Amino Acids & Peptides
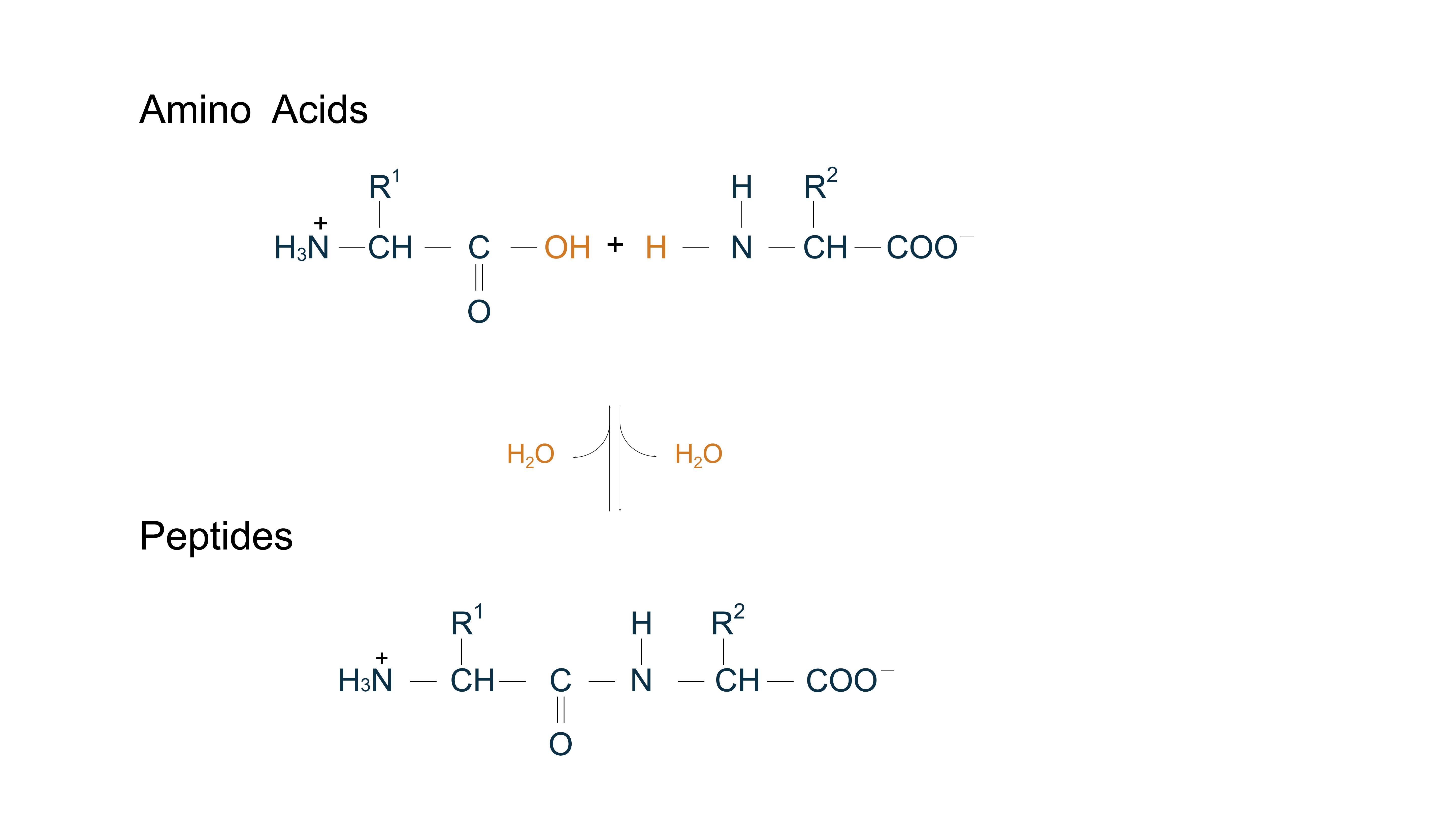

Amino acids are fundamental organic molecules with a common structure: an amino group (–NH₂), a carboxyl group (–COOH), and a side chain (or R group) that differs their properties. 20 α-amino acids are commonly found in proteins, serving as protein building blocks. Some of less common amino acids also have important functions, serving either as constituents of proteins (through modification of common amino acid residues after protein synthesis) or as metabolic intermediates. As amino acids are essential for life, they are used as supplements in cell culture media and as key materials for metabolic studies. Uncommon or modified amino acids are utilized in drug development.
Amino acids can be covalently joined through a peptide bond, formed by dehydration from the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid and the α-amino group of another via condensation reaction, allowing them to polymerize into peptides and proteins. Molecules called peptides generally have molecular weights below 10,000, whereas those called proteins have higher molecular weights. Mainly derived from natural sources or their analogs, peptides exhibit diverse biological activities (antimicrobial, antiviral, antioxidant, immunomodulatory) with high target affinity, stable efficacy, low immunogenicity, and minimal toxicity. Advances in biotechnology and synthesis have expanded their applications in disease research, drug development, and vaccine development. Clinically, peptide-based drugs now address cancer, hepatitis, diabetes, and HIV/AIDS.
-
 BA9695 D-GlucalSummary: D-Glucal is an organic compound belonging to the family of aldoses, which are monosaccharides containing an aldehyde functional group.
BA9695 D-GlucalSummary: D-Glucal is an organic compound belonging to the family of aldoses, which are monosaccharides containing an aldehyde functional group. -
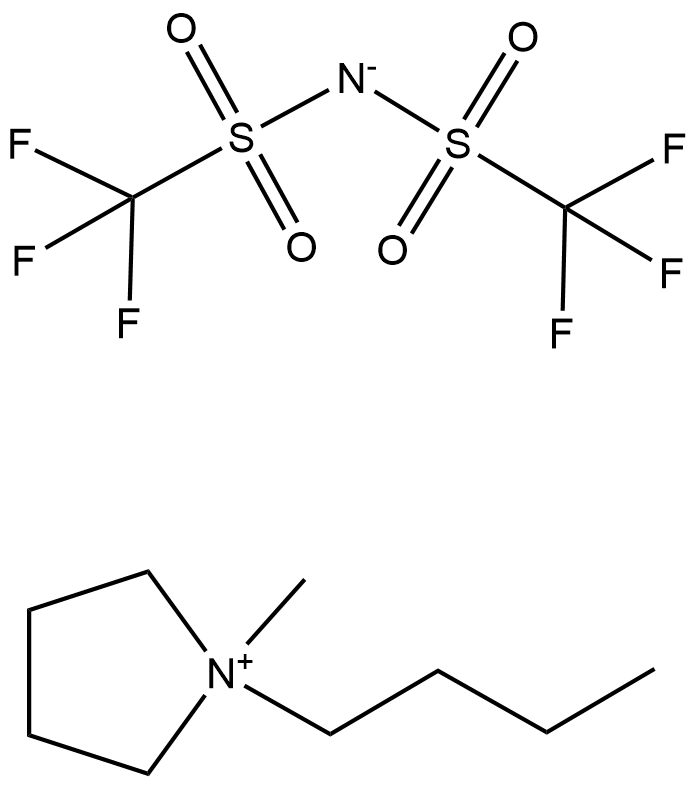 BA9698 PYR14-TFSISummary: PYR14-TFSI is a room temperature ionic liquid (RTIL).
BA9698 PYR14-TFSISummary: PYR14-TFSI is a room temperature ionic liquid (RTIL). -
 BA9714 L-DithiothreitolSummary: L-Dithiothreitol (DTT) is a reducing agent commonly used in various biochemical applications to break disulfide bonds in proteins in order to denature them or prevent the formation of unwanted aggregates.
BA9714 L-DithiothreitolSummary: L-Dithiothreitol (DTT) is a reducing agent commonly used in various biochemical applications to break disulfide bonds in proteins in order to denature them or prevent the formation of unwanted aggregates. -
 BA9723 Fullerene-C60Summary: Fullerene-C60, a representative of carbon nanocompounds, has the potential to be used in photodynamic studies due to its unique physicochemical properties.
BA9723 Fullerene-C60Summary: Fullerene-C60, a representative of carbon nanocompounds, has the potential to be used in photodynamic studies due to its unique physicochemical properties. -
 BA9734 MC-1-F2Summary: MC-1-F2 is an inhibitor that reduces epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) labeling, inhibits cancer stem cell (CSC) properties, and decreases invasiveness of denuded resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) cell lines in breast cancer cell lines.
BA9734 MC-1-F2Summary: MC-1-F2 is an inhibitor that reduces epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) labeling, inhibits cancer stem cell (CSC) properties, and decreases invasiveness of denuded resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) cell lines in breast cancer cell lines. -
 BA9741 IopentolSummary: A non-ionic intravascular contrast agent.
BA9741 IopentolSummary: A non-ionic intravascular contrast agent. -
 BA9744 G3-CNPSummary: G3-CNP is an alpha-amylase substrate.
BA9744 G3-CNPSummary: G3-CNP is an alpha-amylase substrate. -
 BA9746 KaolinSummary: Kaolin is used as a pharmaceutical excipient.
BA9746 KaolinSummary: Kaolin is used as a pharmaceutical excipient. -
 BA9763 VIPhybSummary: VIPAntagonist (compound VIPhyb) is a vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor antagonist.
BA9763 VIPhybSummary: VIPAntagonist (compound VIPhyb) is a vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor antagonist. -
 BA9772 AncymidolSummary: Ancymidol is a biochemical reagent.
BA9772 AncymidolSummary: Ancymidol is a biochemical reagent.


