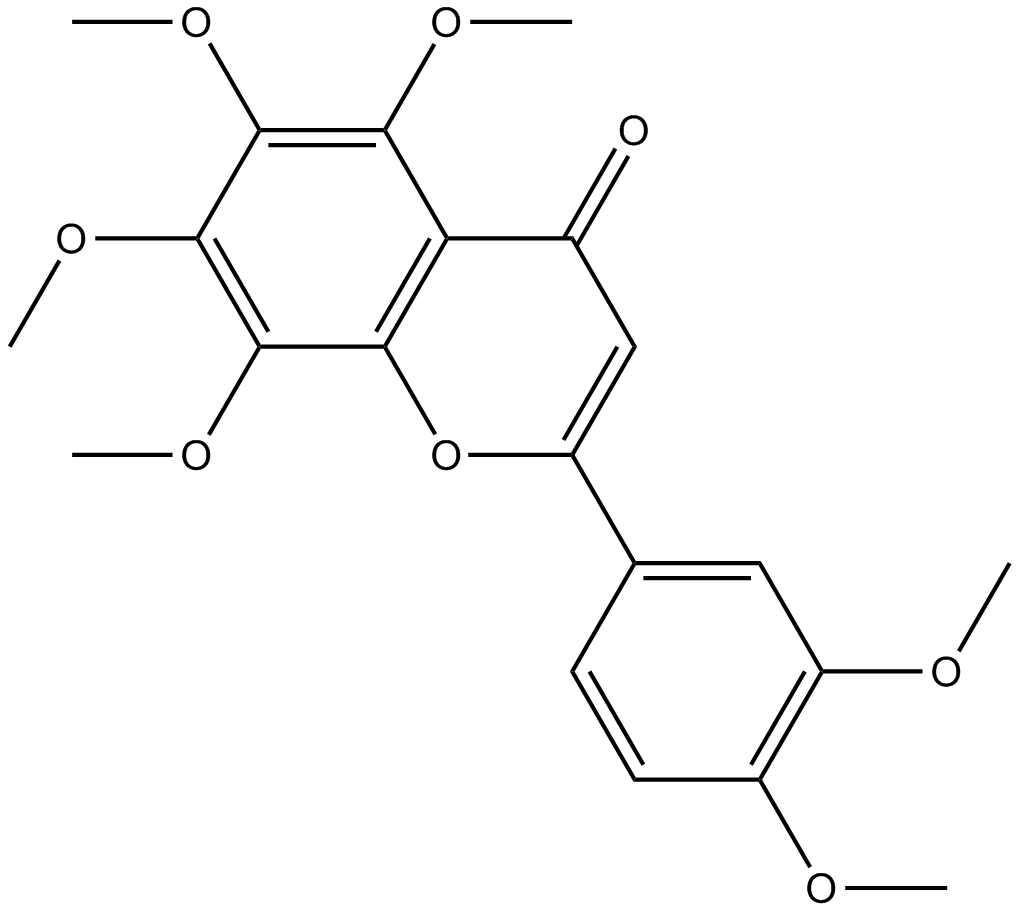 N1311 NobiletinTarget: ERKSummary: ERK inhibitor
N1311 NobiletinTarget: ERKSummary: ERK inhibitor -
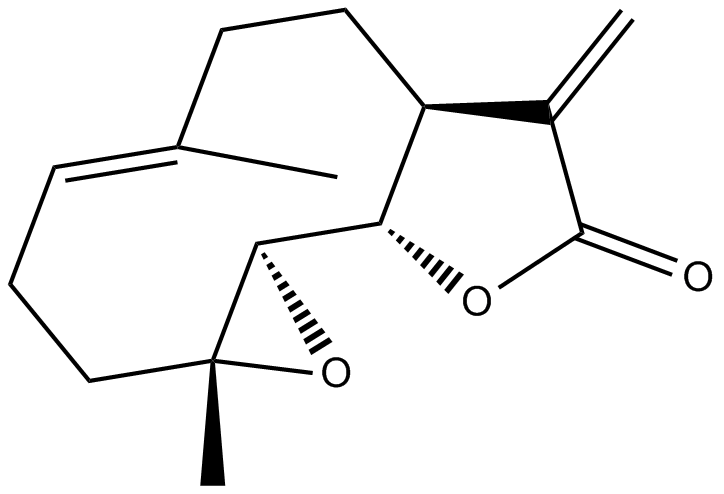 N1315 ParthenolideTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)|MDM2|DNA Methyltransferases|p53|5-HT
N1315 ParthenolideTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)|MDM2|DNA Methyltransferases|p53|5-HT -
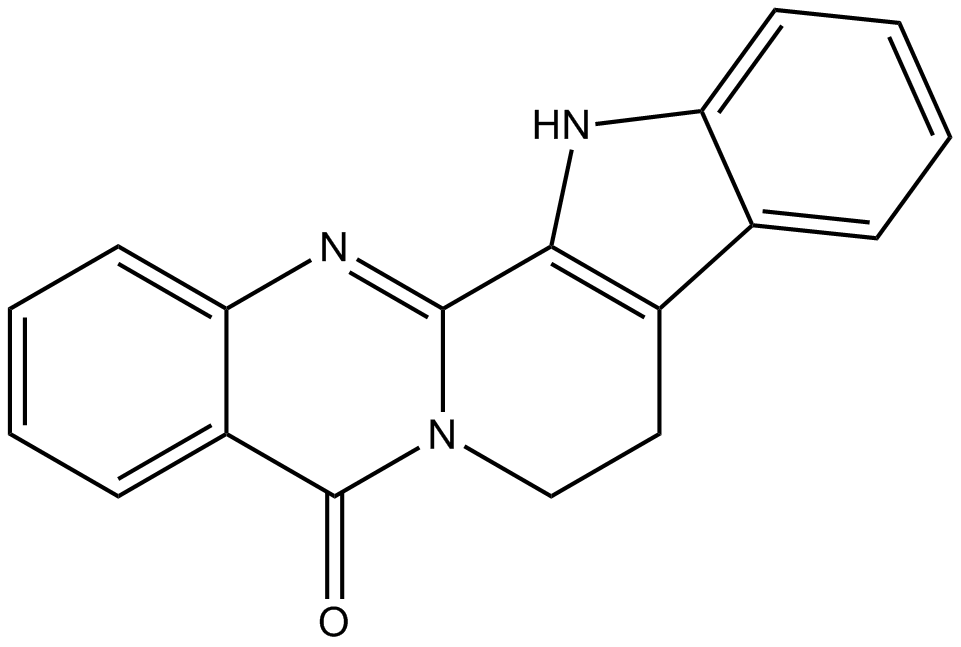 N1344 Rutaecarpine
N1344 Rutaecarpine -
 N1357 Asiaticoside1 Citation
N1357 Asiaticoside1 Citation -
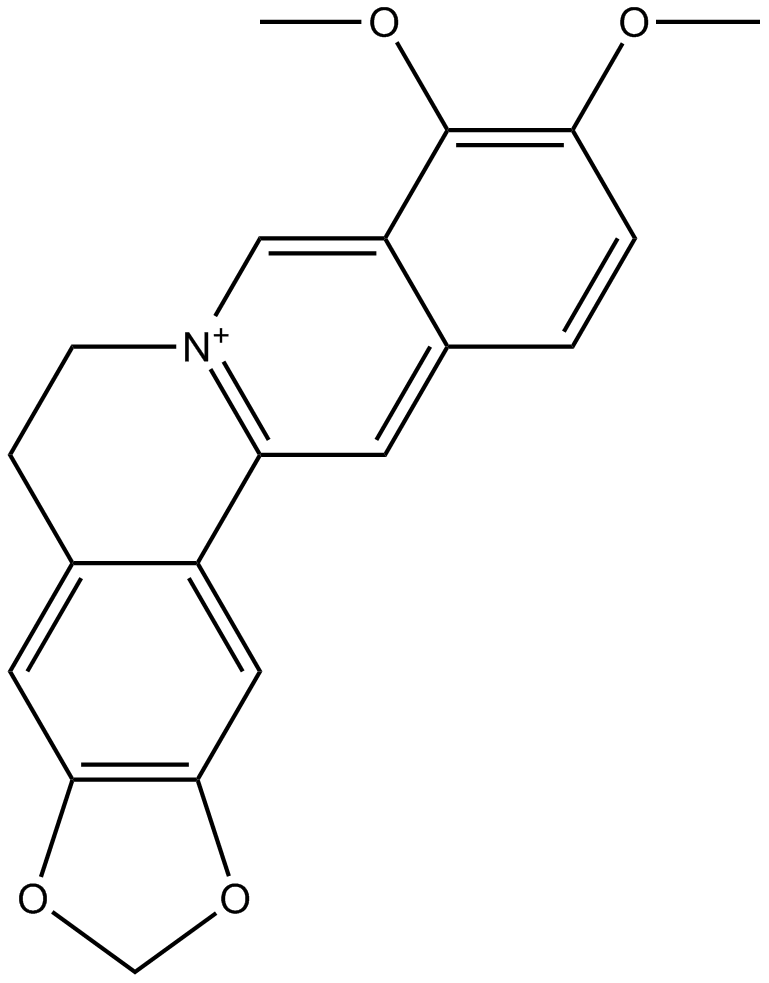 N1368 Berberine
N1368 Berberine -
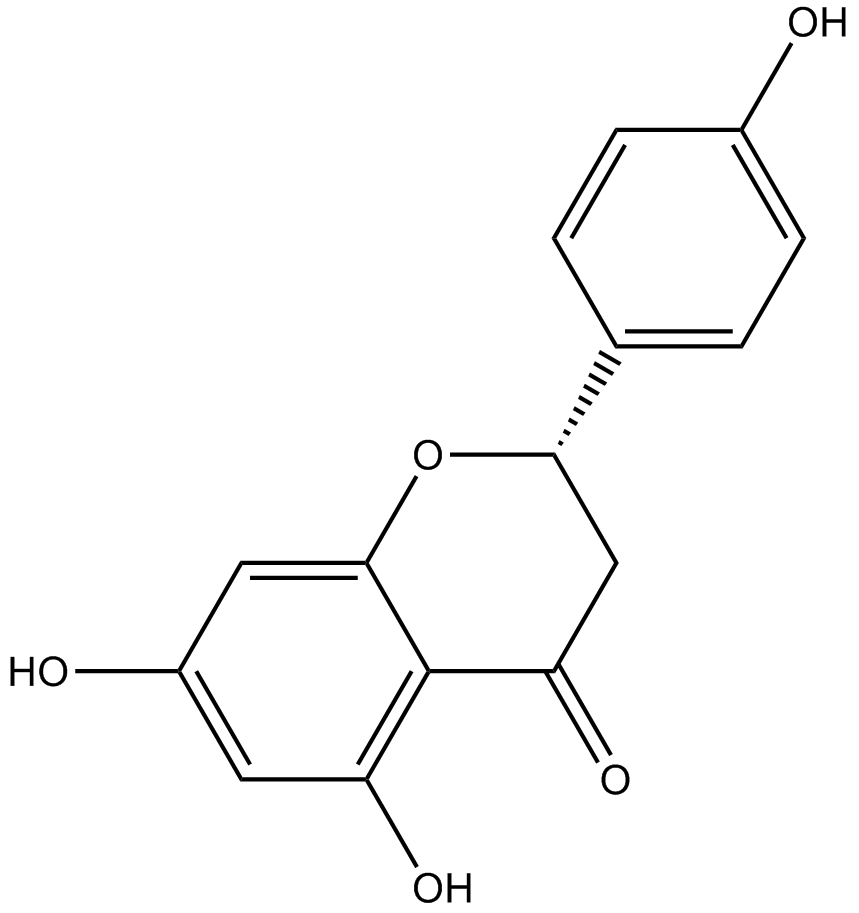 N1370 Naringenin
N1370 Naringenin -
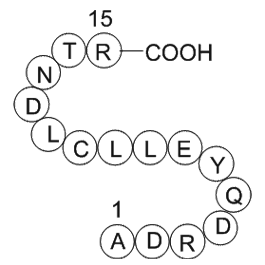 A1093 transferrin fragmentSummary: Transferrin fragment
A1093 transferrin fragmentSummary: Transferrin fragment -
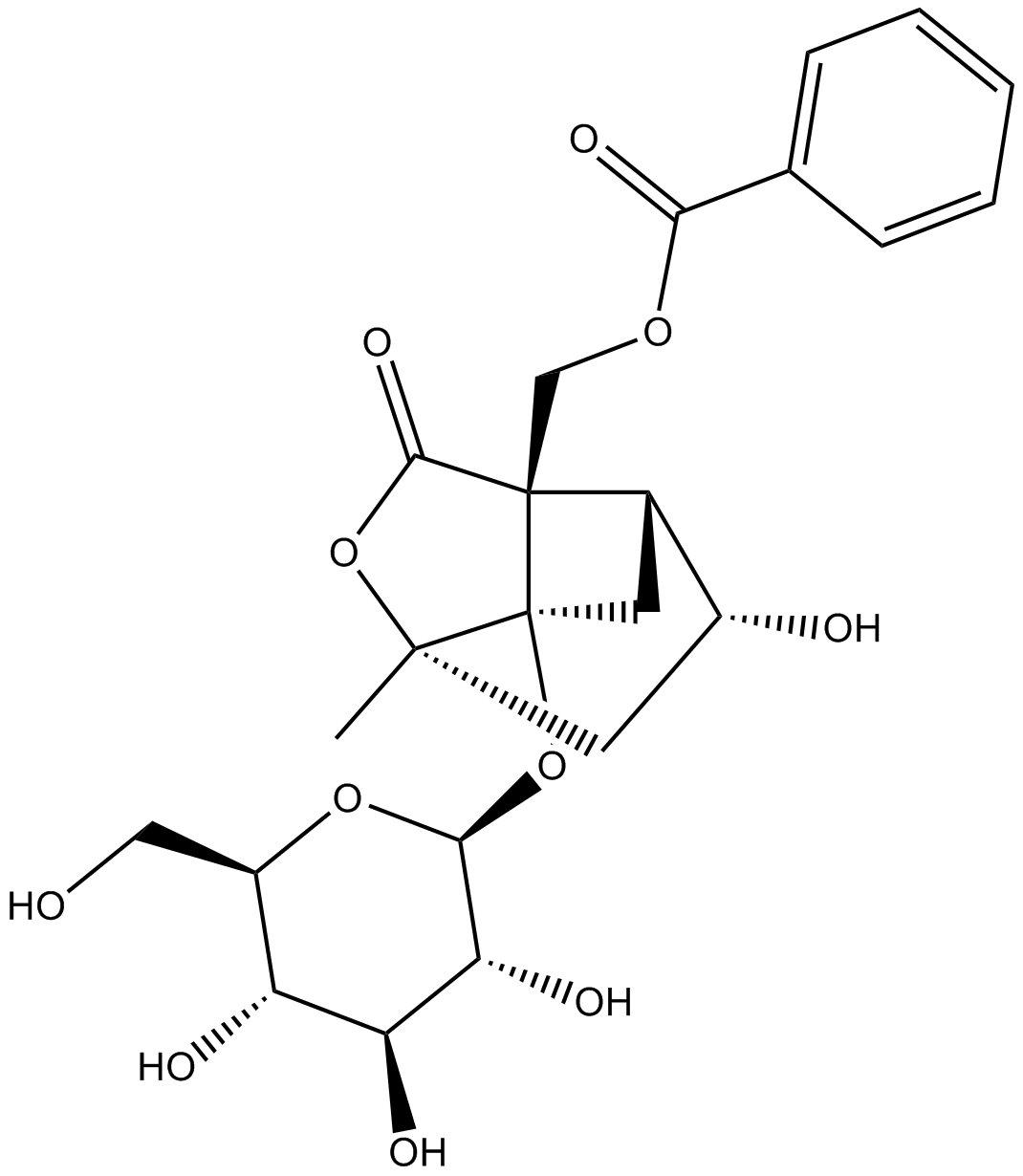 N1404 Alibiflorin
N1404 Alibiflorin -
 N1413 Calycosin-7-glucoside
N1413 Calycosin-7-glucoside


