GPCR/G protein
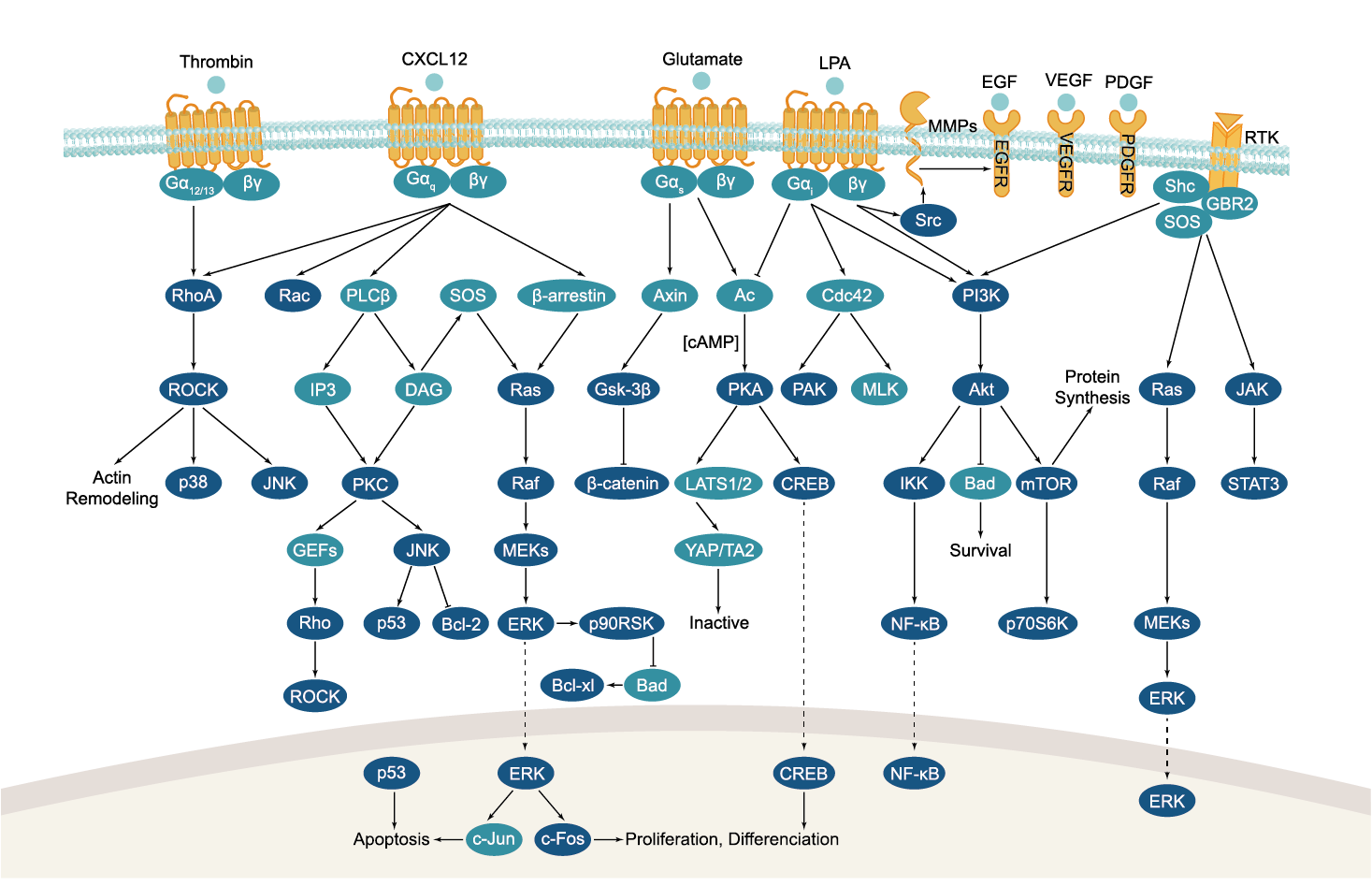

All GPCRs share a common seven trans-membrane structure. GPCRs are associated with heterotrimeric G-proteins which are GTP-binding proteins made of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. When a ligand binds to GPCR, it activates the attached G-protein, the GDP is replaced with GTP. The activated G-protein then dissociates into an alpha and a beta-gamma complex which activates downstream signaling pathways. These intracellular signaling pathways include cAMP/PKA, calcium/NFAT, phospholipase C, protein tyrosine kinases, MAP kinases, PI-3-kinase, nitric oxide/cGMP, Rho, and JAK/STAT.
GPCRs are one of the most important therapeutic targets for various diseases, over 30% of all modern medicinal drugs target this family. Aberrant GPCR functions are involved in pathological conditions such as neurological, immunological and hormonal disorders. A large number of GPCRs have been identified, but whose ligands are not known, are classified as orphan receptors.
-
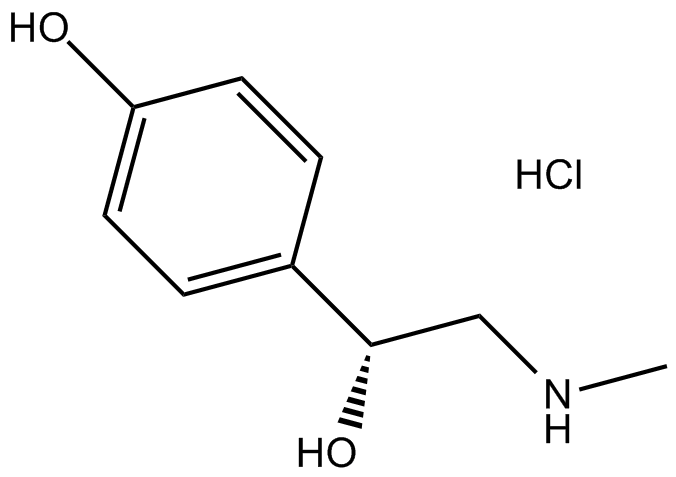 B1370 Synephrine HCl1 CitationSummary: Sympathomimetic α-adrenergic receptor (AR) agonist
B1370 Synephrine HCl1 CitationSummary: Sympathomimetic α-adrenergic receptor (AR) agonist -
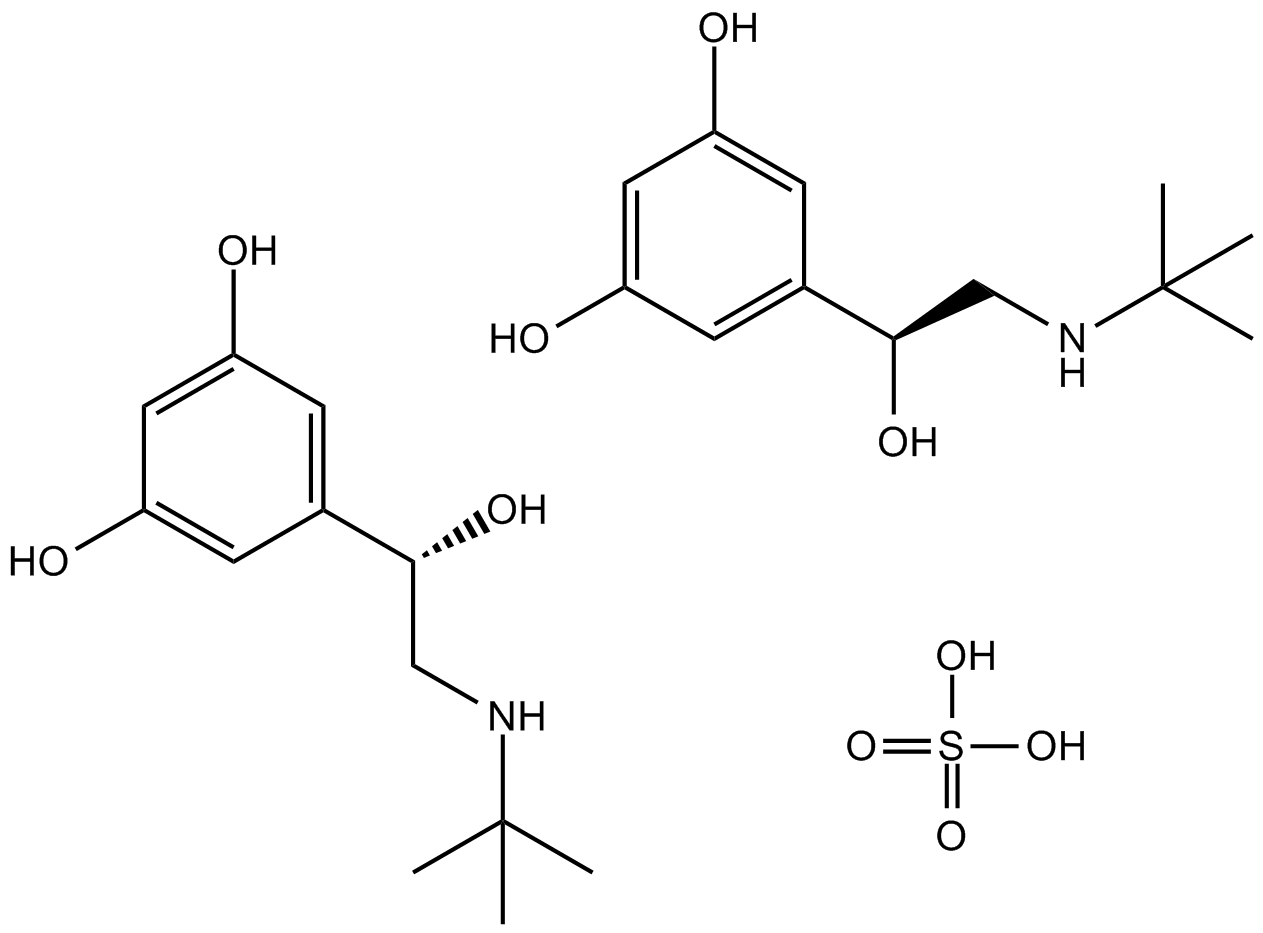 B1328 Terbutaline SulfateSummary: Selective β2-adrenergic receptor agonist
B1328 Terbutaline SulfateSummary: Selective β2-adrenergic receptor agonist -
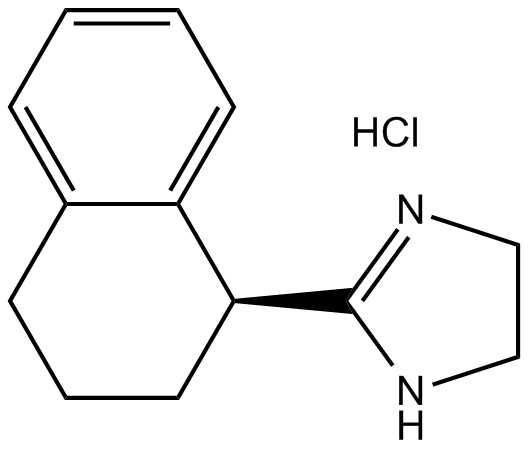 B1349 Tetrahydrozoline HClSummary: Adrenergic receptor agonist
B1349 Tetrahydrozoline HClSummary: Adrenergic receptor agonist -
 B1329 Tolazoline HClSummary: non-selective competitive α-adrenergic receptor antagonist
B1329 Tolazoline HClSummary: non-selective competitive α-adrenergic receptor antagonist -
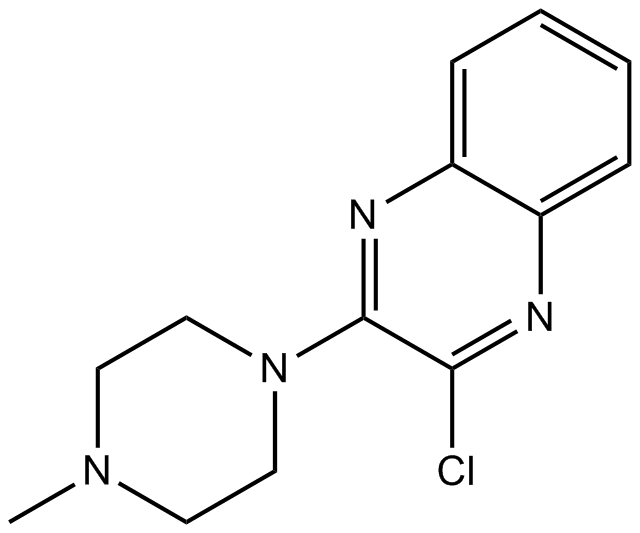 B2259 VUF 10166Target: 5-HT3 ReceptorsSummary: 5-HT3 receptor antagonist
B2259 VUF 10166Target: 5-HT3 ReceptorsSummary: 5-HT3 receptor antagonist -
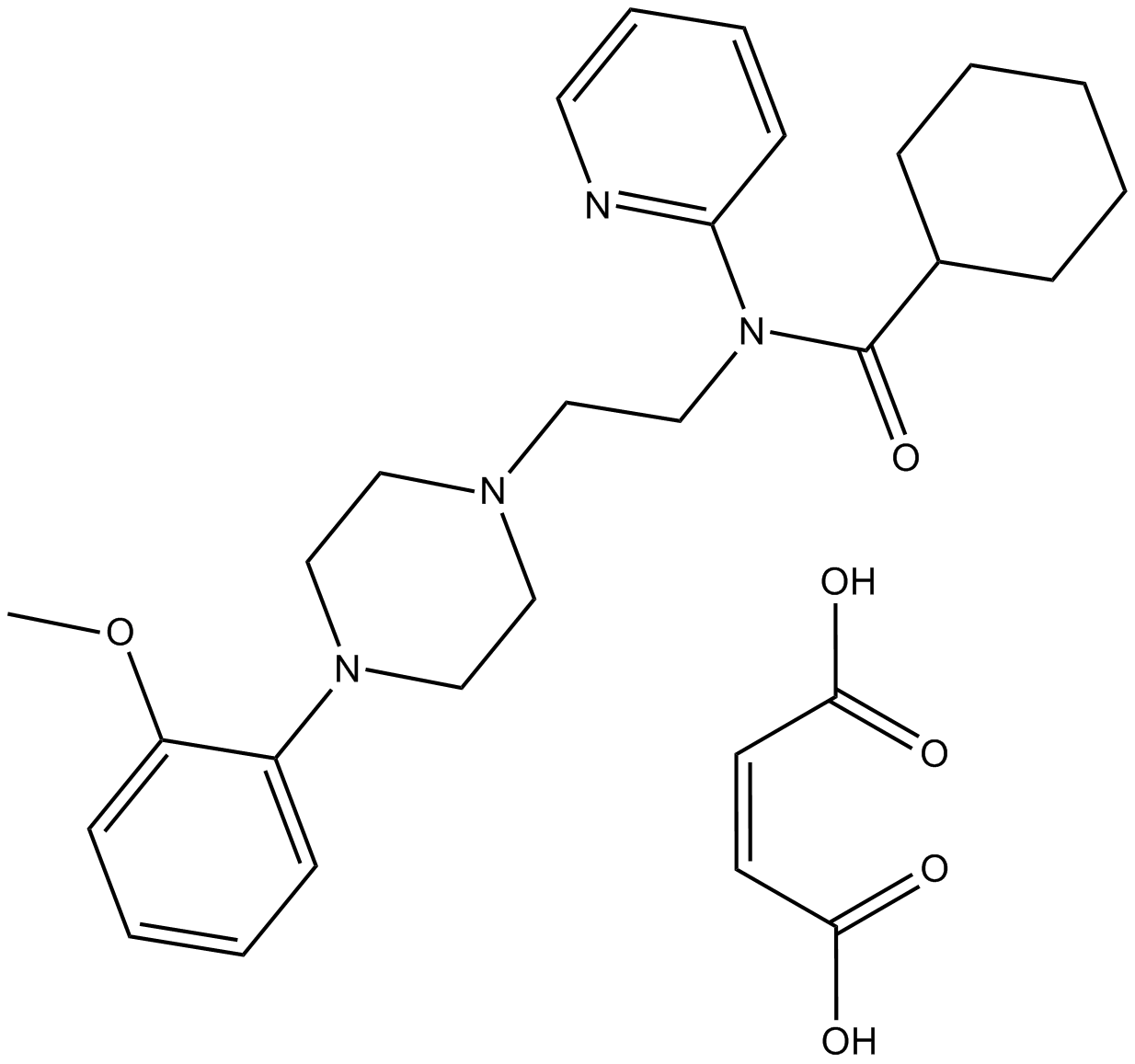 B2260 WAY-100635 maleate saltSummary: 5-HT1A receptor antagonist
B2260 WAY-100635 maleate saltSummary: 5-HT1A receptor antagonist -
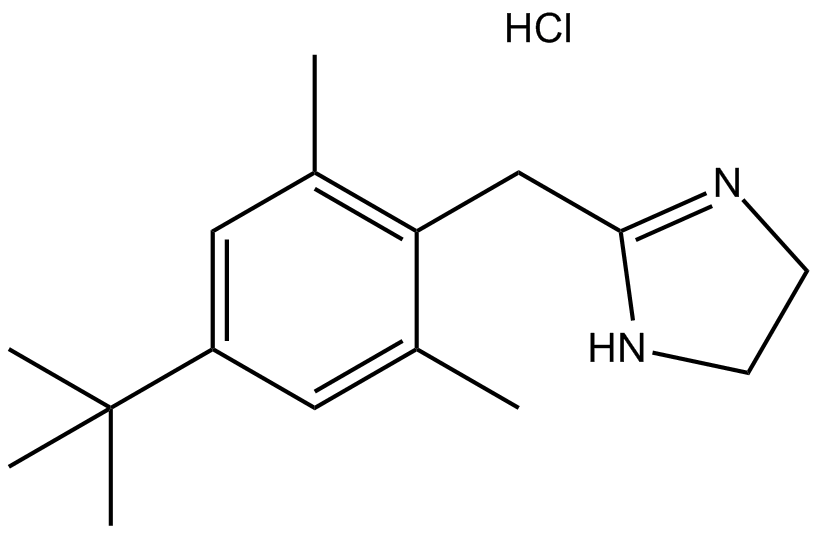 B2066 Xylometazoline HClSummary: α1 and α2 adrenergic receptor agonist
B2066 Xylometazoline HClSummary: α1 and α2 adrenergic receptor agonist -
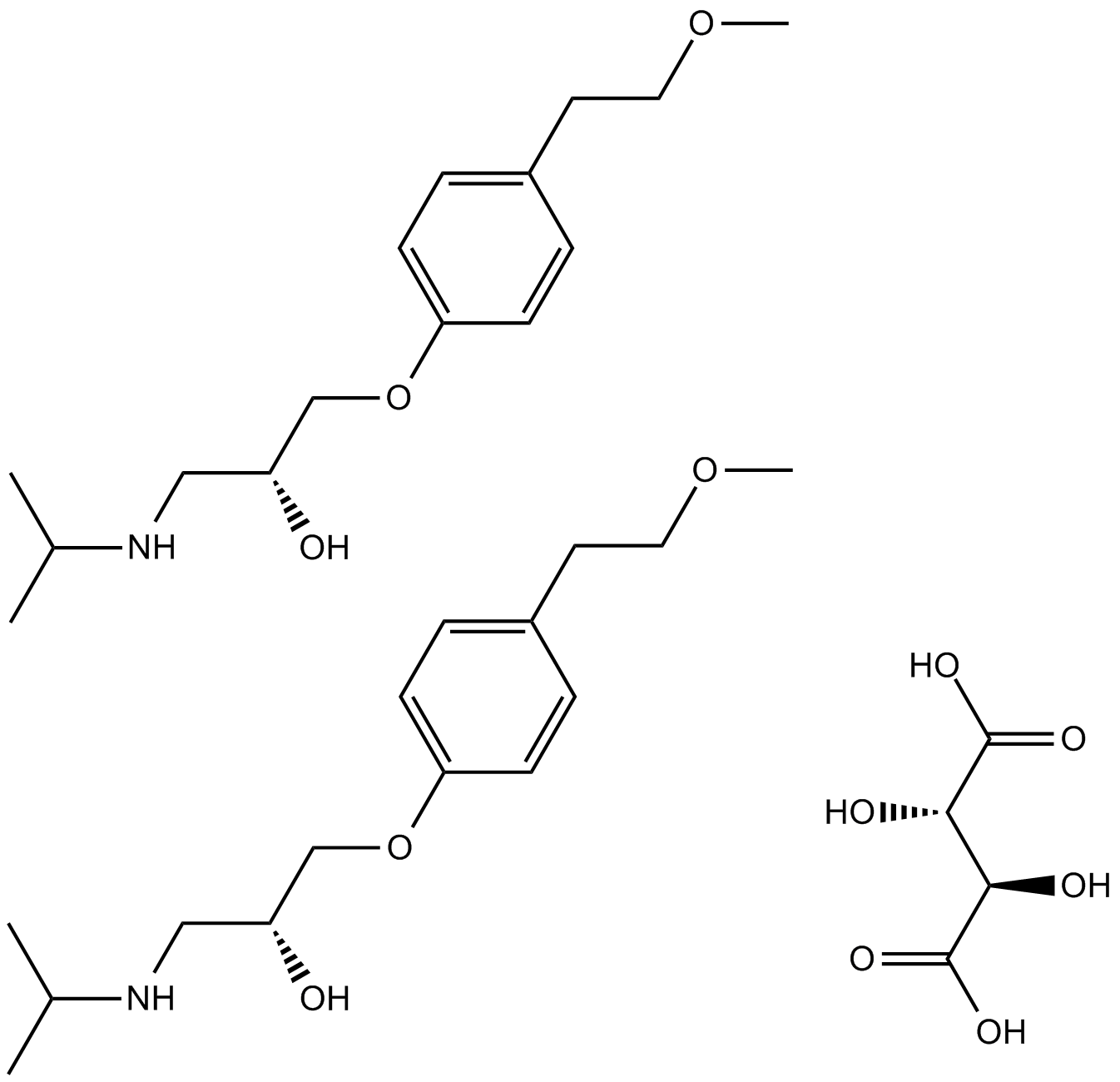 B1339 Metoprolol Tartrate1 CitationSummary: β1-adrenergic blocking agent
B1339 Metoprolol Tartrate1 CitationSummary: β1-adrenergic blocking agent -
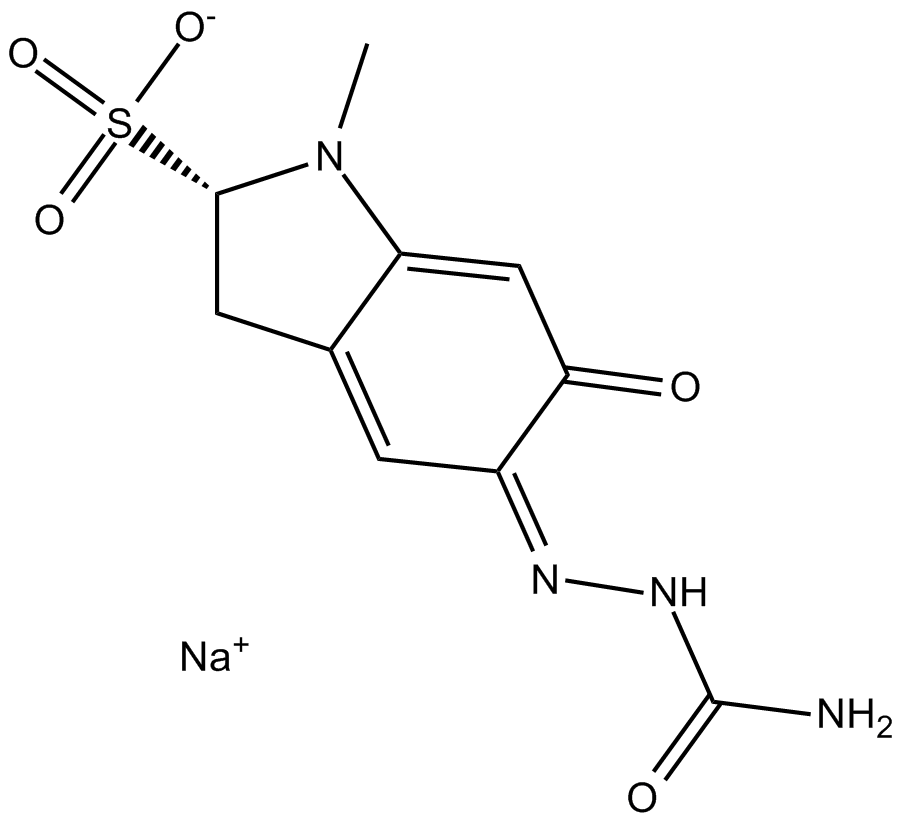 B1903 Carbazochrome sodium sulfonate (AC-17)Target: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)Summary: antihemorrhagic agent
B1903 Carbazochrome sodium sulfonate (AC-17)Target: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)Summary: antihemorrhagic agent -
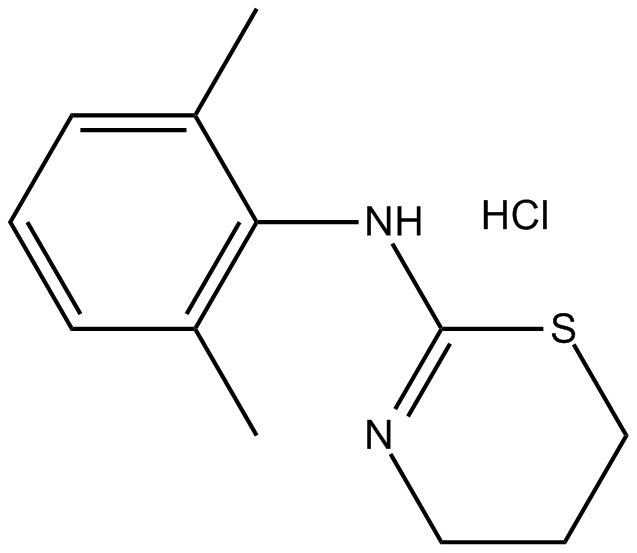 B1351 Xylazine HClSummary: α2 Adrenoceptor agonist
B1351 Xylazine HClSummary: α2 Adrenoceptor agonist


