Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel


Membrane Transporters mediate the movement of ions and molecules via binding and moving the substance across the membrane. There are two main actions of transporter: facilitated diffusion (passive transport) and active transport. Membrane transporters which bind the hydrolysis of ATP to the transport of target molecules are referred to as ATPases. For instance, Na+,K+-ATPases or Na+,K+-pumps are responsible for the transport of Na+ out of and K+ into cells.
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
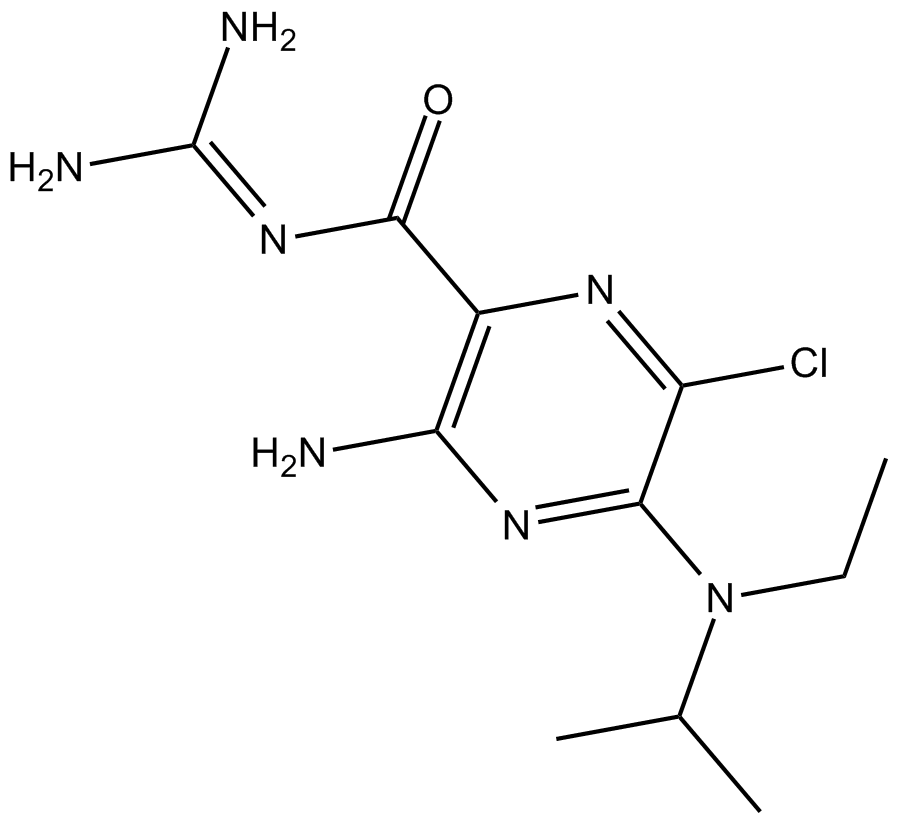 B7389 EIPA3 CitationTarget: Na /H Exchangers (NHEs)Summary: TRPP3 channel inhibitor
B7389 EIPA3 CitationTarget: Na /H Exchangers (NHEs)Summary: TRPP3 channel inhibitor -
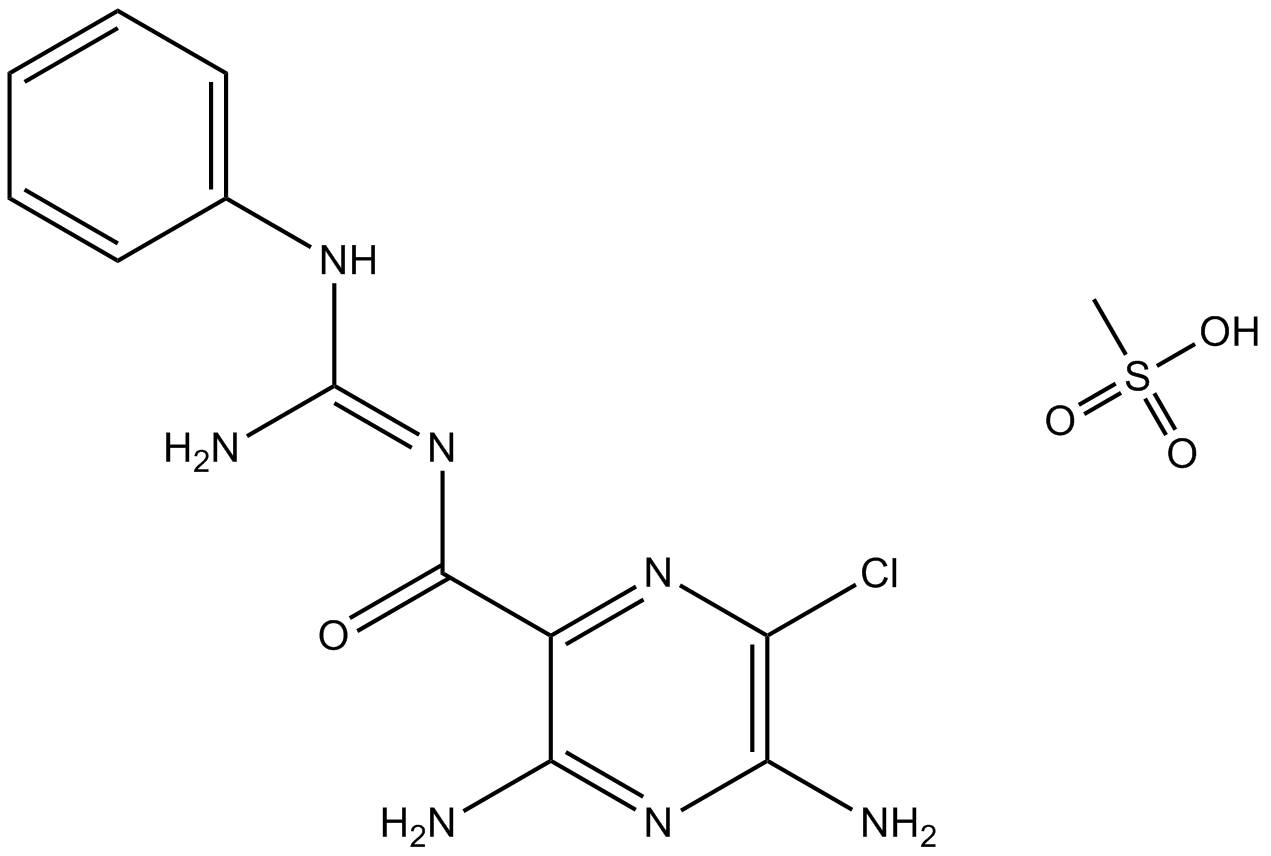 B7390 PhenamilSummary: TRPP3 channel inhibitor
B7390 PhenamilSummary: TRPP3 channel inhibitor -
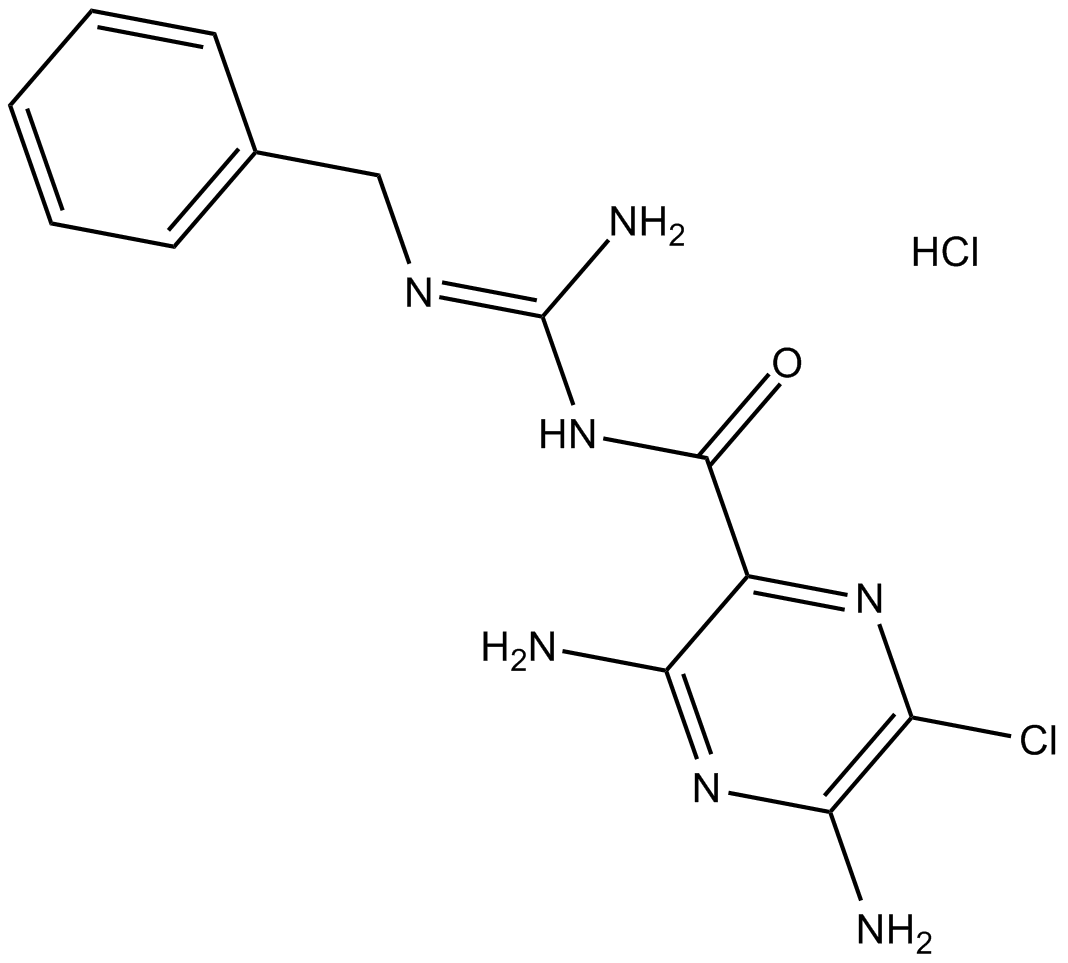 B7391 BenzamilSummary: Na+/Ca2+ exhanger (NCX) inhibitor
B7391 BenzamilSummary: Na+/Ca2+ exhanger (NCX) inhibitor -
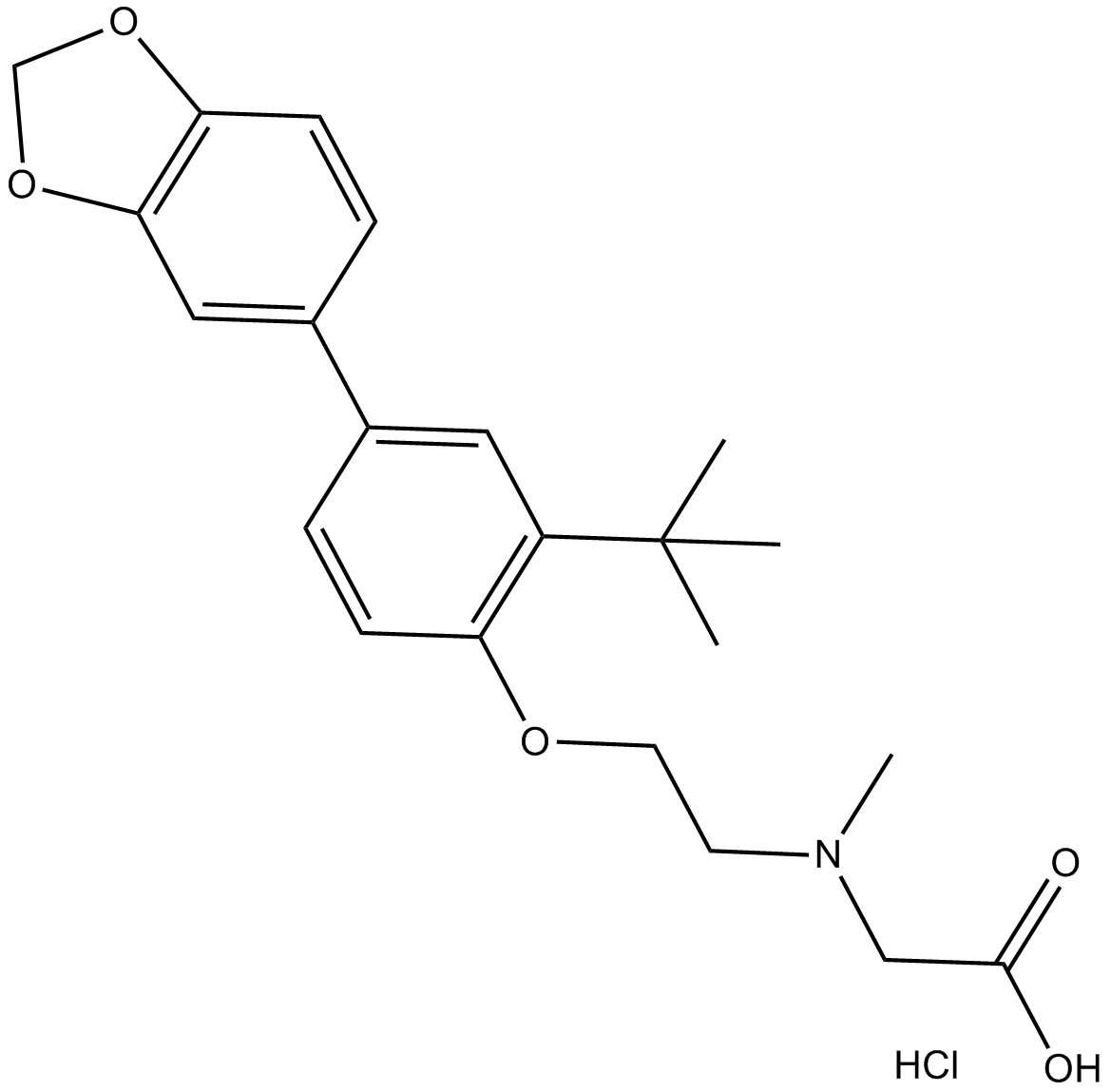 B7394 LY 2365109 hydrochlorideSummary: glycine transporter 1 (GlyT1) inhibitor
B7394 LY 2365109 hydrochlorideSummary: glycine transporter 1 (GlyT1) inhibitor -
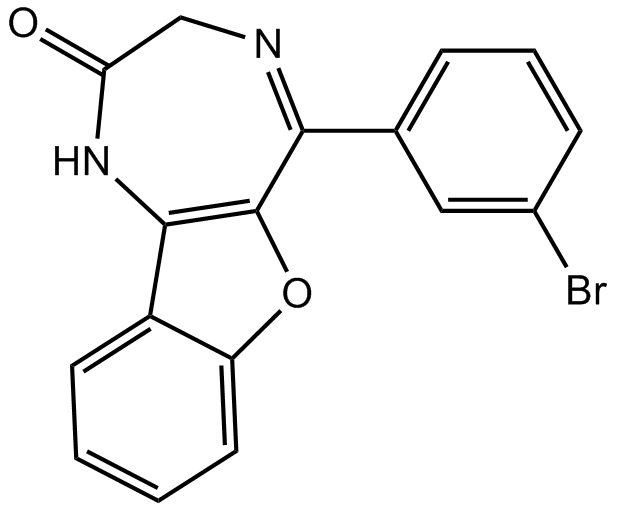 B7436 5-BDBDSummary: P2X4 receptor antagonist
B7436 5-BDBDSummary: P2X4 receptor antagonist -
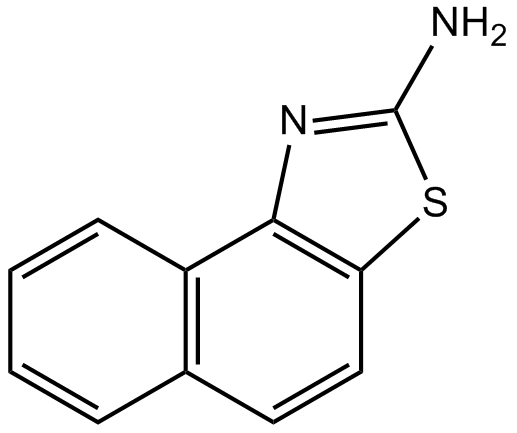 B7462 SKA 31Summary: Activator of KCa3.1 and KCa2 channels
B7462 SKA 31Summary: Activator of KCa3.1 and KCa2 channels -
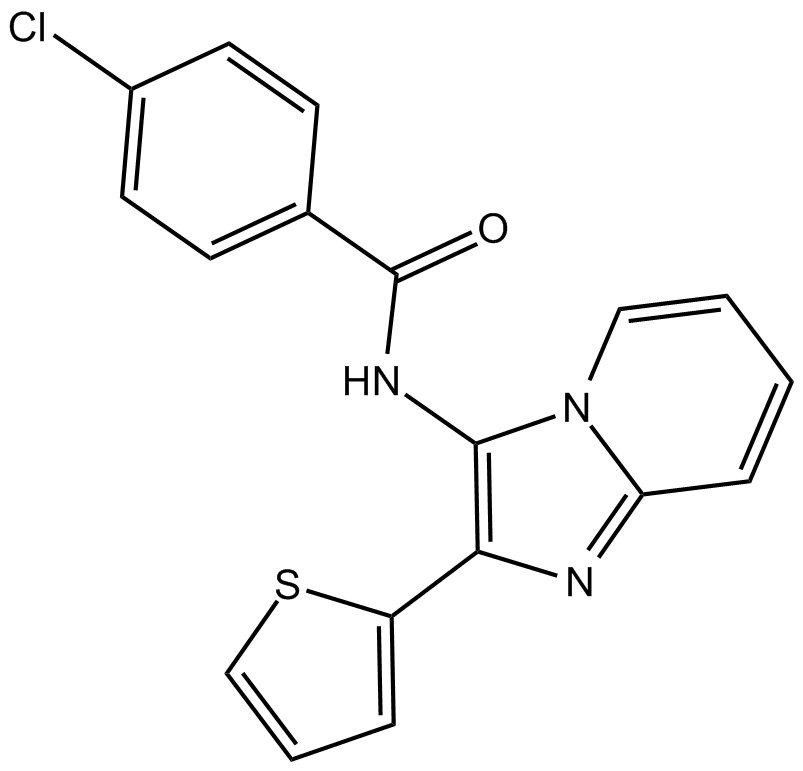 B7467 DS2Summary: Positive allosteric modulator of δ-subunit containing GABAA receptors
B7467 DS2Summary: Positive allosteric modulator of δ-subunit containing GABAA receptors -
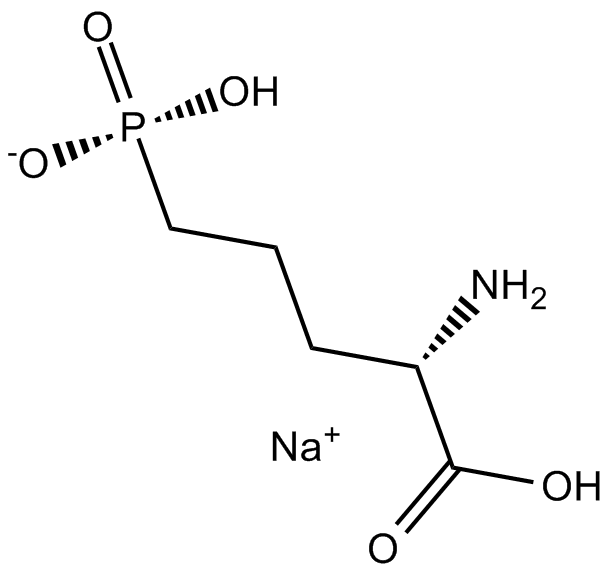 B7473 DL-AP5 Sodium saltSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist
B7473 DL-AP5 Sodium saltSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist -
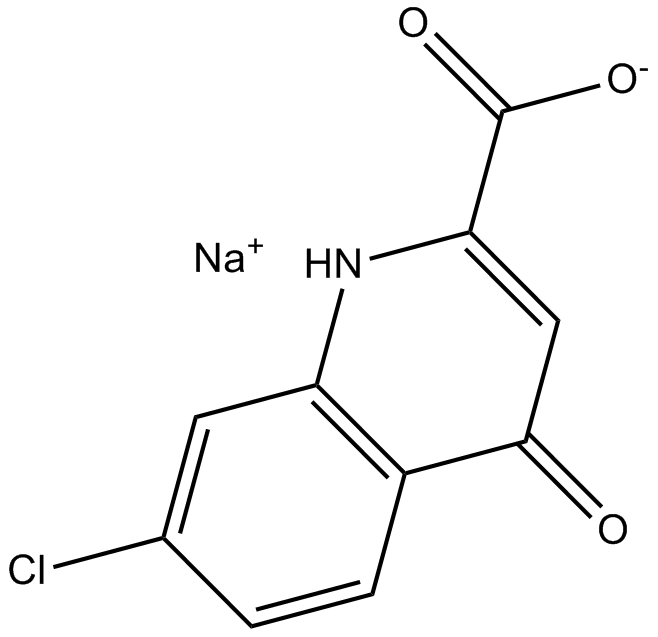 B7477 7-Chlorokynurenic acid sodium saltSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist acting at the glycine site
B7477 7-Chlorokynurenic acid sodium saltSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist acting at the glycine site -
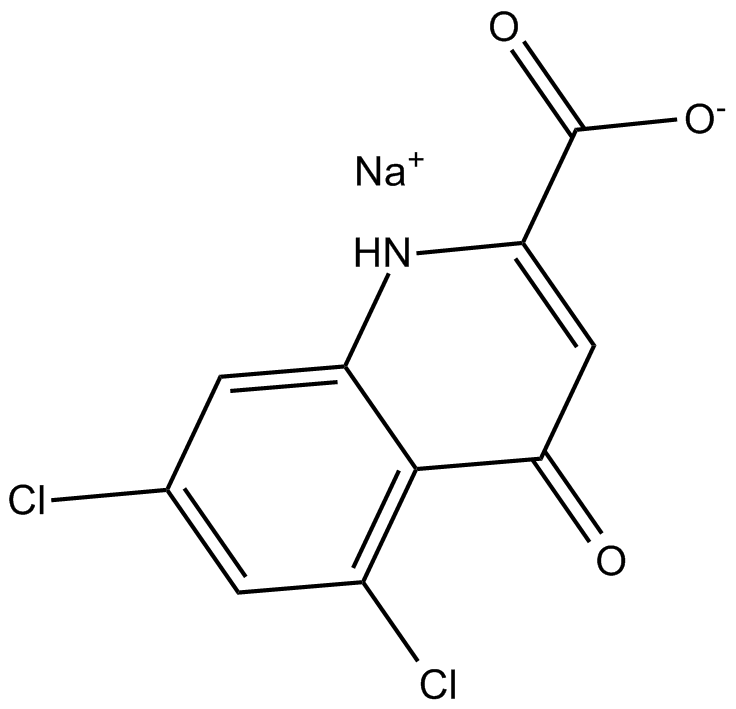 B7478 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid sodium saltSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist
B7478 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid sodium saltSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist


