Search results for: 'signaling pathways tgf b smad signaling'
-
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
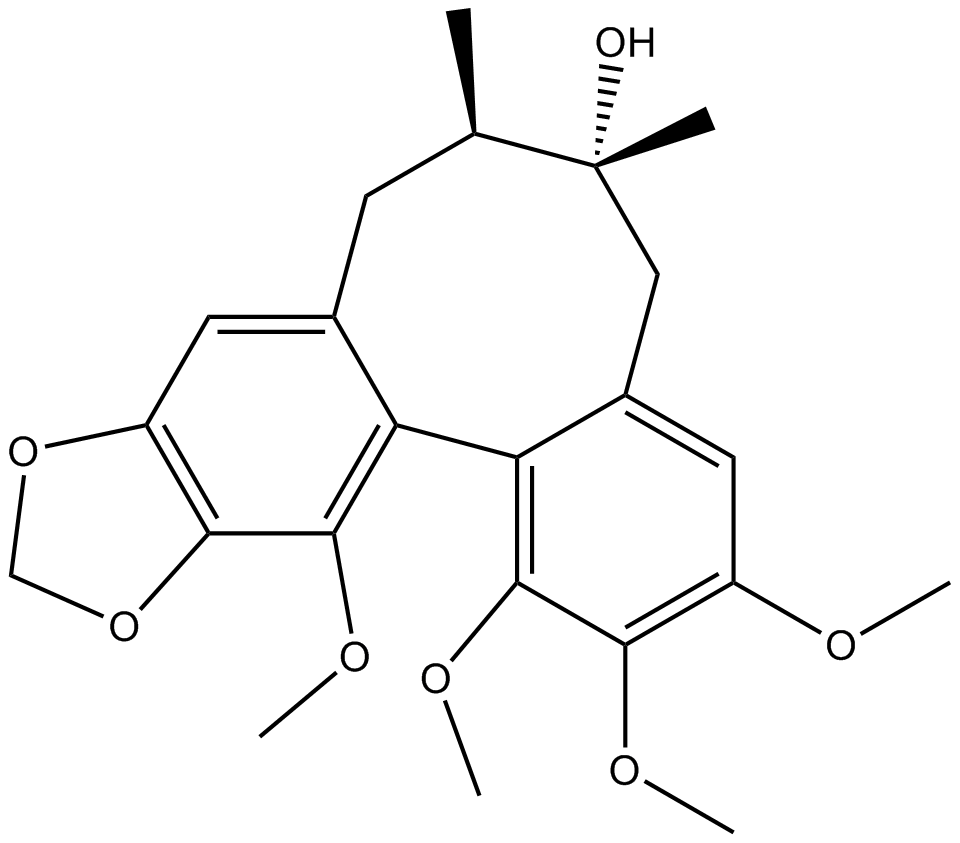 N1190 Schisandrol B
N1190 Schisandrol B -
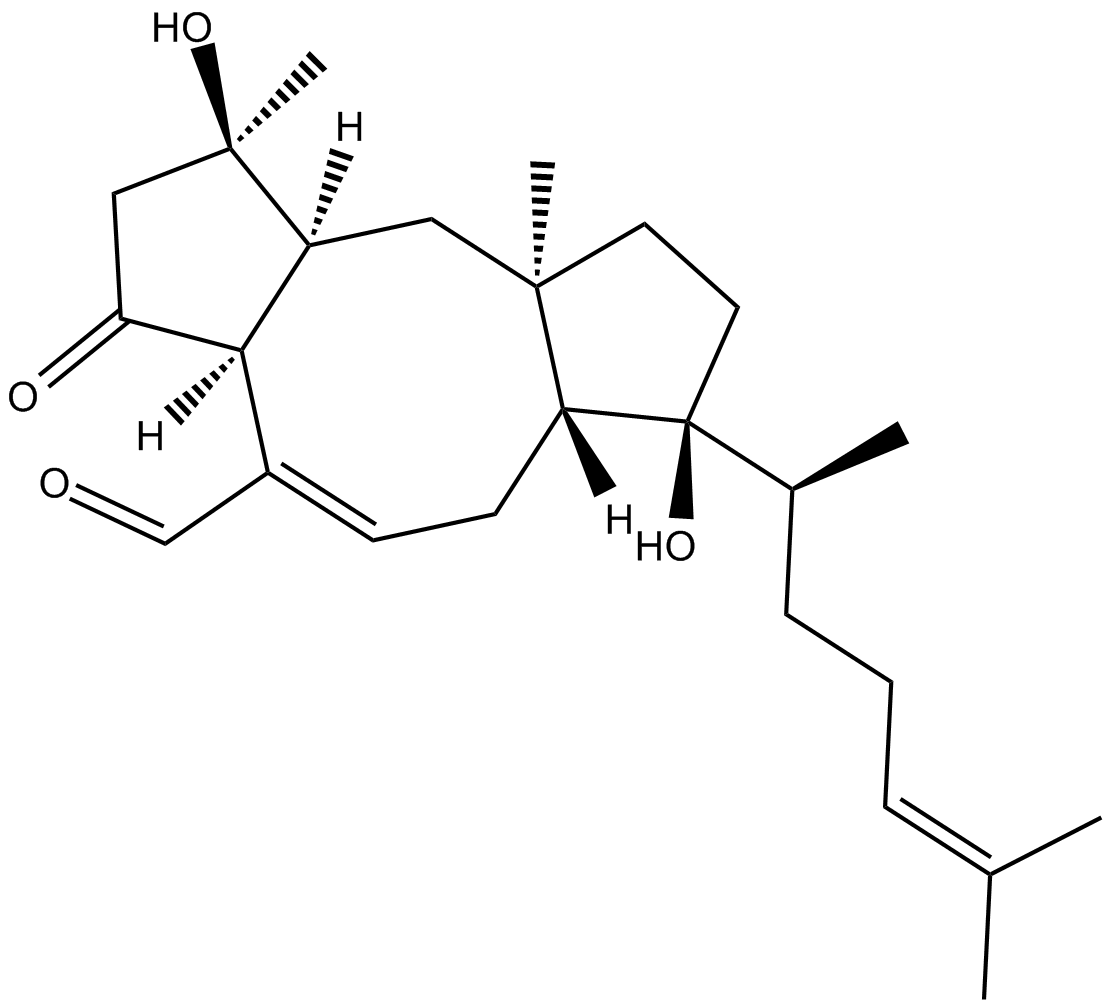 C3839 Ophiobolin BSummary: calmodulin antagonist
C3839 Ophiobolin BSummary: calmodulin antagonist -
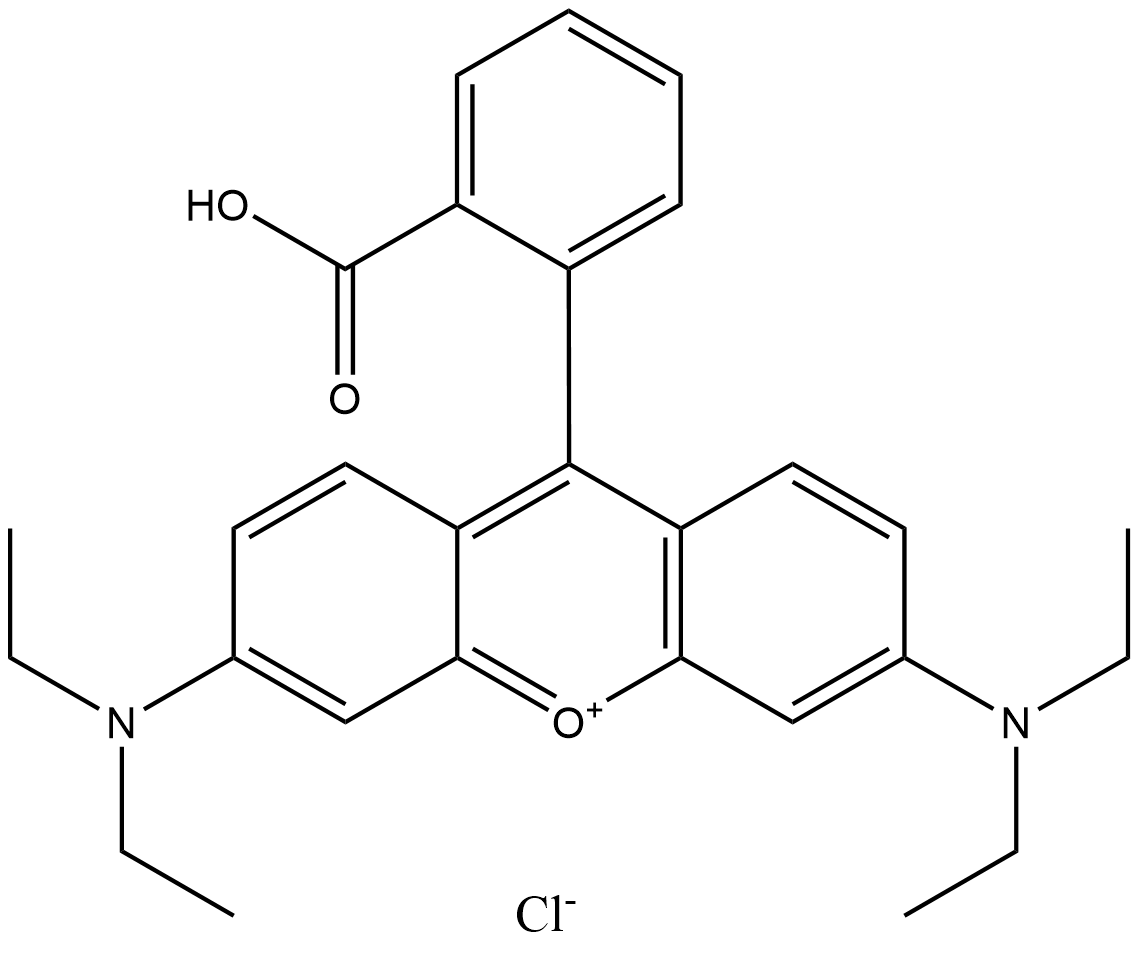 A4705 Rhodamine B
A4705 Rhodamine B -
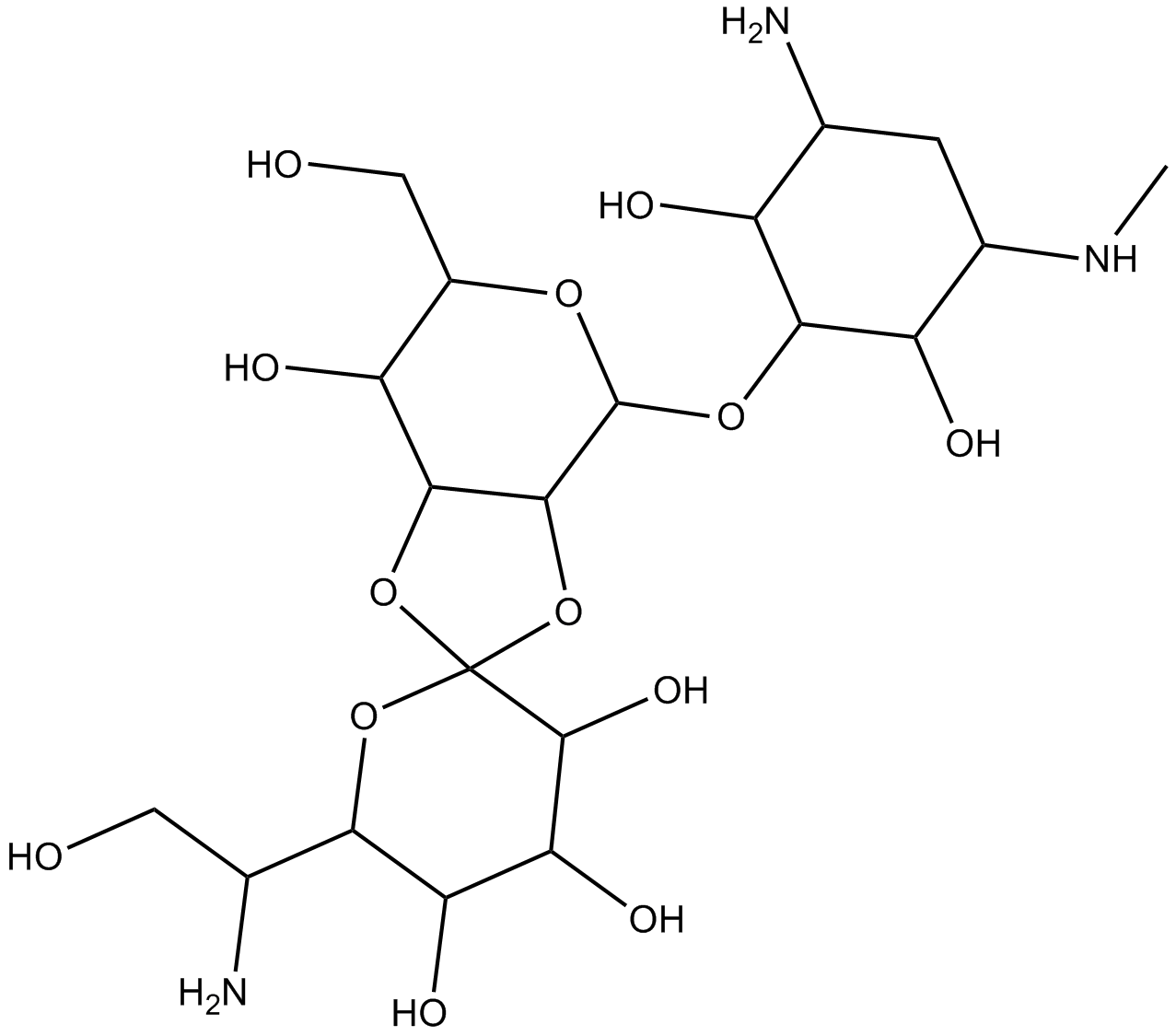 A2515 Hygromycin BSummary: Hygromycin B
A2515 Hygromycin BSummary: Hygromycin B -
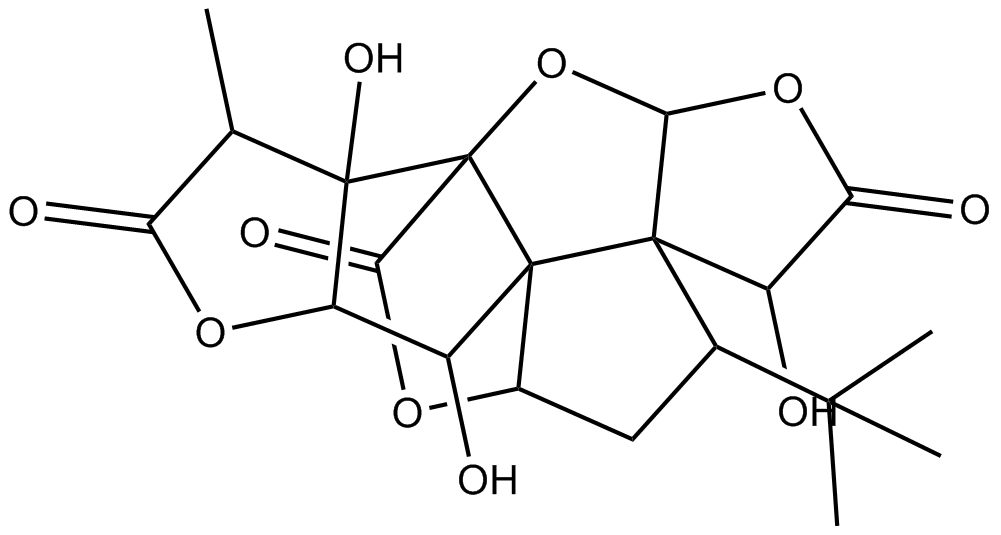 N1879 Ginkgolide BSummary: PAF receptor antagonist
N1879 Ginkgolide BSummary: PAF receptor antagonist -
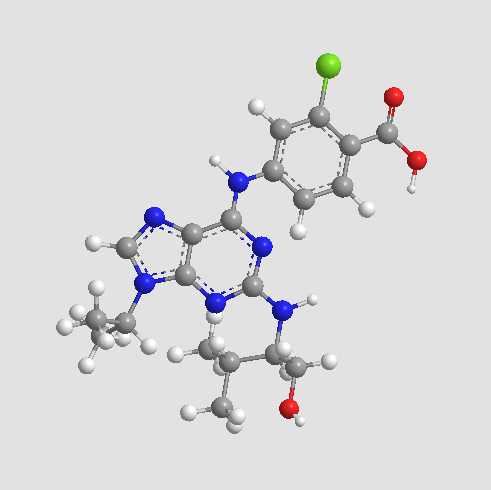 A8565 Purvalanol B1 CitationTarget: Cyclin-Dependent KinasesSummary: CDK1/CDK2/CDK4 inhibitor
A8565 Purvalanol B1 CitationTarget: Cyclin-Dependent KinasesSummary: CDK1/CDK2/CDK4 inhibitor


