Amino Acids & Peptides
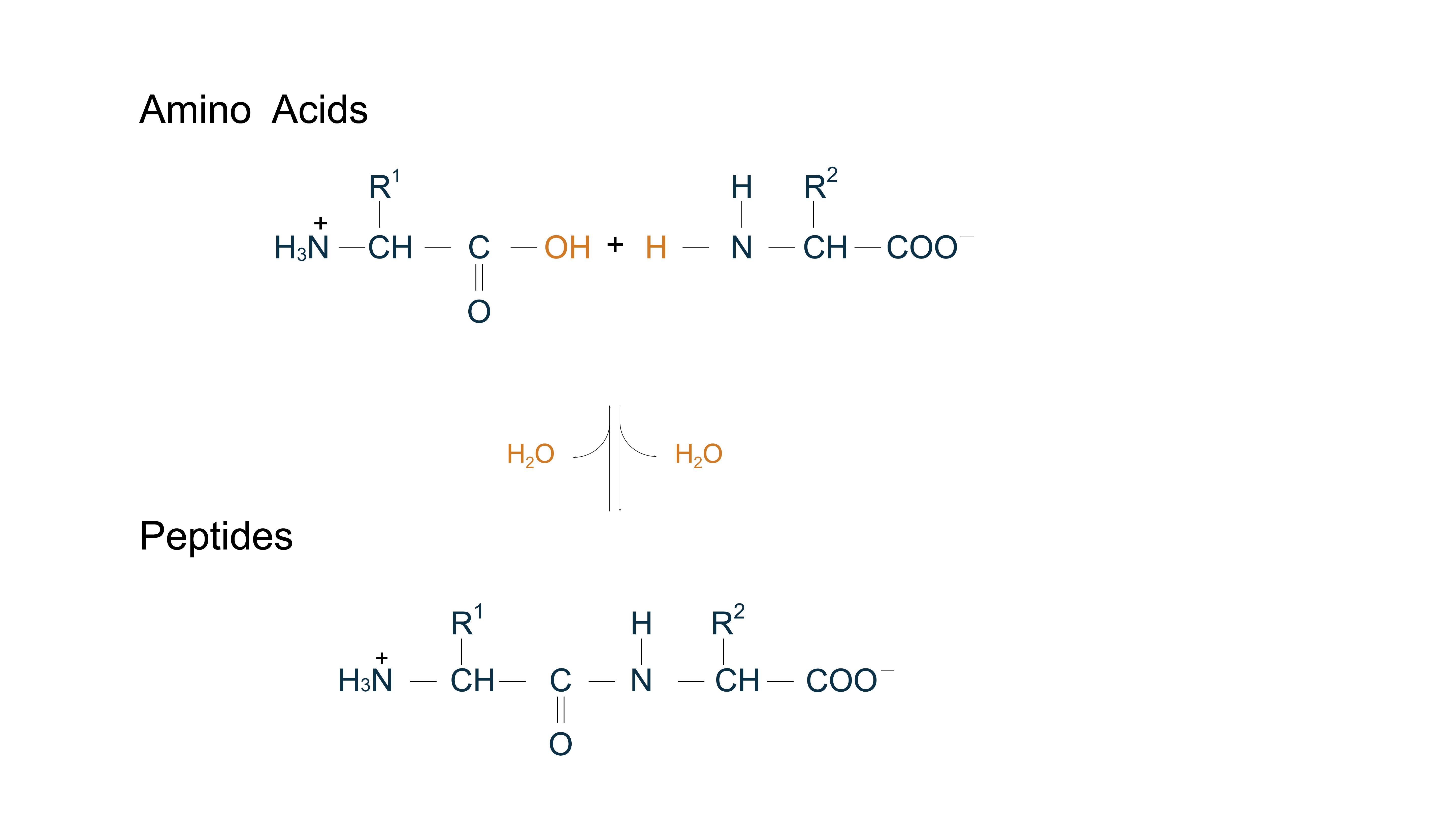

Amino acids are fundamental organic molecules with a common structure: an amino group (–NH₂), a carboxyl group (–COOH), and a side chain (or R group) that differs their properties. 20 α-amino acids are commonly found in proteins, serving as protein building blocks. Some of less common amino acids also have important functions, serving either as constituents of proteins (through modification of common amino acid residues after protein synthesis) or as metabolic intermediates. As amino acids are essential for life, they are used as supplements in cell culture media and as key materials for metabolic studies. Uncommon or modified amino acids are utilized in drug development.
Amino acids can be covalently joined through a peptide bond, formed by dehydration from the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid and the α-amino group of another via condensation reaction, allowing them to polymerize into peptides and proteins. Molecules called peptides generally have molecular weights below 10,000, whereas those called proteins have higher molecular weights. Mainly derived from natural sources or their analogs, peptides exhibit diverse biological activities (antimicrobial, antiviral, antioxidant, immunomodulatory) with high target affinity, stable efficacy, low immunogenicity, and minimal toxicity. Advances in biotechnology and synthesis have expanded their applications in disease research, drug development, and vaccine development. Clinically, peptide-based drugs now address cancer, hepatitis, diabetes, and HIV/AIDS.
-
 BA9530 Z-Gln-OHSummary: A glutamine derivative.
BA9530 Z-Gln-OHSummary: A glutamine derivative. -
 BA9531 H-Asp-OMeSummary: An aspartic acid derivative.
BA9531 H-Asp-OMeSummary: An aspartic acid derivative. -
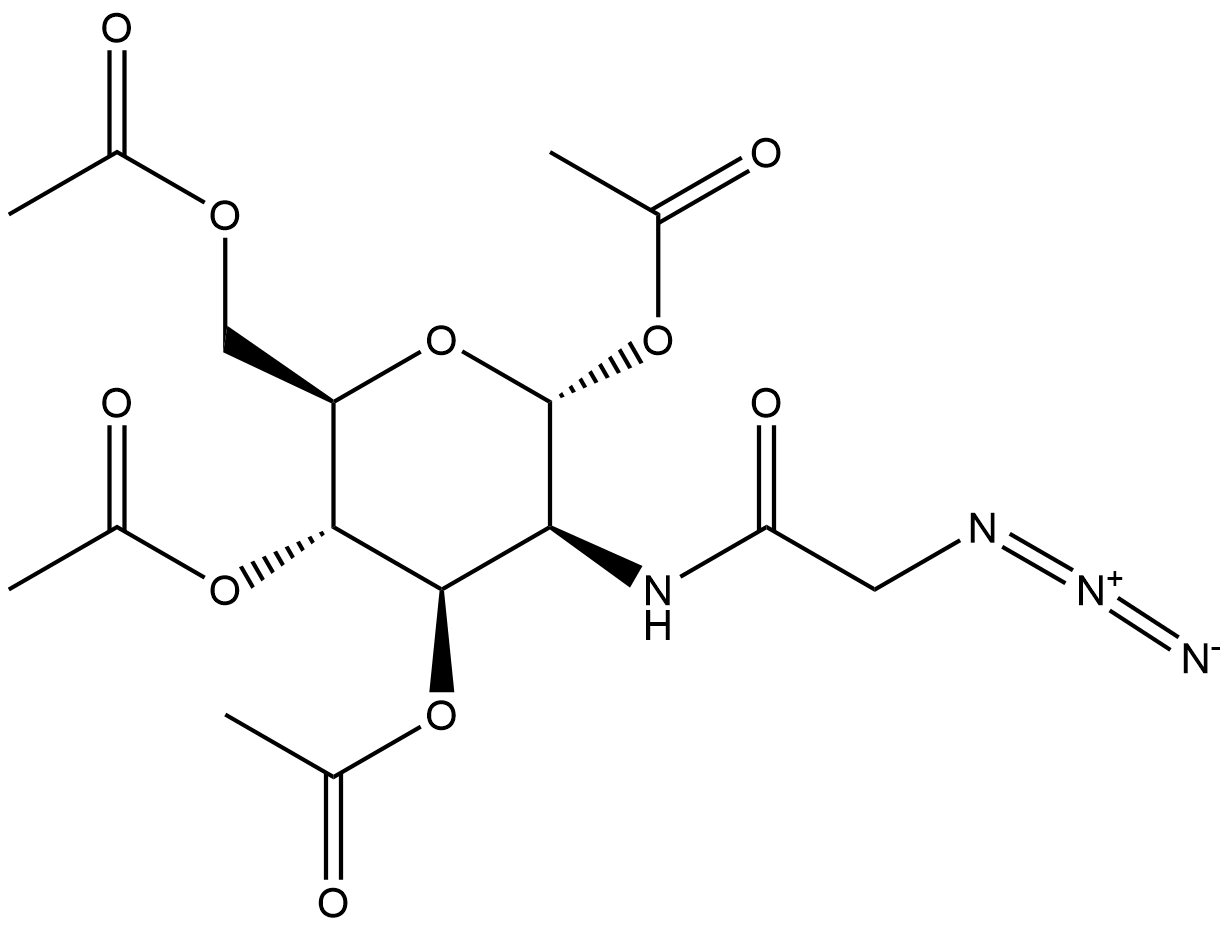 BA9533 Ac4ManNAzSummary: Ac4ManNAz can be taken up by cells and is an azide group-containing metabolic glycoprotein labeling reagent while selectively modifying proteins.
BA9533 Ac4ManNAzSummary: Ac4ManNAz can be taken up by cells and is an azide group-containing metabolic glycoprotein labeling reagent while selectively modifying proteins. -
 BA9534 NAI-N3Summary: NAI-N3 is an RNA acylation reagent that enables RNA purification.
BA9534 NAI-N3Summary: NAI-N3 is an RNA acylation reagent that enables RNA purification. -
 BA9535 Glyco-diosgeninSummary: A synthetic surfactant and detergent.
BA9535 Glyco-diosgeninSummary: A synthetic surfactant and detergent. -
 BA9542 ONPGSummary: ONPG is a colorimetric and spectrophotometric substrate.
BA9542 ONPGSummary: ONPG is a colorimetric and spectrophotometric substrate. -
 BA9543 DBCO-PEG4-BiotinSummary: DBCO-PEG4-Biotin is an azadibenzocyclooctyne-biotin derivative containing a biotin moiety and 4 PEGs.
BA9543 DBCO-PEG4-BiotinSummary: DBCO-PEG4-Biotin is an azadibenzocyclooctyne-biotin derivative containing a biotin moiety and 4 PEGs. -
 BA9545 ATP-polyamine-biotinSummary: ATP-polyamine-biotin, the first cell-permeable ATP analog, is a potent kinase co-substrate.
BA9545 ATP-polyamine-biotinSummary: ATP-polyamine-biotin, the first cell-permeable ATP analog, is a potent kinase co-substrate. -
 BA9547 3-AminopropyltriethoxysilaneSummary: 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) serves as a strong adhesive capable of immobilizing biomolecules (e.g., antibodies and enzymes) on silicon and silicon derivatives (e.g., silicon nitride (SiN)).
BA9547 3-AminopropyltriethoxysilaneSummary: 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) serves as a strong adhesive capable of immobilizing biomolecules (e.g., antibodies and enzymes) on silicon and silicon derivatives (e.g., silicon nitride (SiN)). -
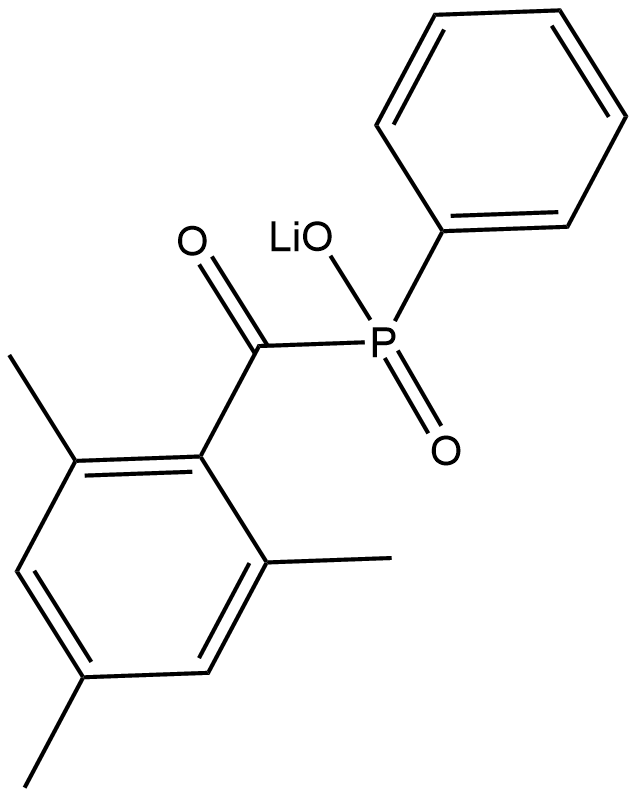 BA9550 LAPSummary: LAP (Lithiumphenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate) is a free radical initiator.
BA9550 LAPSummary: LAP (Lithiumphenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate) is a free radical initiator.


