Tyrosine Kinase
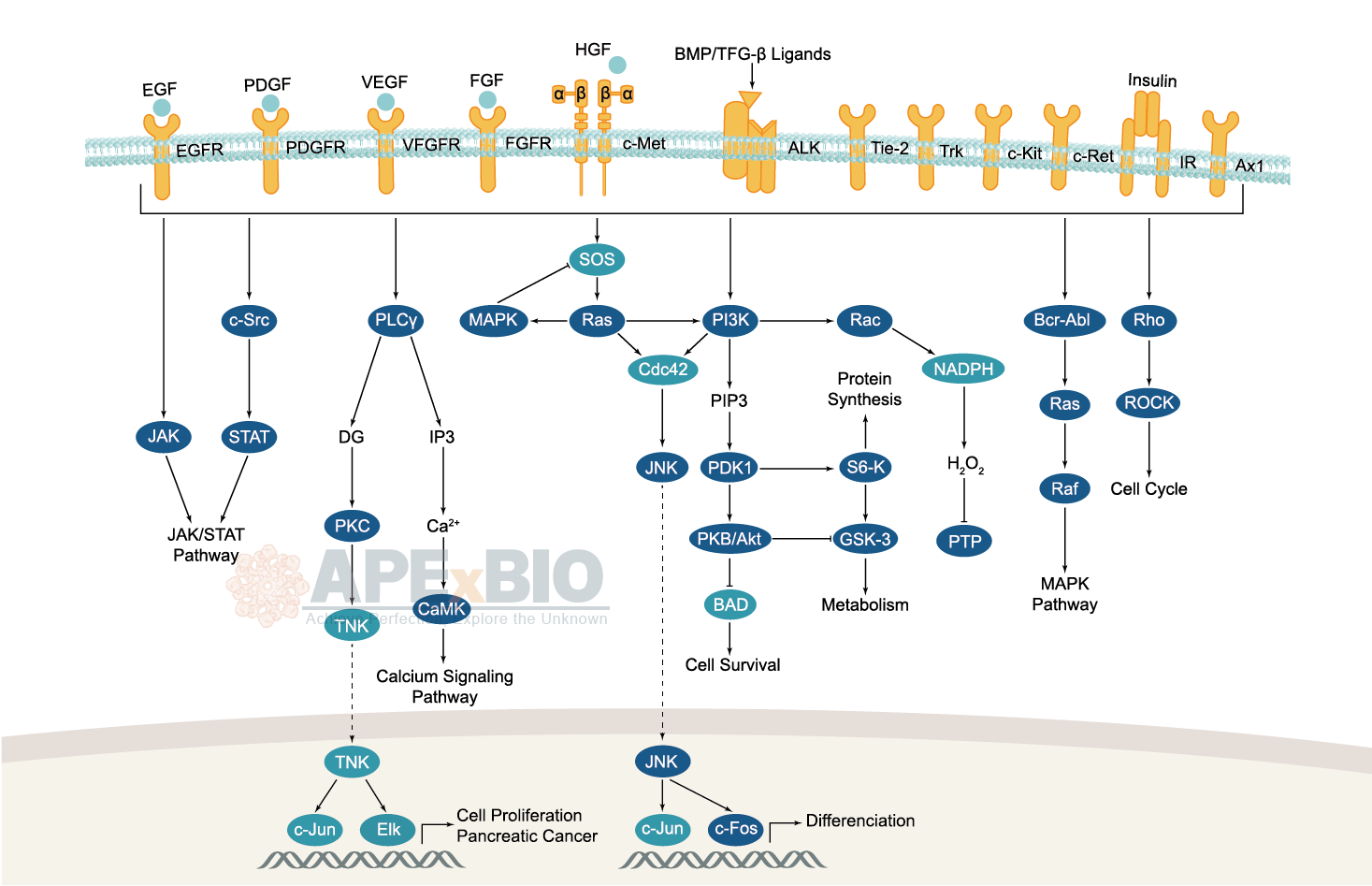

Receptor tyrosine kinases bind to extracellular ligands/growth factors, which promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine residues. This triggers a cascade of downstream events through phosphorylation of intracellular proteins that ultimately transduce the extracellular signal to the nucleus, causing changes in gene expression. Receptor tyrosine kinases include EGFR/ErbB, PDGFR, VEGFR, FGFR and MET subfamilies etc. Dysfunctions in tyrosine phosphorylation are linked to oncogenic transformation. In additions, various adaptor and effector proteins couple to carboxy-terminal of an active kinase. For instance, binding of the GRB2 adaptor protein activates EGFR and MAPK/ERK signaling.
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases involve many well-defined proteins (e.g. the Src family kinases, c-Abl, and Jak kinases) and other kinases which regulates cell growth and differentiation. For example, Src family kinases are curial for activating and inhibitory pathways in the innate immune response.
-
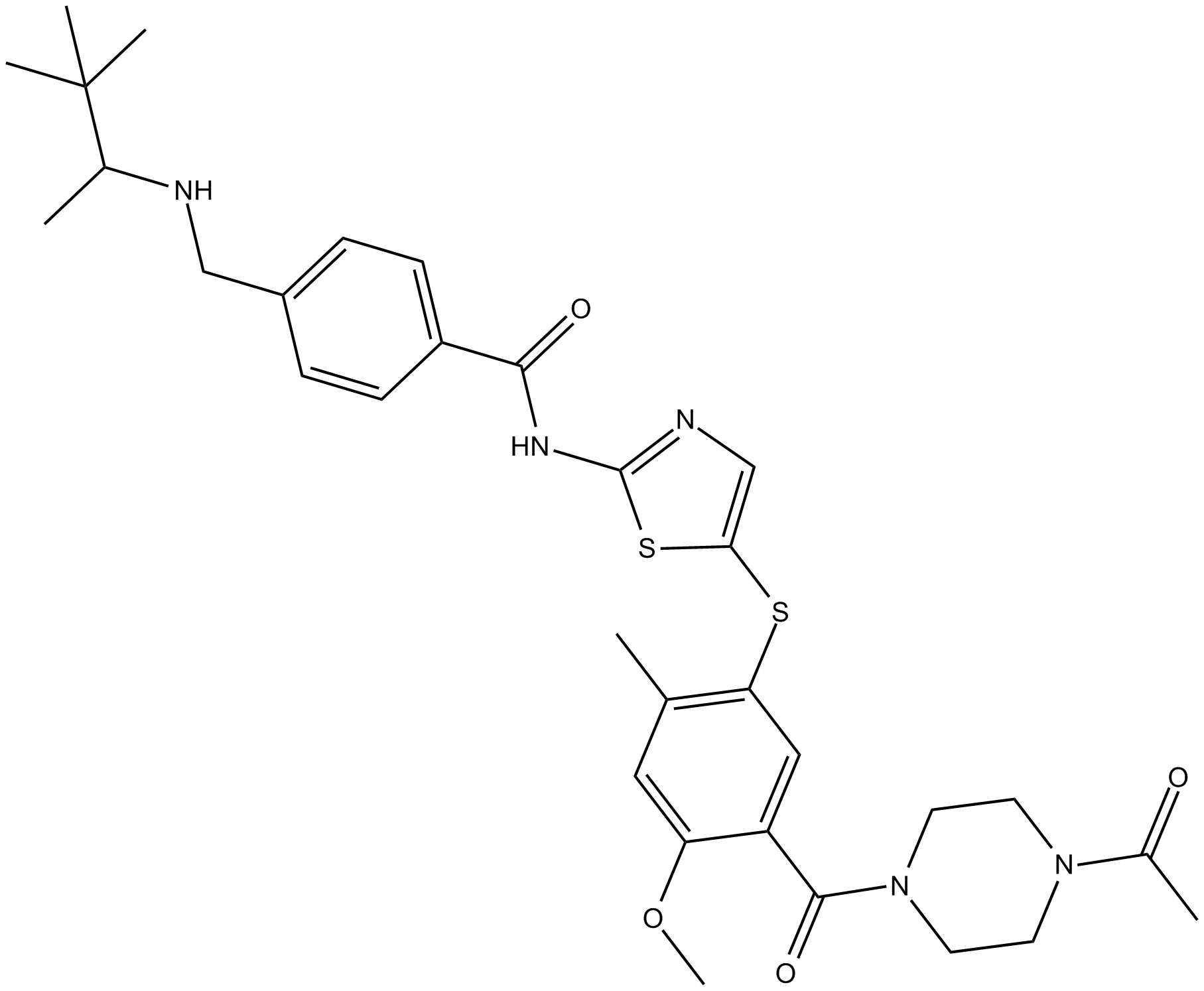 A3250 BMS-509744Target: ITKSummary: Itk inhibitor,potent and selective
A3250 BMS-509744Target: ITKSummary: Itk inhibitor,potent and selective -
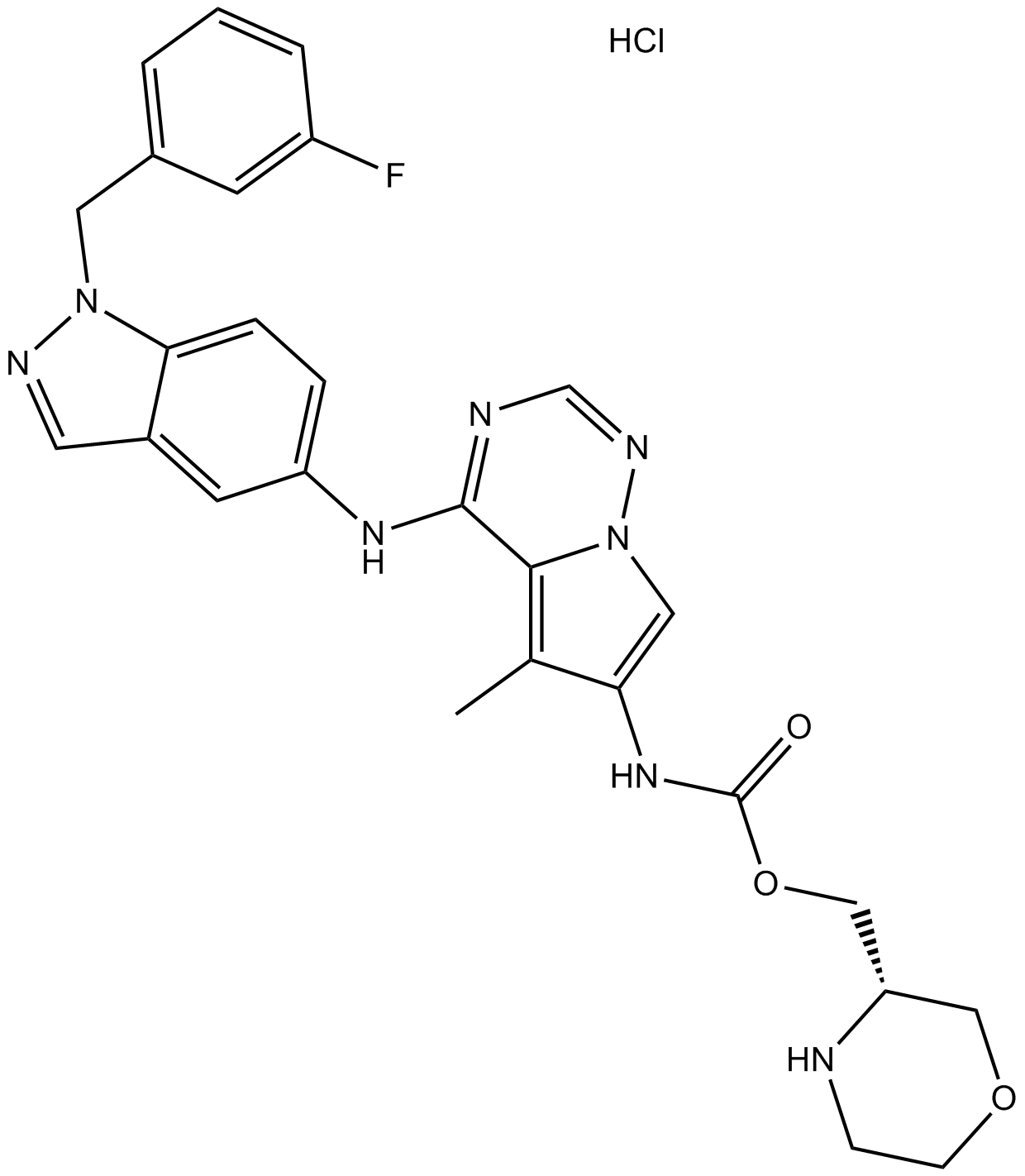 A3252 BMS-599626 HydrochlorideSummary: EGFR/HER2 inhibitor,potent and selective
A3252 BMS-599626 HydrochlorideSummary: EGFR/HER2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
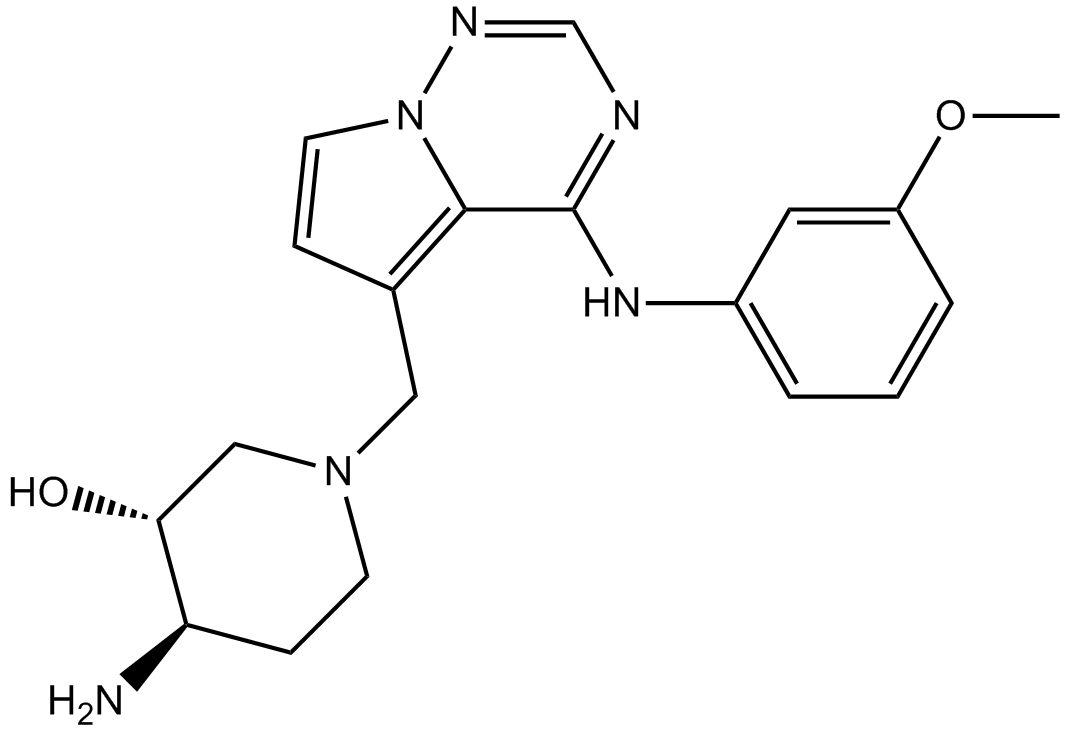 A3256 BMS-690514Summary: HER/EGFR inhibitor
A3256 BMS-690514Summary: HER/EGFR inhibitor -
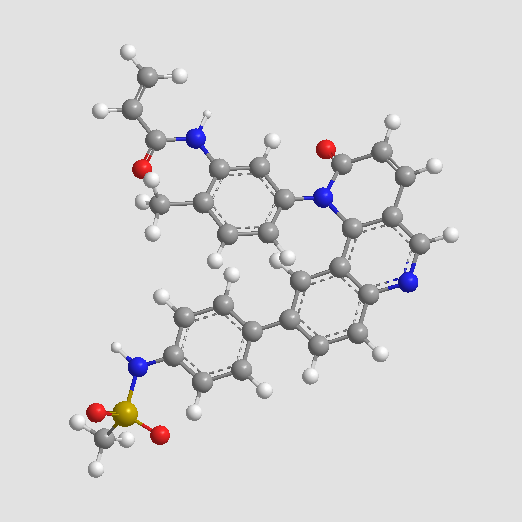 A3260 BMX-IN-1Summary: BMX (also termed ETK) kinase inhibitor
A3260 BMX-IN-1Summary: BMX (also termed ETK) kinase inhibitor -
 A3276 Canertinib dihydrochlorideSummary: Pan-ErbB inhibitor, potent and selective
A3276 Canertinib dihydrochlorideSummary: Pan-ErbB inhibitor, potent and selective -
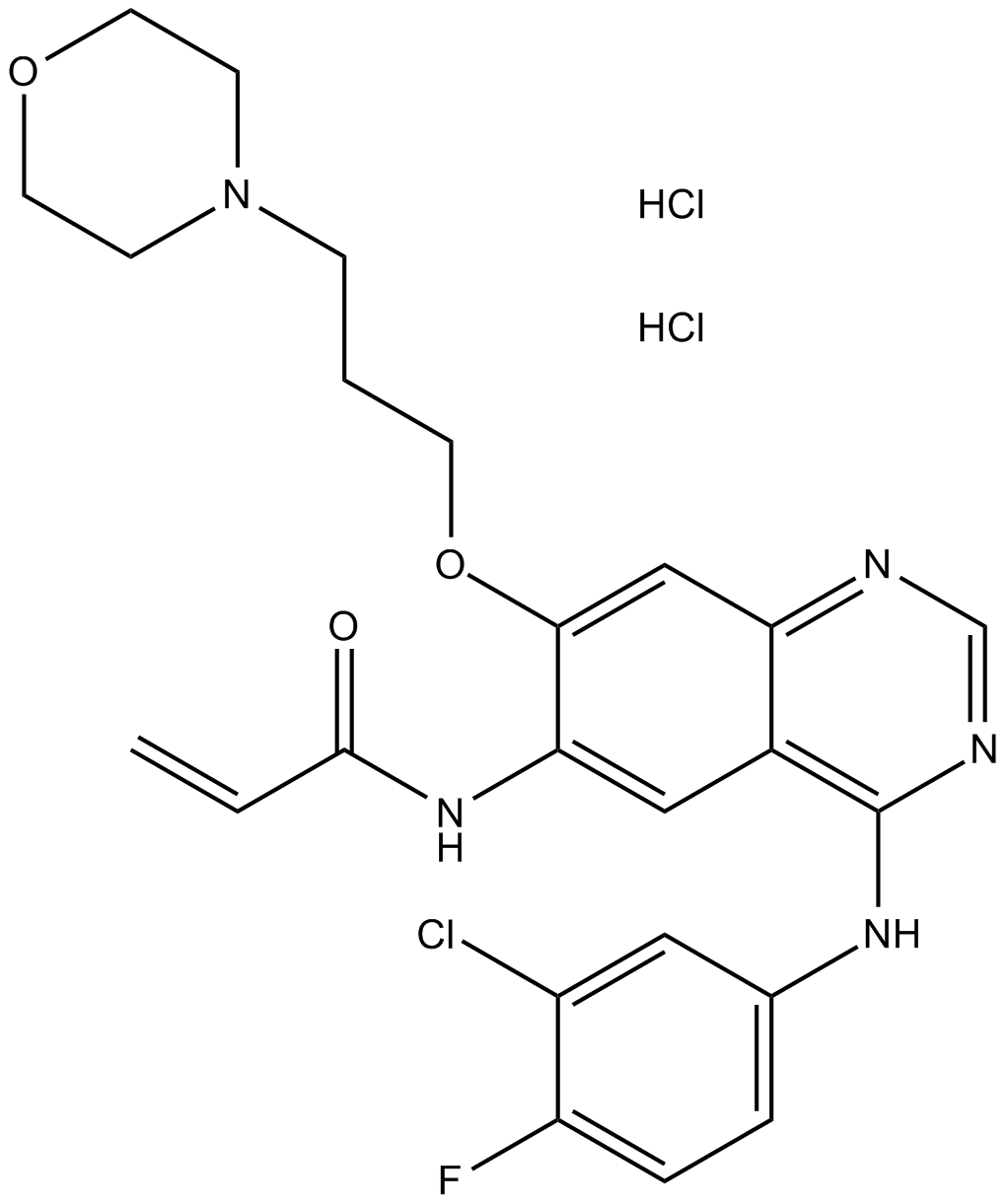
 A3320 CO-1686 (AVL-301)1 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: EGFR inhibitor
A3320 CO-1686 (AVL-301)1 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: EGFR inhibitor -
 A3351 Dasatinib hydrochlorideSummary: Multi-BCR/Abl and Src kinase inhibitor, oral active
A3351 Dasatinib hydrochlorideSummary: Multi-BCR/Abl and Src kinase inhibitor, oral active -
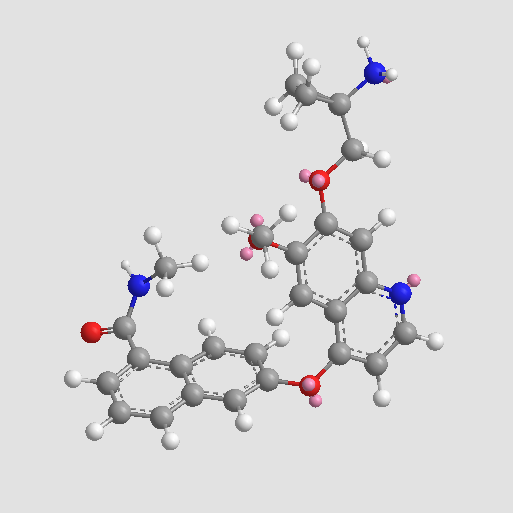 A3378 E-3810Summary: VEGF/FGF dual inhibitor, potent and selective
A3378 E-3810Summary: VEGF/FGF dual inhibitor, potent and selective -
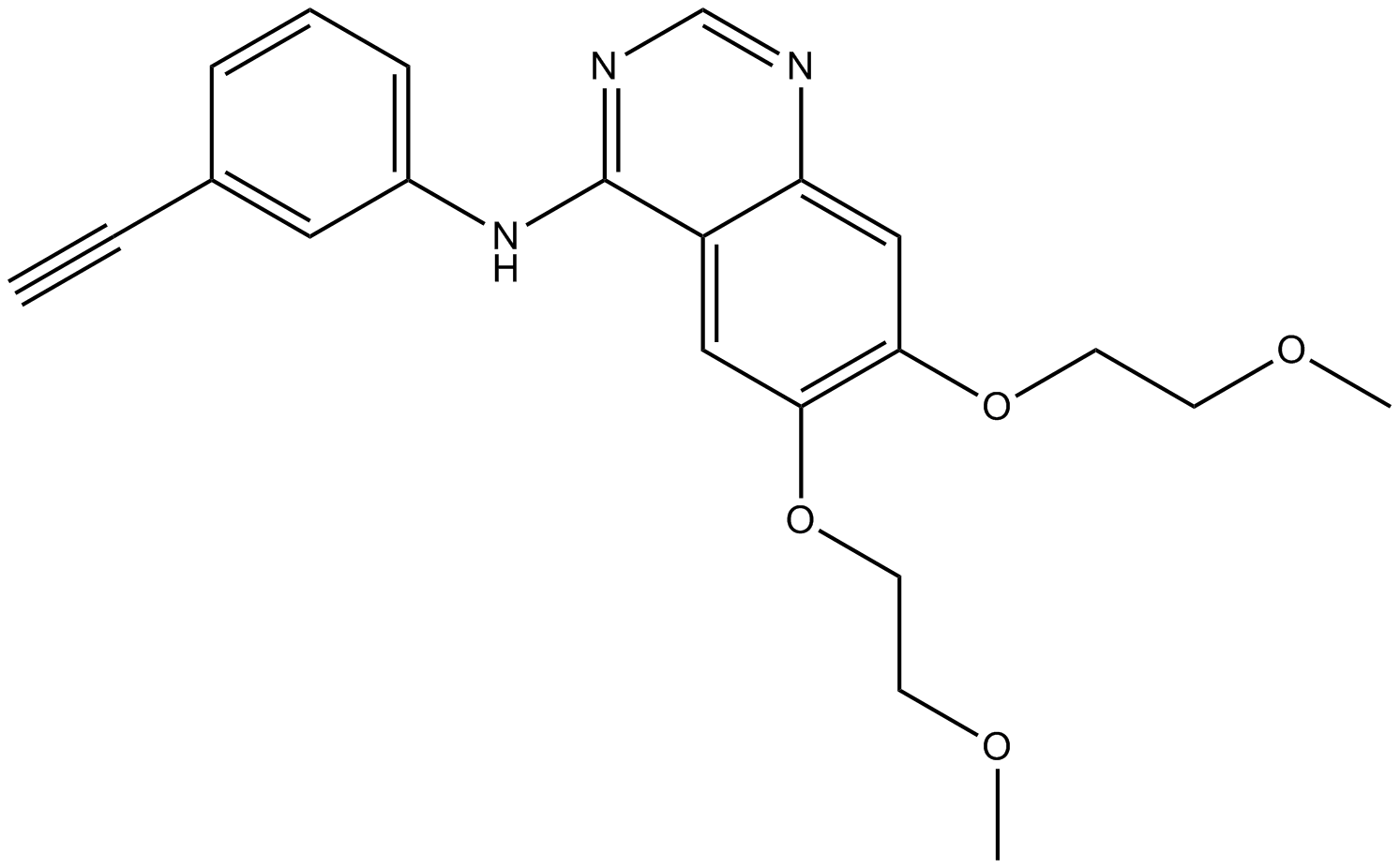 A3397 Erlotinib6 CitationSummary: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
A3397 Erlotinib6 CitationSummary: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor -
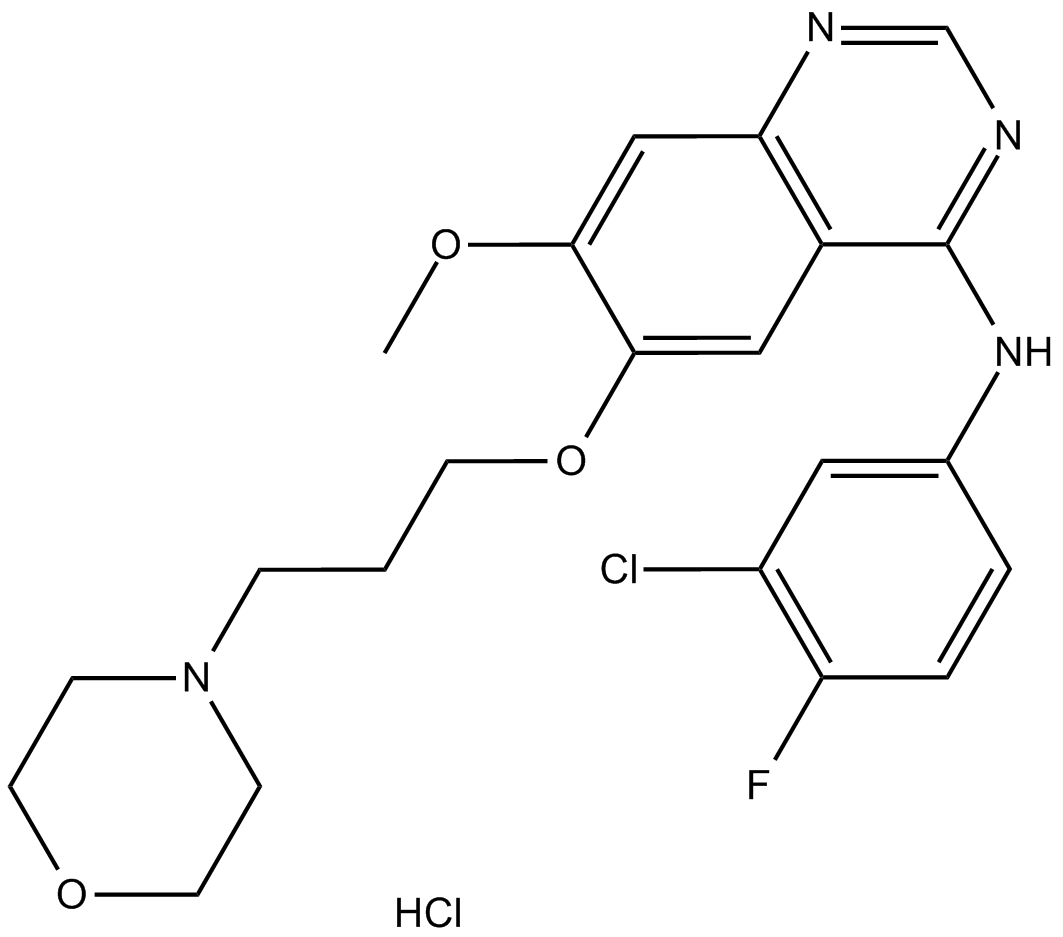 A3433 Gefitinib hydrochlorideTarget: EGFRSummary: Potent EGFR inhibitor
A3433 Gefitinib hydrochlorideTarget: EGFRSummary: Potent EGFR inhibitor


