Neuroscience
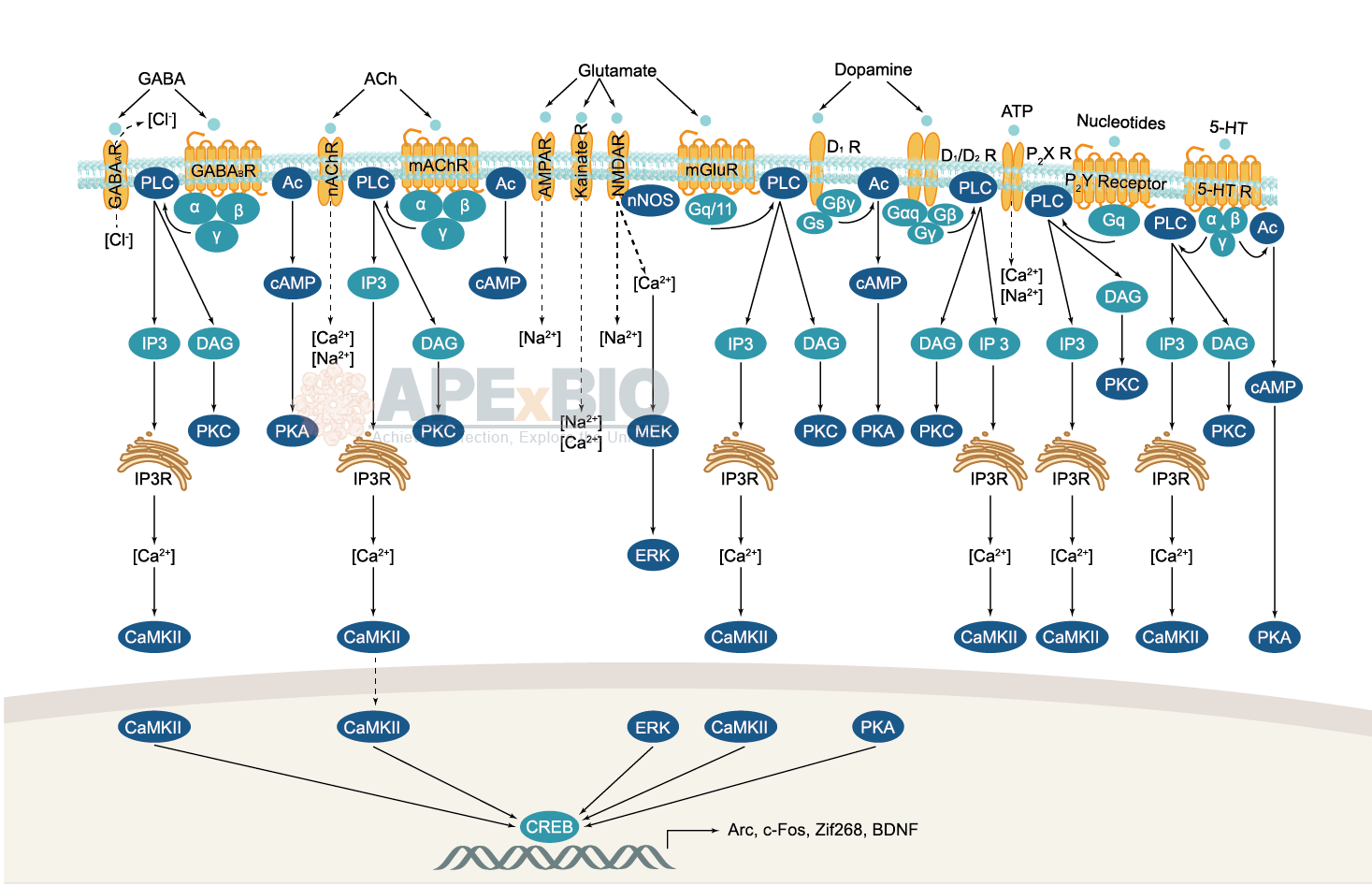

Neurons are the foundations of the sophisticated neural networks. Neurotransmitters such as dopamine, glutamate, and GABA, are crucial signaling molecules for the delivery of neuronal signals. Neurons synthesize/import neurotransmitters, and store them in presynaptic vesicles. A neuronal impulse is propagated by the vesicles released from presynaptic neurons.
Neurotransmitter receptors function via various G-protein coupled and G-protein independent mechanisms that activate downstream intracellular signaling pathways such as cAMP/PKA, PI3K/AKT, phospholipase A2, and phospholipase C pathways. For instance, dopamine receptors act through adenylate cyclase to activate PKA and other signaling molecules, thereby mediate gene expression through the actions of CREB and other transcription factors. Other neurotransmitters such as NMDAR or AMPAR are associated with ion channels that control flux of Ca2+ and Na+, thus propagating the action potential across the post-synaptic neuron.
Dysfunctions in GABAergic/glutamatergic/serotonergic/dopaminergic pathways result in a broad range of neurological disorders such as chronic pain, neurodegenerative diseases, and insomnia, as well as mental disorders including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, and addiction.
-
 B1481 DomperidoneSummary: Drug for gastroparesis
B1481 DomperidoneSummary: Drug for gastroparesis -
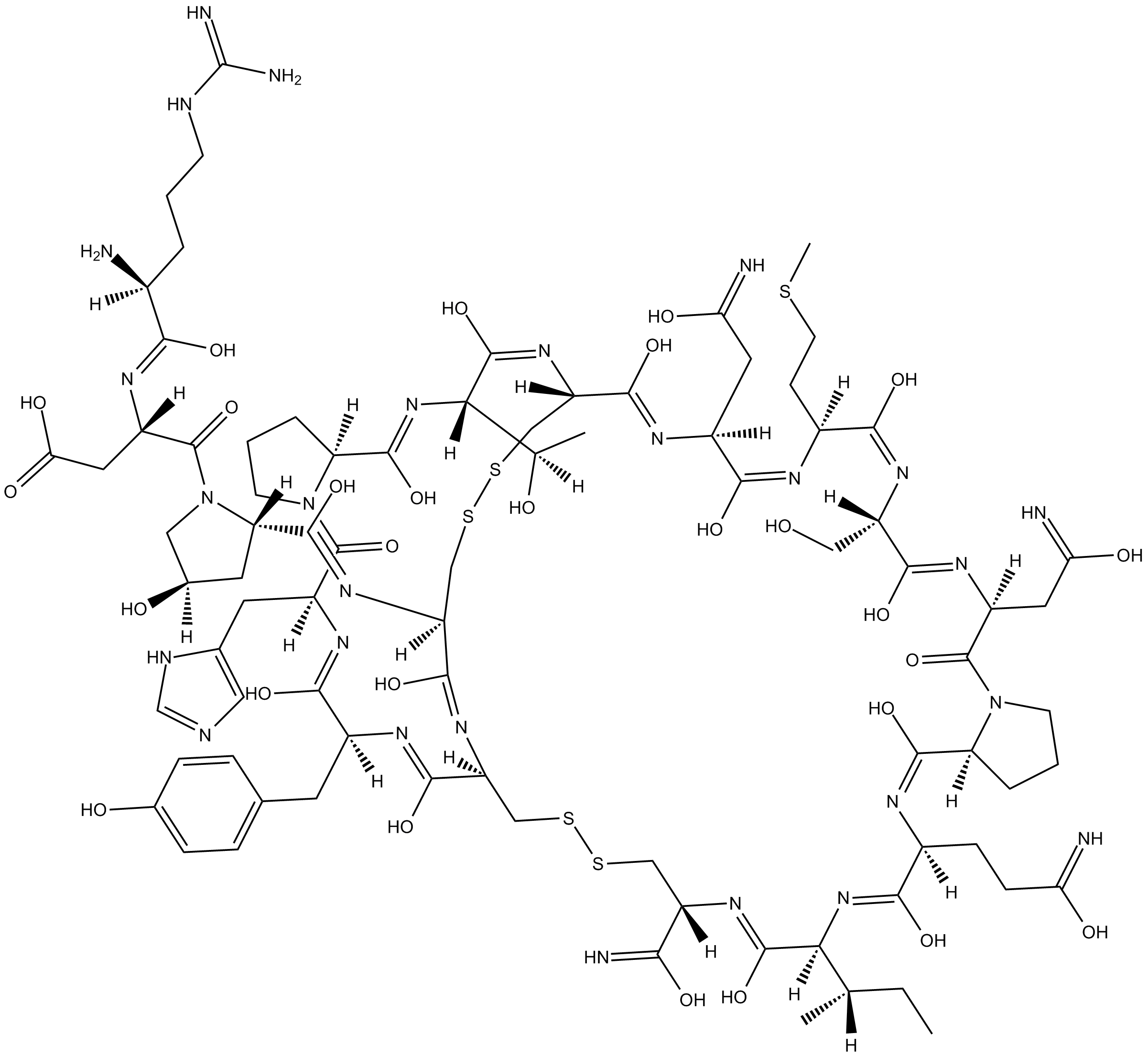 B5380 α-Conotoxin EISummary: α-Conotoxin EI is a selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) modulator that potentiates α₁β₁γδ and α₄β₂ subtypes at low concentrations and inhibits α₁β₁γδ and α₃β₄ subtypes at high concentrations.
B5380 α-Conotoxin EISummary: α-Conotoxin EI is a selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) modulator that potentiates α₁β₁γδ and α₄β₂ subtypes at low concentrations and inhibits α₁β₁γδ and α₃β₄ subtypes at high concentrations. -
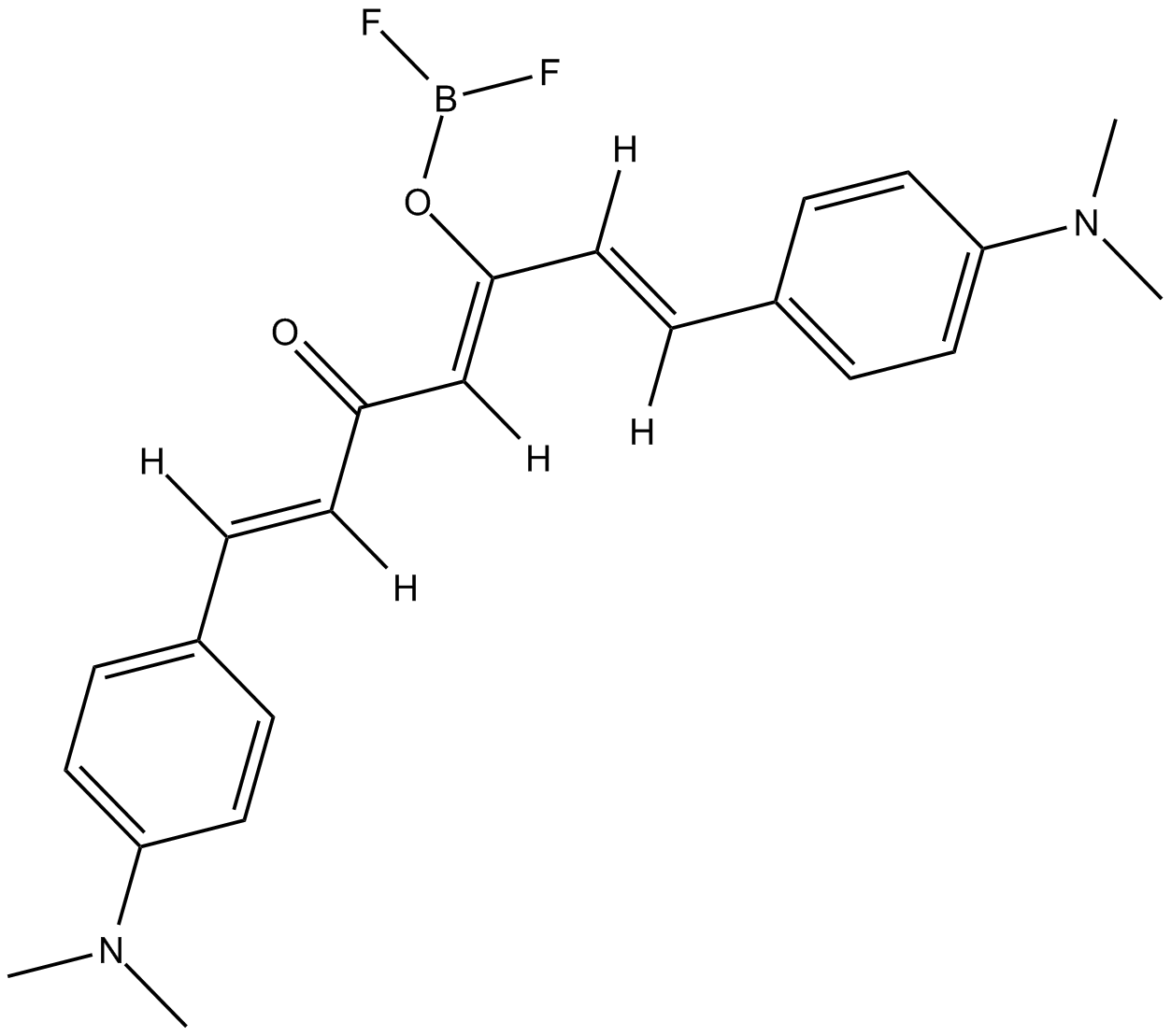 B5719 CRANAD 2Summary: near-infrared probe that binds to Aβ40 aggregates
B5719 CRANAD 2Summary: near-infrared probe that binds to Aβ40 aggregates -
 B7488 PristimerinSummary: monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) inhibitor
B7488 PristimerinSummary: monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) inhibitor -
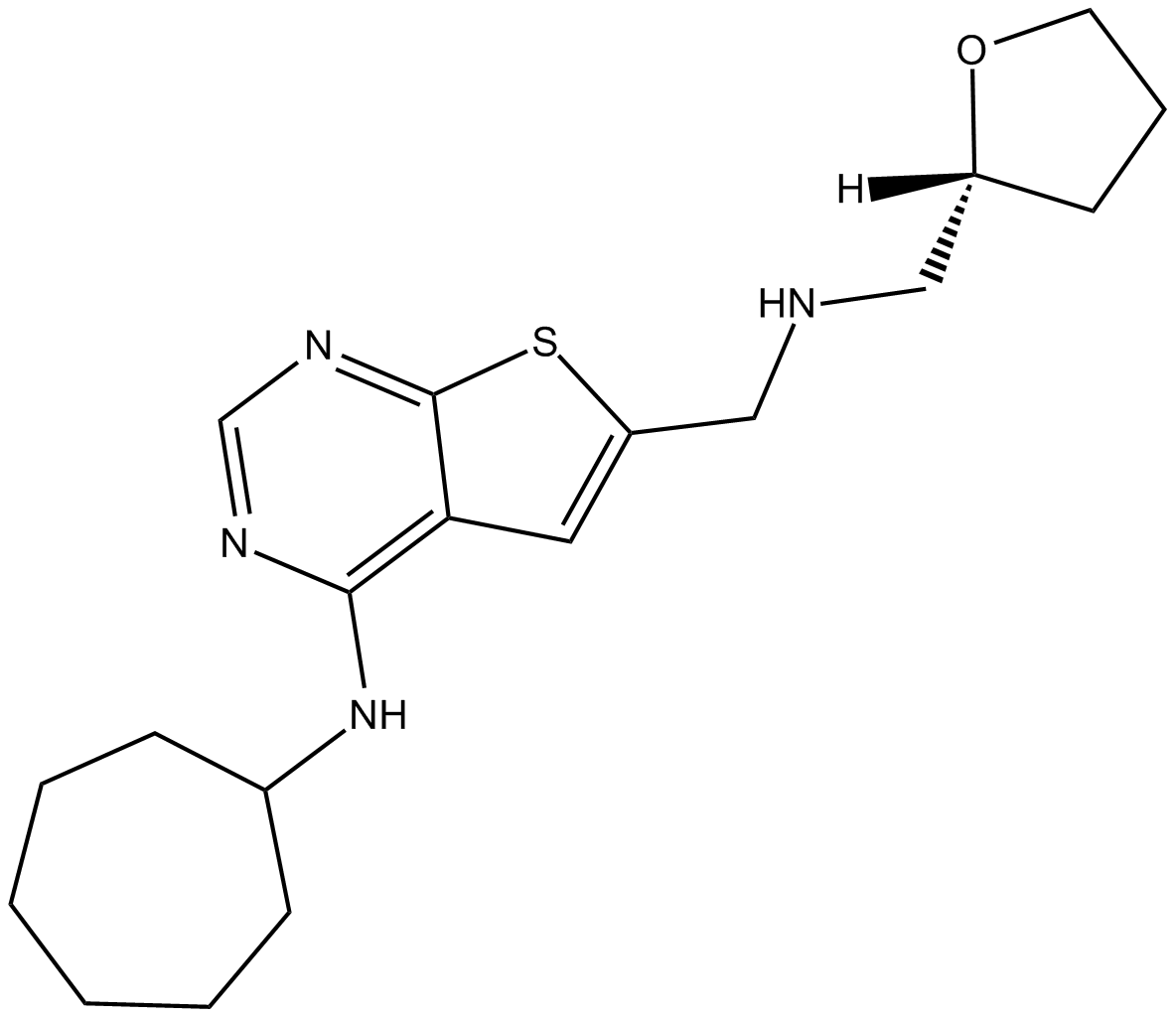 B5355 YM 230888Summary: Selective mGlu1 antagonist
B5355 YM 230888Summary: Selective mGlu1 antagonist -
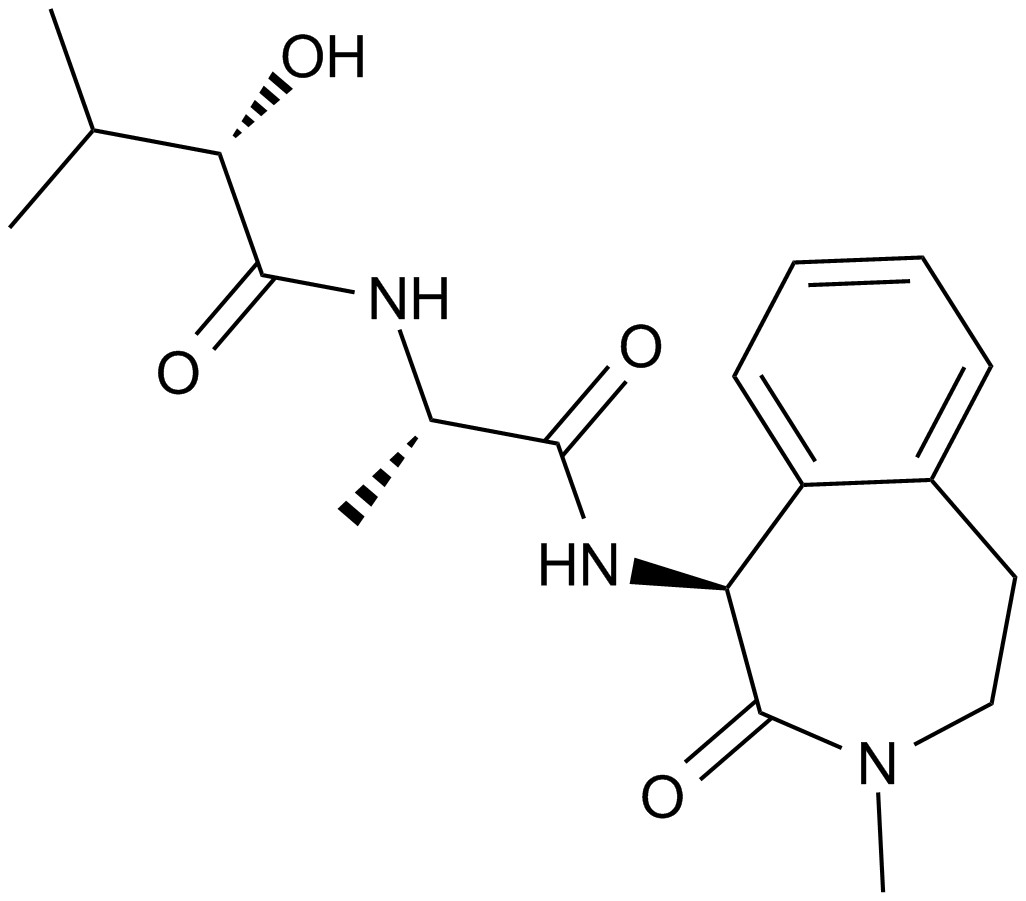 A8190 Semagacestat (LY450139)Summary: γ-secretase inhibitor
A8190 Semagacestat (LY450139)Summary: γ-secretase inhibitor -
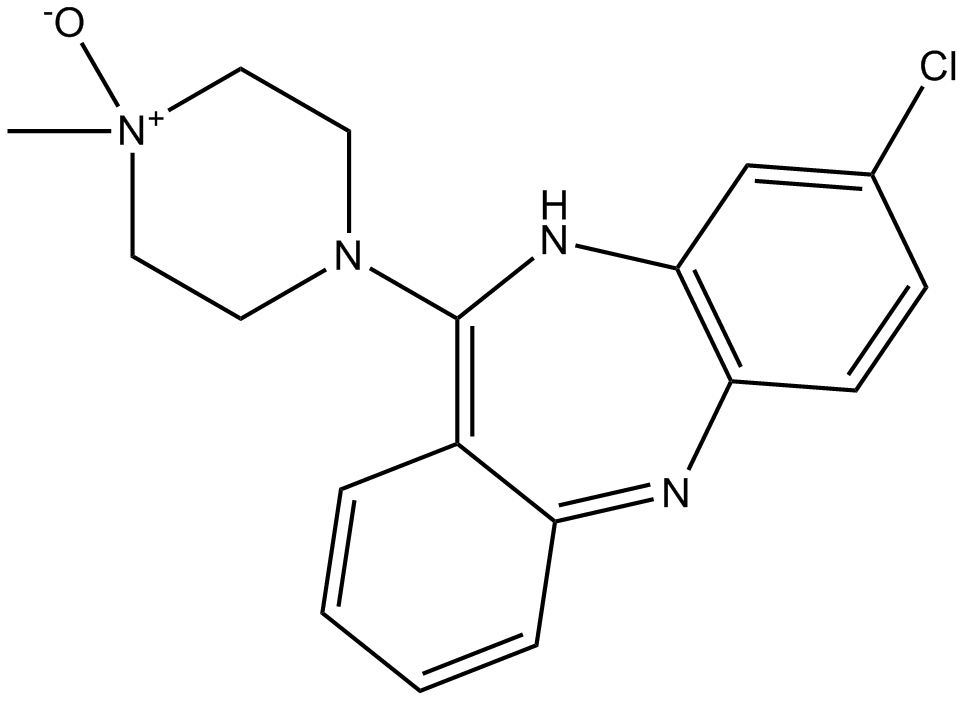 A3317 Clozapine N-oxide (CNO)46 CitationTarget: DREADD LigandsSummary: Metabolite of clozapine
A3317 Clozapine N-oxide (CNO)46 CitationTarget: DREADD LigandsSummary: Metabolite of clozapine -
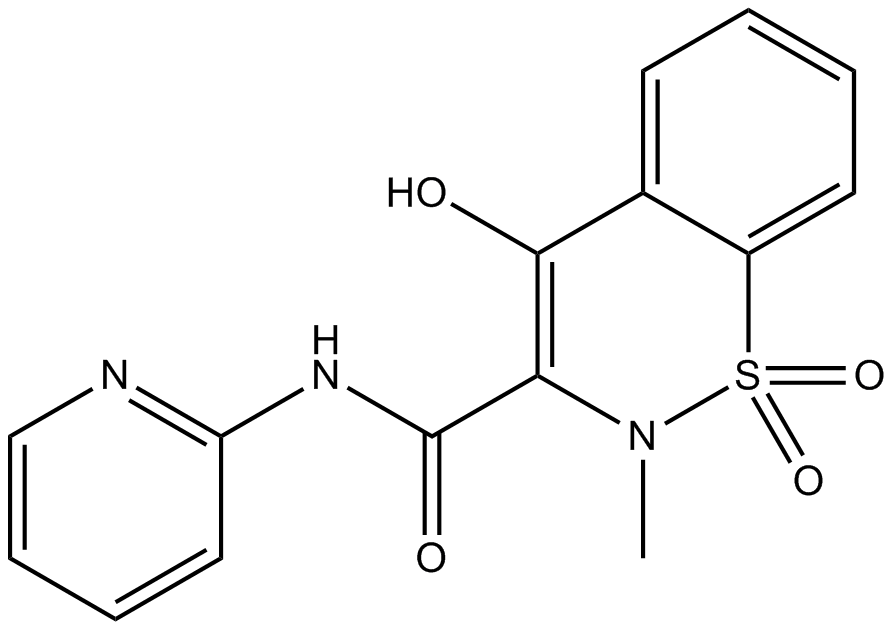 A8503 PiroxicamTarget: COX|Prostaglandin synthesisSummary: Prostaglandin synthesis/Coxinhibitor
A8503 PiroxicamTarget: COX|Prostaglandin synthesisSummary: Prostaglandin synthesis/Coxinhibitor -
 A8414 Diphemanil MethylsulfateSummary: AChR antagonist
A8414 Diphemanil MethylsulfateSummary: AChR antagonist -
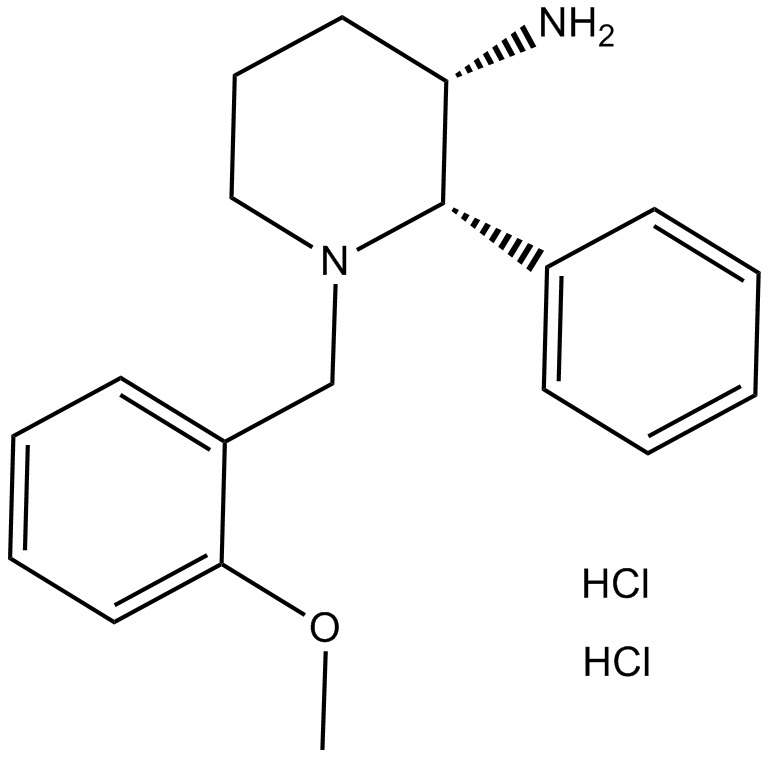 B5422 CP 99994 dihydrochlorideSummary: High affinity NK1 antagonist
B5422 CP 99994 dihydrochlorideSummary: High affinity NK1 antagonist


