Endocrinology and Hormones
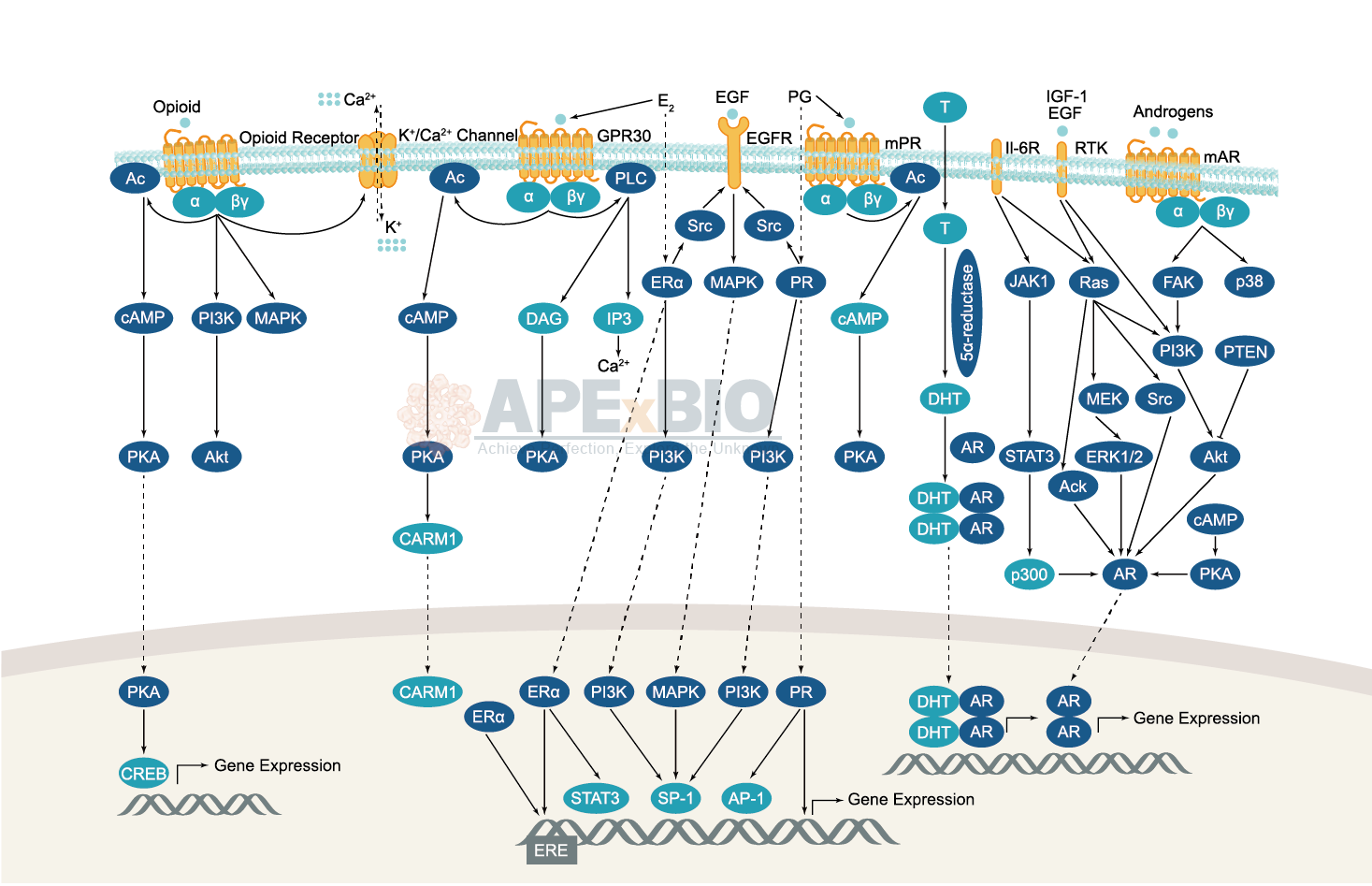

Endocrinology is the study of hormones, their receptors and intracellular signaling pathways, as well as the related diseases. The endocrine system functions can be broadly classified into several categories, including reproduction and sexual differentiation, development and growth, maintenance of the internal environment, and regulation of metabolism/nutrient supply.
There are three types of hormones based on their chemical composition: Amines (e.g. dopamine, adrenalin and noradrenalin); Steroids (e.g. estrogen, testosterone and glucocorticoids); Peptides (e.g. the peptide hormones insulin, ghrelin and vasopressin). Peptide hormones produced by secretory nervous tissue are known as neuropeptides. For example, thyroid hormone plays important parts in development, homeostasis and metabolism, while cortisol is essential for growth, nutrient supply and immune function. Moreover, the regulation of blood glucose involves several pancreatic peptide insulin and its counter regulatory hormone, glucagon, as well as cortisol, growth hormone and epinephrine.
Dysregulations in endocrine system are implicated in diseases such as Acromegaly, Cushing Syndrome, Diabetes, Dwarfism, Graves Disease, Hermaphroditism, Delayed and Precocious Puberty and Thyroid Diseases.
-
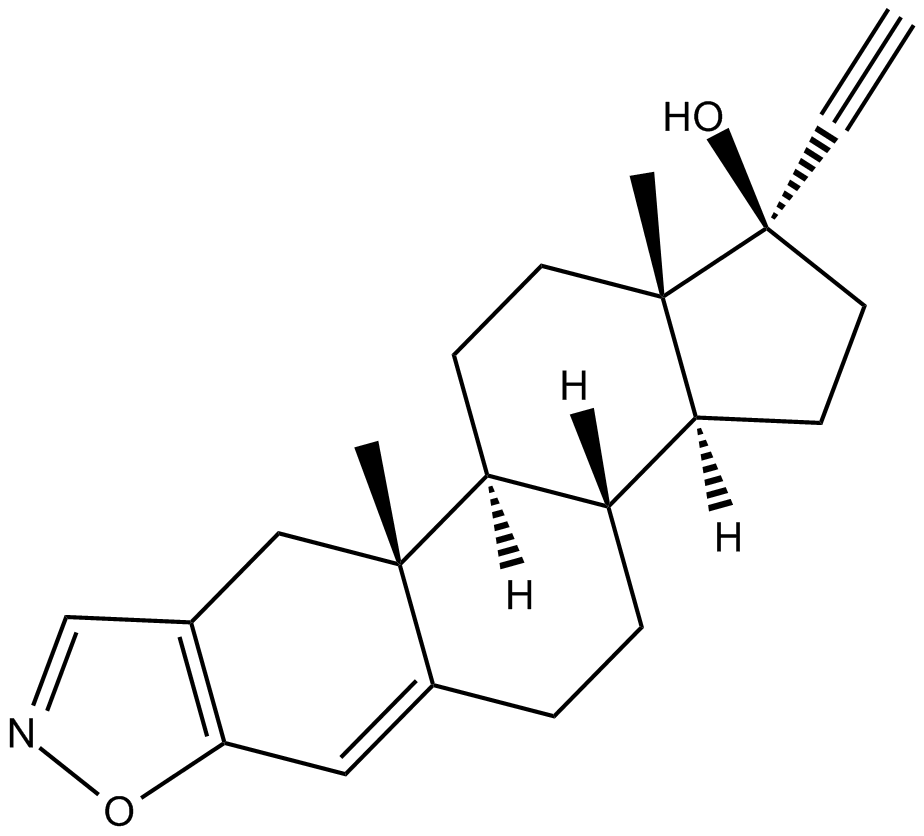 C3644 DanazolSummary: weak androgenic effects
C3644 DanazolSummary: weak androgenic effects -
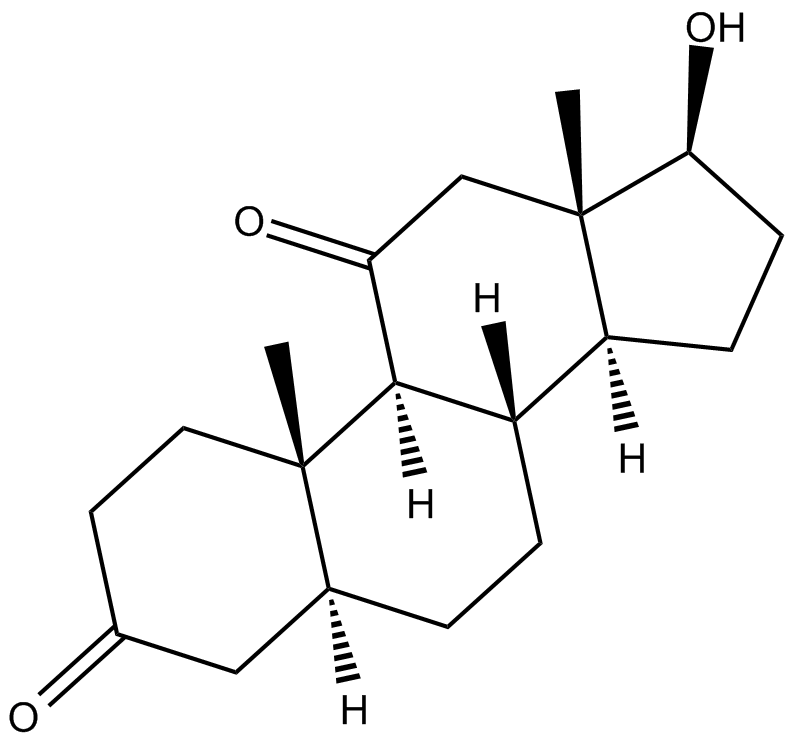 C4317 5α-dihydro-11-keto TestosteroneSummary: androgen receptor agonist
C4317 5α-dihydro-11-keto TestosteroneSummary: androgen receptor agonist -
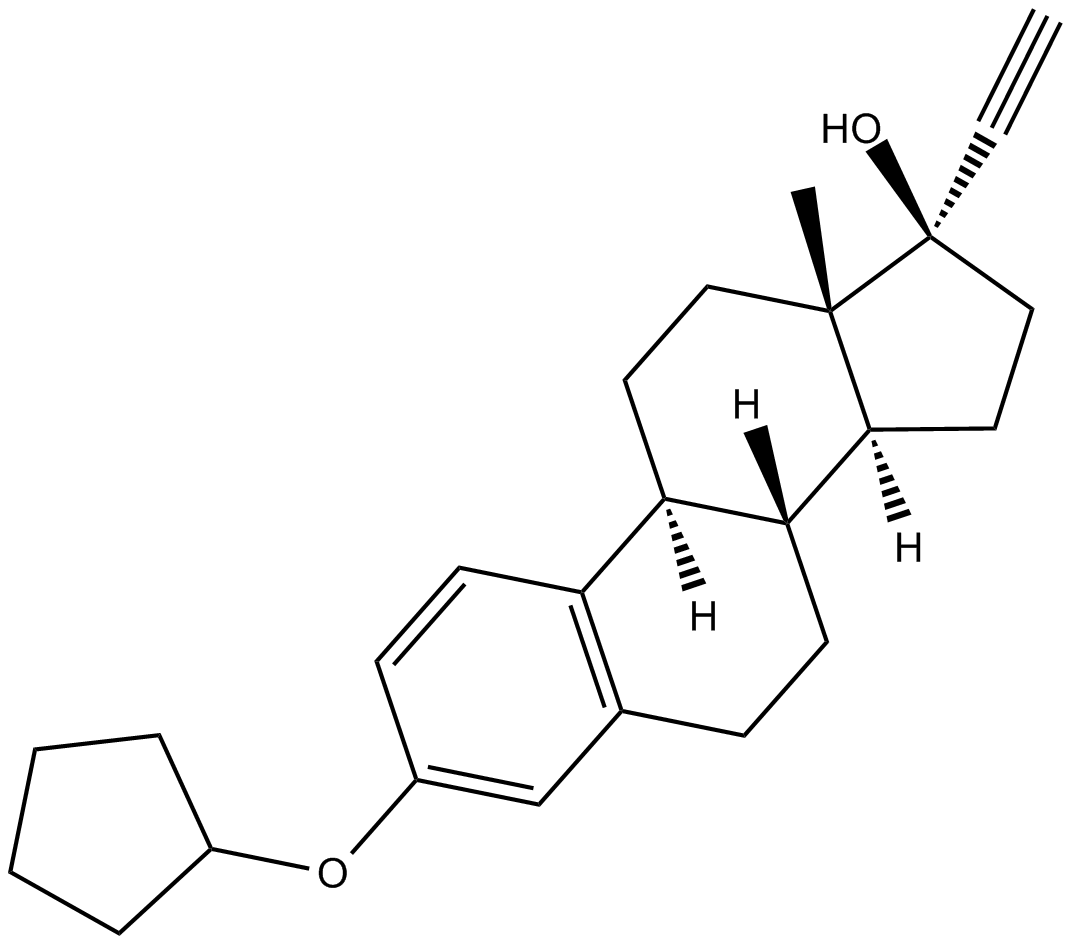 C4274 QuinestrolSummary: synthetic estrogen that is effective in hormone replacement therapy
C4274 QuinestrolSummary: synthetic estrogen that is effective in hormone replacement therapy -
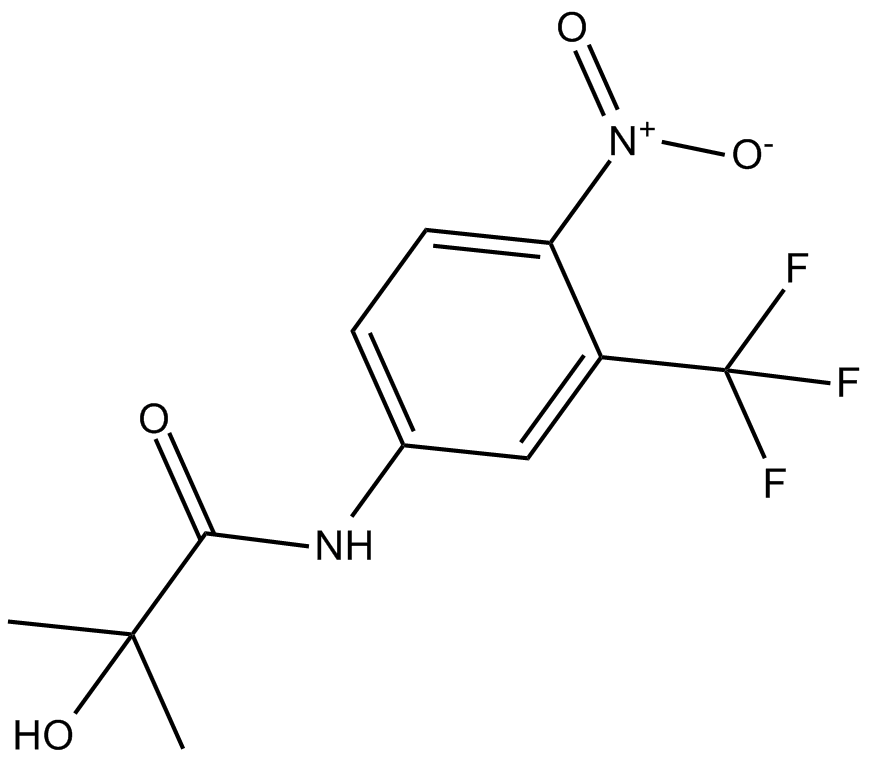 C4721 2-hydroxy FlutamideSummary: androgen receptor inhibitor
C4721 2-hydroxy FlutamideSummary: androgen receptor inhibitor -
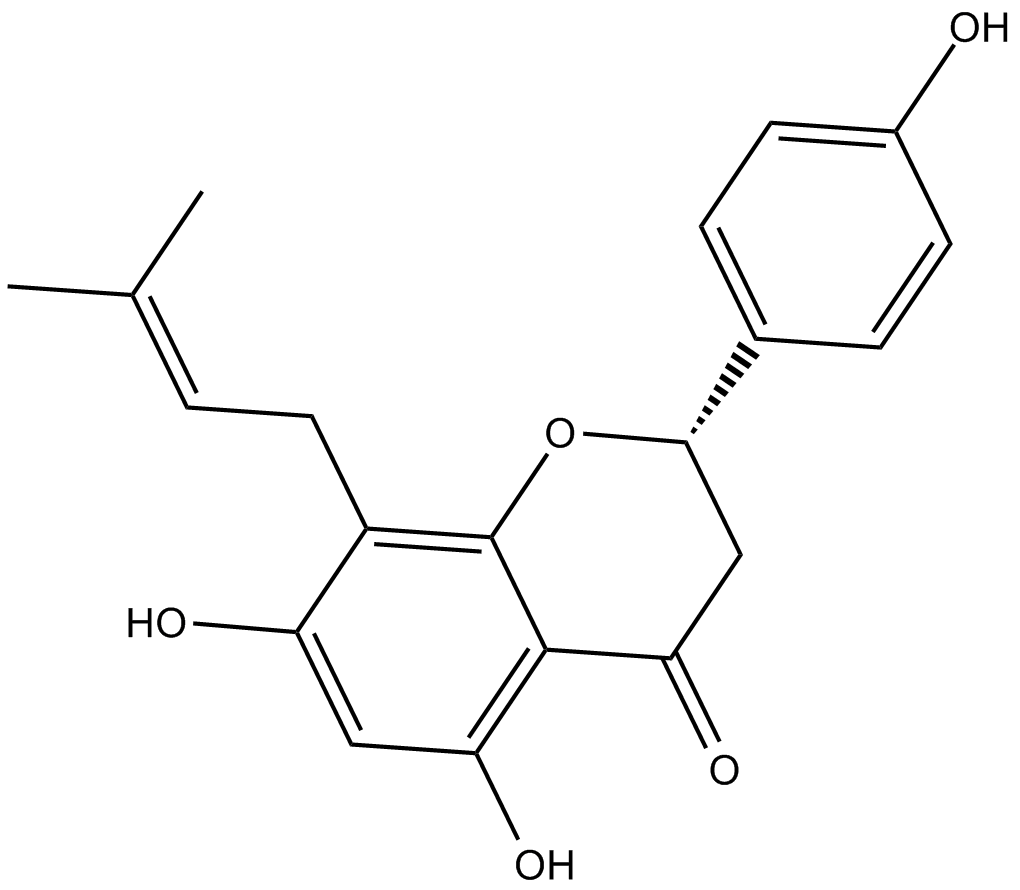 C4481 8-PrenylnaringeninSummary: estrogen receptor inhibitor
C4481 8-PrenylnaringeninSummary: estrogen receptor inhibitor -
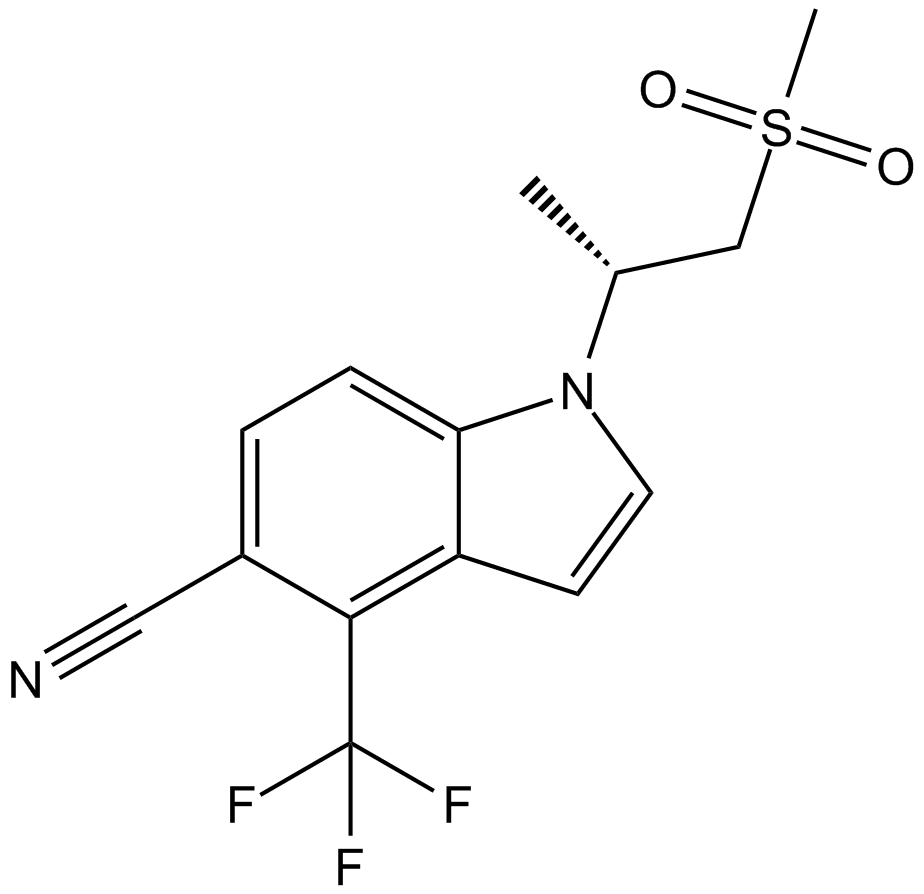 C4768 GSK2881078Summary: selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM)
C4768 GSK2881078Summary: selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) -
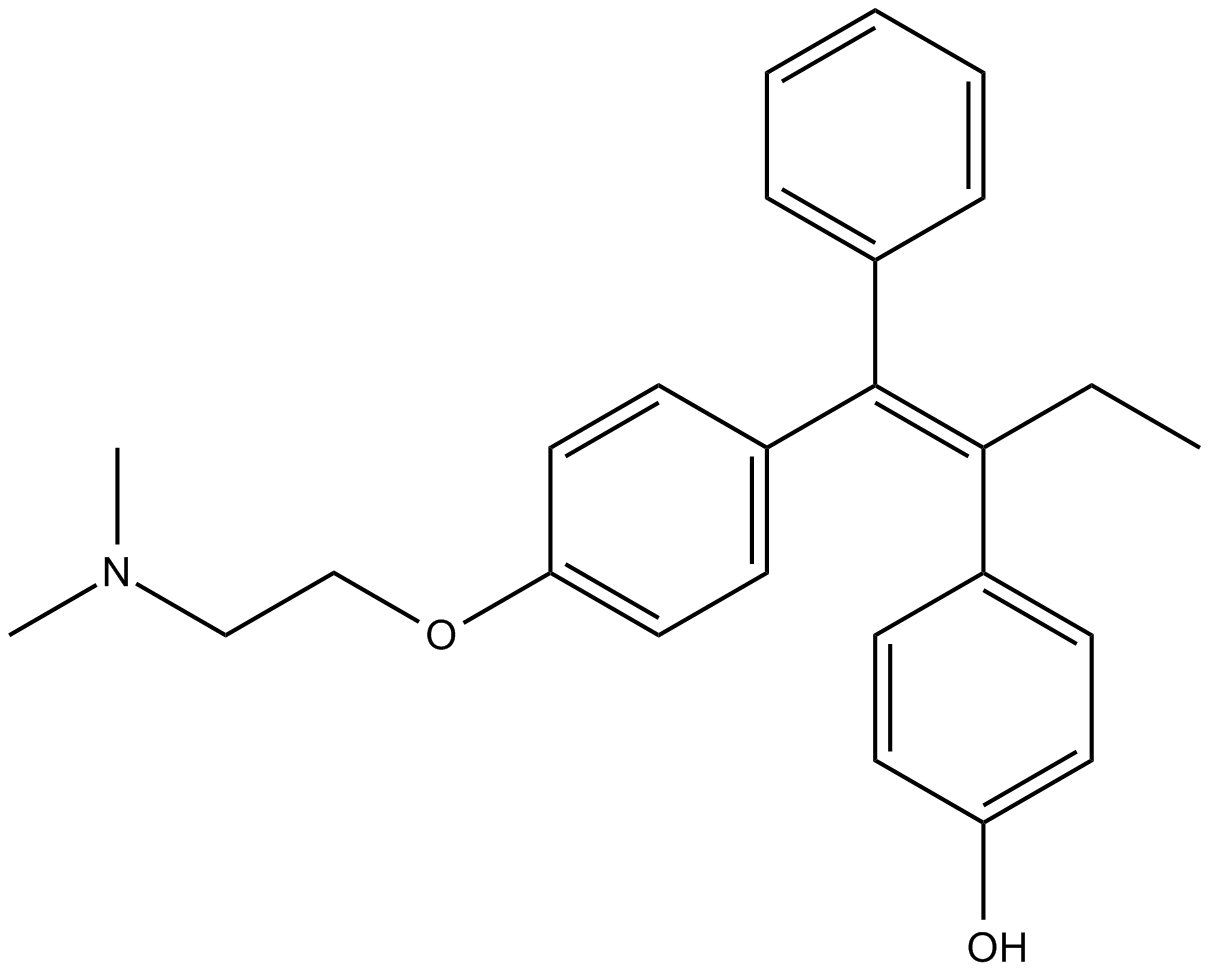 C4624 4’-hydroxy TamoxifenSummary: metabolite of tamoxifen, an estrogen receptor modulator
C4624 4’-hydroxy TamoxifenSummary: metabolite of tamoxifen, an estrogen receptor modulator -
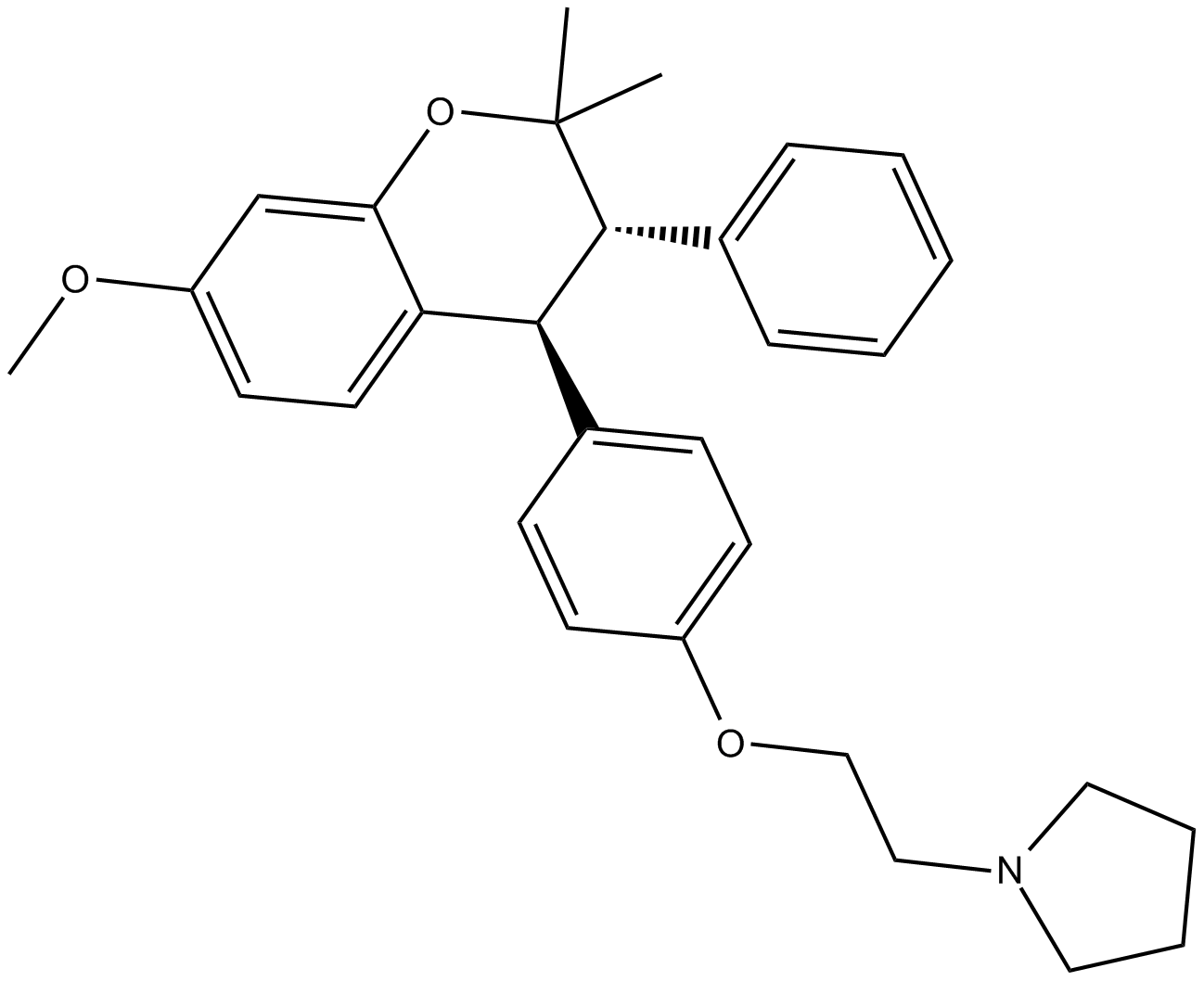 C4747 OrmeloxifeneSummary: estrogen receptor modulator
C4747 OrmeloxifeneSummary: estrogen receptor modulator -
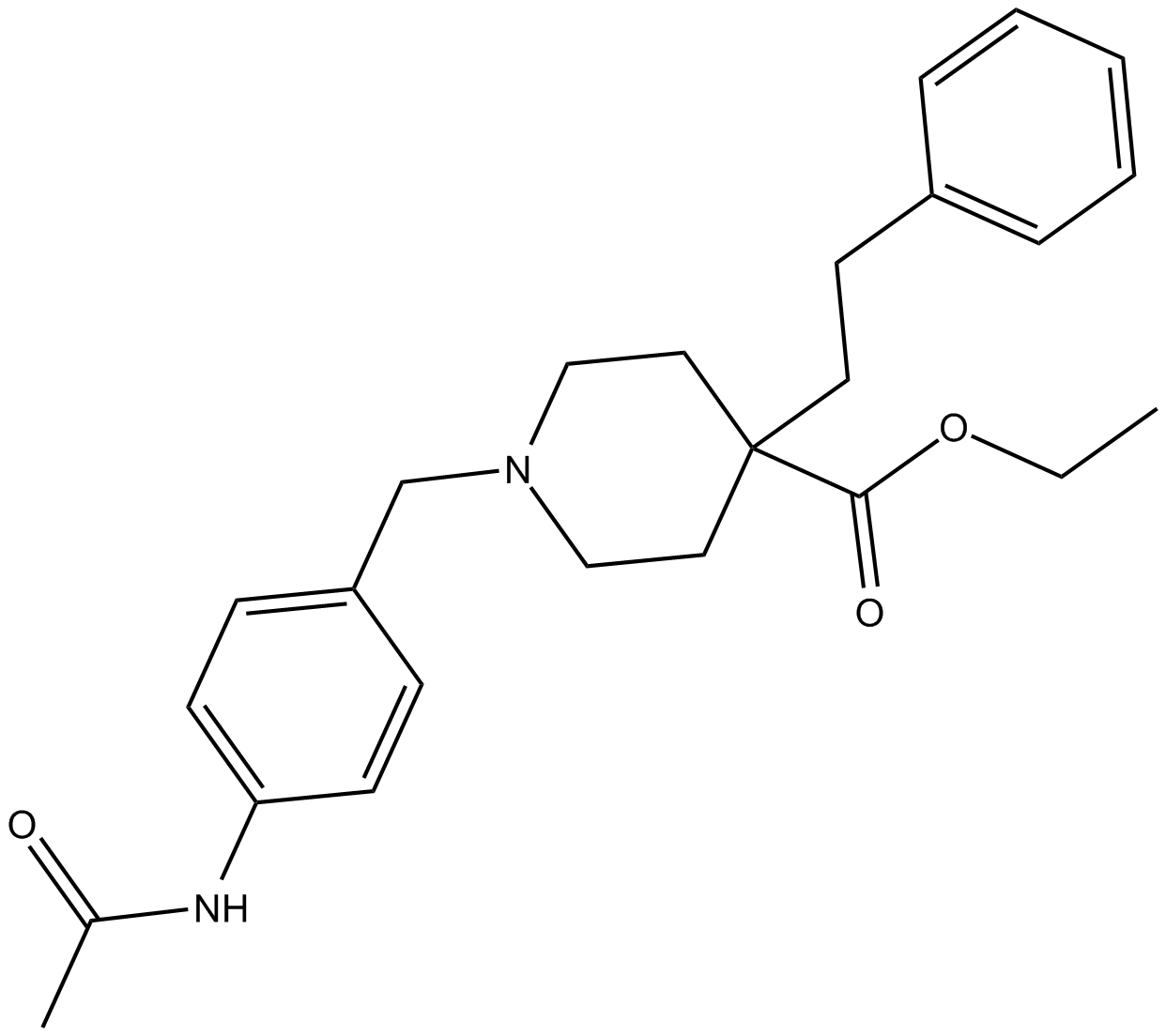 C4792 ML-335Summary: agonist for OPRM1-OPRD1 heterodimerization
C4792 ML-335Summary: agonist for OPRM1-OPRD1 heterodimerization -
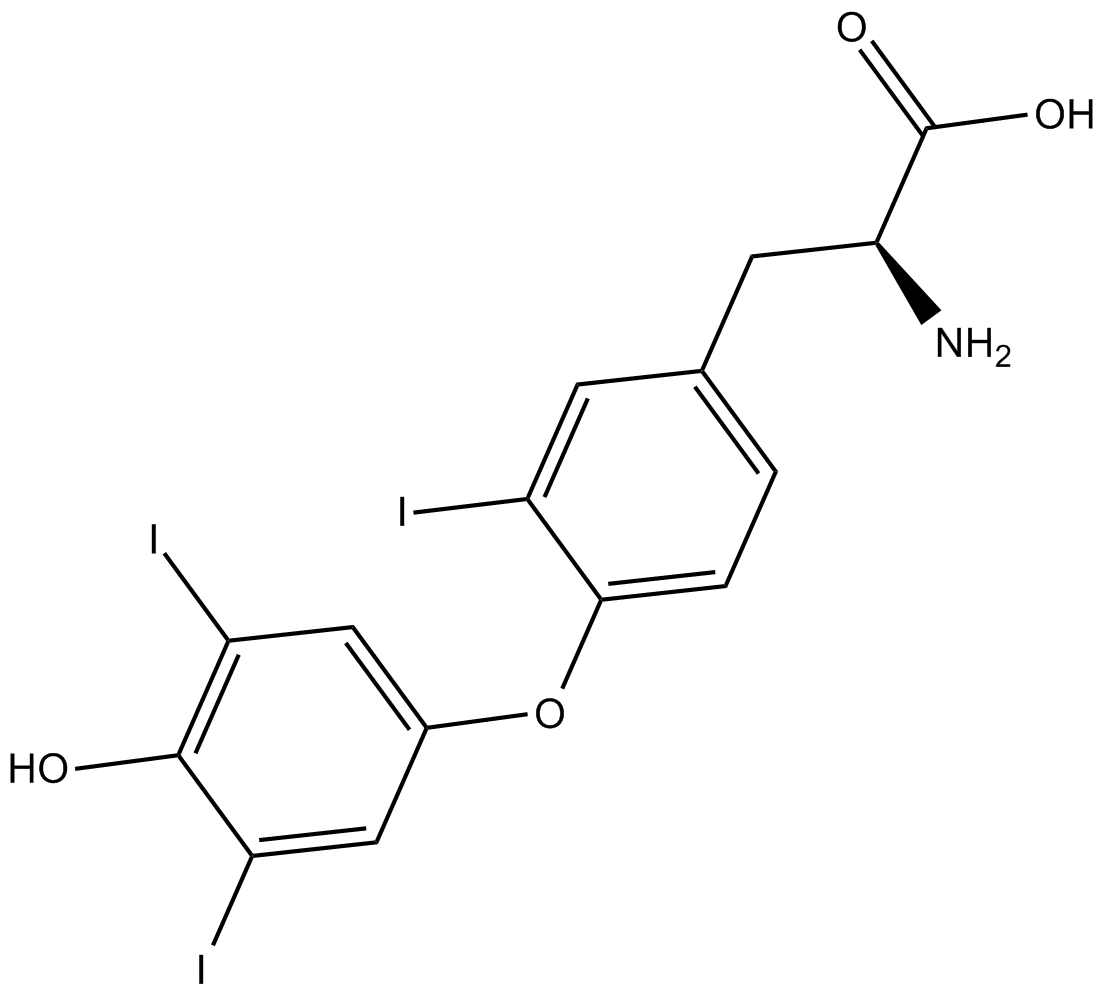 C5014 3,3',5'-Triiodo-L-thyronineSummary: TRΔα1 activator
C5014 3,3',5'-Triiodo-L-thyronineSummary: TRΔα1 activator


