Anti-infection

Anti-infectives are agents that eliminate or inhibit the spread of infectious organisms, encompassing antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, and antiprotozoals.
Antibiotics are a class of antimicrobial agents specifically designed to target bacterial pathogens. They exert their effects by interfering with essential bacterial processes such as cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, nucleic acid replication, and metabolic pathways, thereby either inhibiting bacterial growth or inducing bacterial death.
Antifungals are antimicrobial agents employed to combat fungal infections (mycoses) in humans and animals. Common antifungal classes include azoles, polyenes, echinocandins, and allylamines, which function by disrupting unique fungal structures or pathways, such as the synthesis or integrity of ergosterol-containing cell membranes and β-glucan-based cell walls, or by interfering with nucleic acid or protein synthesis.
Antivirals are compounds developed to inhibit the replication and spread of viruses within host organisms. Antivirals typically act by blocking viral entry, genome replication, protein processing, or virion assembly and release. Representative examples include nucleoside analogs, protease inhibitors, and neuraminidase inhibitors.
Antiprotozoals are drugs used to treat infections caused by protozoan parasites, including malaria, amebiasis, giardiasis, and trypanosomiasis. They act through a variety of mechanisms, including inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis, interference with mitochondrial function, and disruption of heme detoxification pathways in susceptible parasites.
-
 BA1246 DeoxyshikoninSummary: Deoxyshikonin increases HMVEC-dLy neutralizing mRNA expression, promotes HIF-1α and HIF-1β subunit interactions, and binds to specific DNA sequences.
BA1246 DeoxyshikoninSummary: Deoxyshikonin increases HMVEC-dLy neutralizing mRNA expression, promotes HIF-1α and HIF-1β subunit interactions, and binds to specific DNA sequences. -
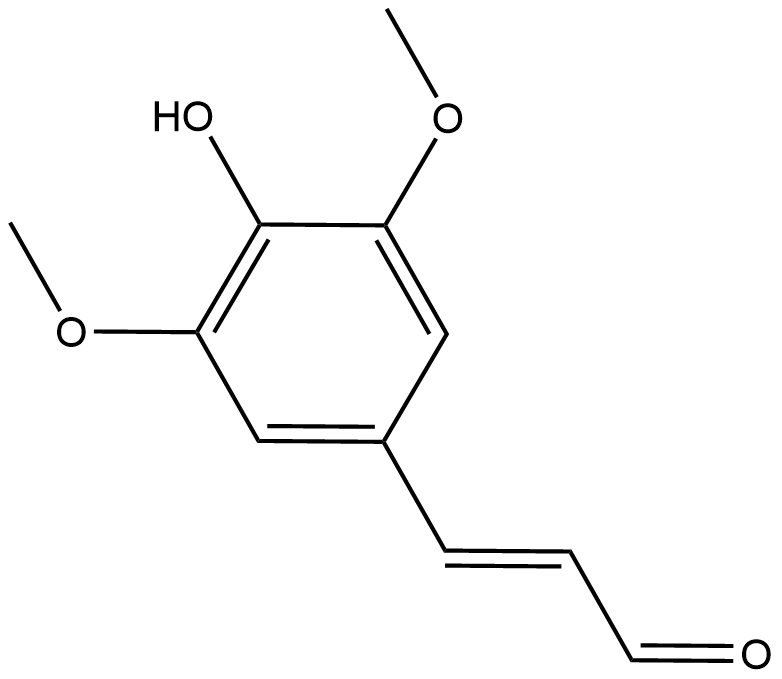 BA1247 SinapaldehydeSummary: Sinapaldehyde has moderate antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA0) and Escherichia coli.
BA1247 SinapaldehydeSummary: Sinapaldehyde has moderate antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA0) and Escherichia coli. -
 BA1248 MonolaurinSummary: Possesses antiviral and antibacterial activity.
BA1248 MonolaurinSummary: Possesses antiviral and antibacterial activity. -
 BA1249 KyotorphinSummary: Kytorphin is an endogenous neuroactive dipeptide that can be used in studies of pain-relieving properties.
BA1249 KyotorphinSummary: Kytorphin is an endogenous neuroactive dipeptide that can be used in studies of pain-relieving properties. -
 BA1250 TargocilSummary: Targocil is used as a bacteriostatic inhibitor of phospholambanic acid (WTA) biosynthesis.
BA1250 TargocilSummary: Targocil is used as a bacteriostatic inhibitor of phospholambanic acid (WTA) biosynthesis. -
 BA1252 DprE1-IN-1Summary: DprE1-IN-1 is a potent and orally active inhibitor with good hepatocyte stability, low cytotoxicity and low hERG channel inhibition.
BA1252 DprE1-IN-1Summary: DprE1-IN-1 is a potent and orally active inhibitor with good hepatocyte stability, low cytotoxicity and low hERG channel inhibition. -
 BA1254 Leu-AMSSummary: Leu-AMS, a leucine analog, is a potent leucyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitor.
BA1254 Leu-AMSSummary: Leu-AMS, a leucine analog, is a potent leucyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitor. -
 BA1255 MaltotetraoseSummary: Can be used as a substrate for enzyme-linked assays of amylase activity in biofluids.
BA1255 MaltotetraoseSummary: Can be used as a substrate for enzyme-linked assays of amylase activity in biofluids. -
 BA1256 NacubactamSummary: Nacubactam (OP0595 free acid) is a potent non-β-lactam-β-lactamase inhibitor with activity against class A and C beta-lactamases.
BA1256 NacubactamSummary: Nacubactam (OP0595 free acid) is a potent non-β-lactam-β-lactamase inhibitor with activity against class A and C beta-lactamases. -
 BA1257 MAC13772Summary: MAC13772 is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme (=250nM), the penultimate step in biotin synthesis.
BA1257 MAC13772Summary: MAC13772 is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme (=250nM), the penultimate step in biotin synthesis.


