Tyrosine Kinase
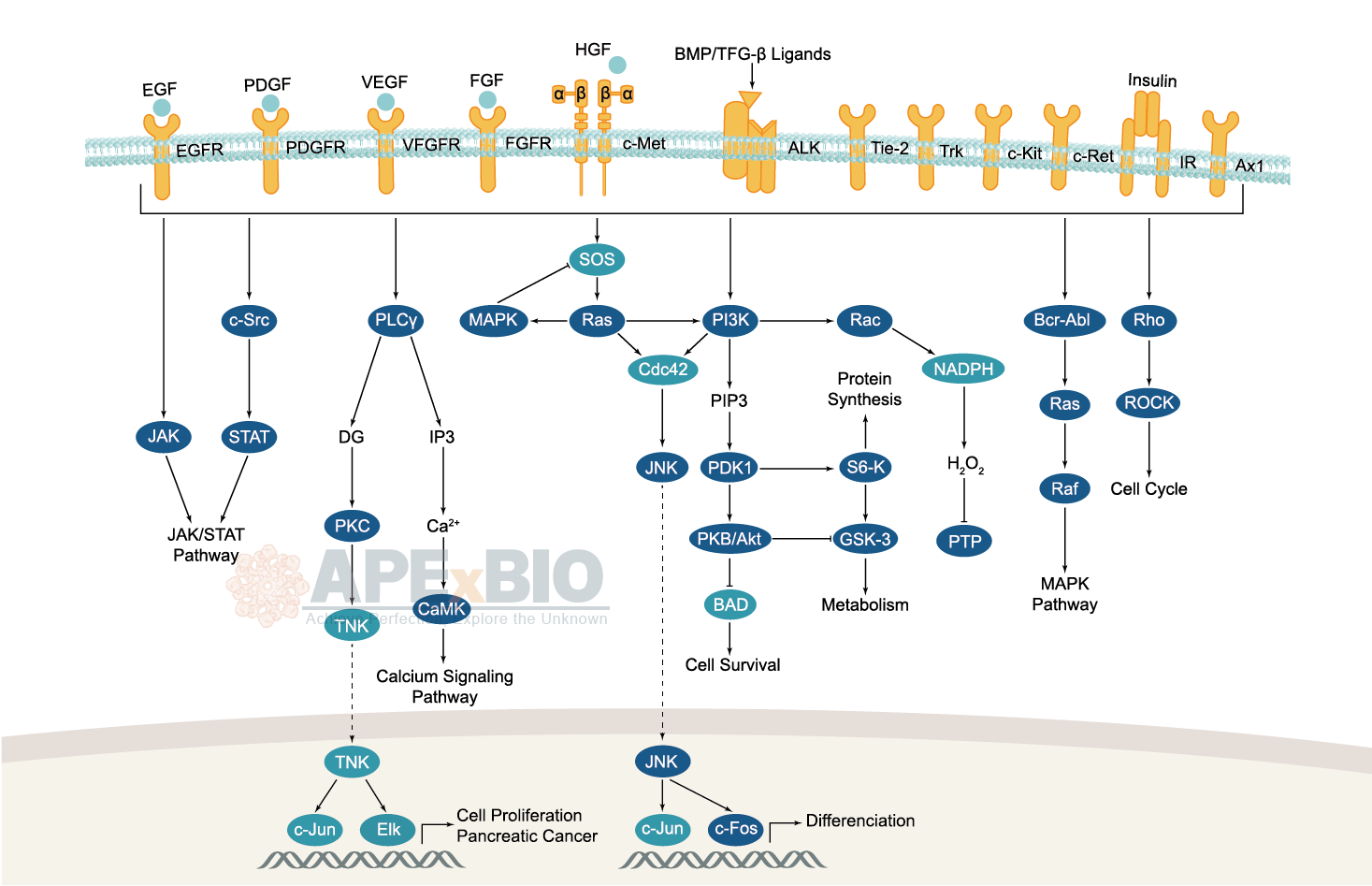

Receptor tyrosine kinases bind to extracellular ligands/growth factors, which promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine residues. This triggers a cascade of downstream events through phosphorylation of intracellular proteins that ultimately transduce the extracellular signal to the nucleus, causing changes in gene expression. Receptor tyrosine kinases include EGFR/ErbB, PDGFR, VEGFR, FGFR and MET subfamilies etc. Dysfunctions in tyrosine phosphorylation are linked to oncogenic transformation. In additions, various adaptor and effector proteins couple to carboxy-terminal of an active kinase. For instance, binding of the GRB2 adaptor protein activates EGFR and MAPK/ERK signaling.
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases involve many well-defined proteins (e.g. the Src family kinases, c-Abl, and Jak kinases) and other kinases which regulates cell growth and differentiation. For example, Src family kinases are curial for activating and inhibitory pathways in the innate immune response.
-
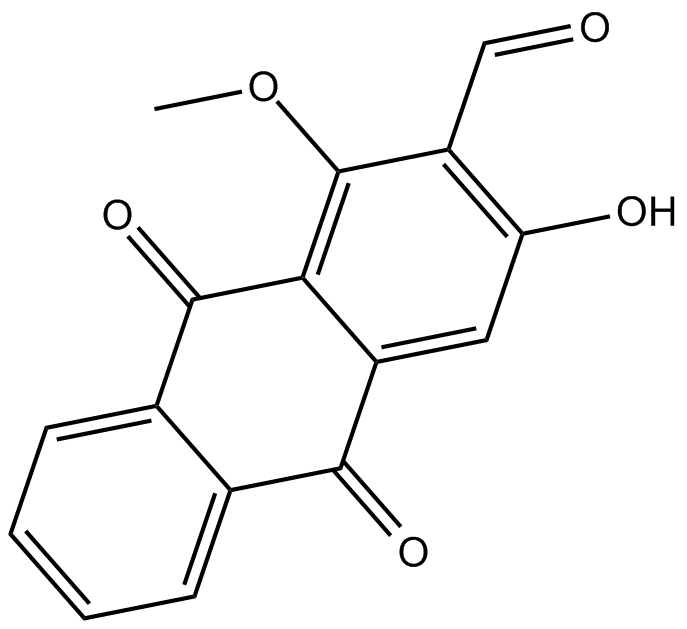 B6891 DamnacanthalSummary: p56lck tyrosine kinase inhibitor
B6891 DamnacanthalSummary: p56lck tyrosine kinase inhibitor -
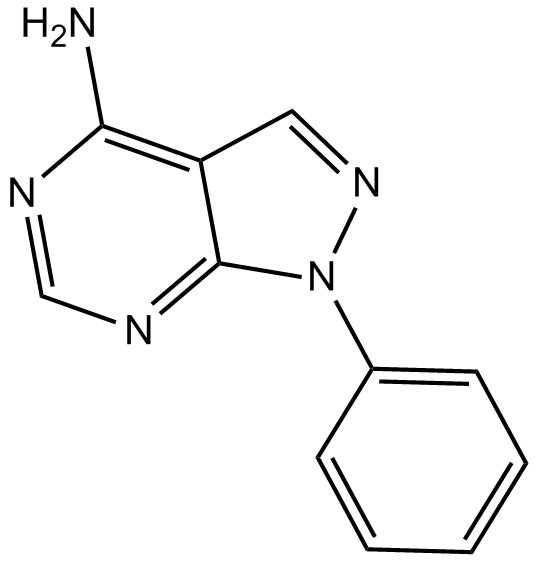 B7190 PP 31 CitationSummary: Negative control for the Src kinase inhibitor PP 2
B7190 PP 31 CitationSummary: Negative control for the Src kinase inhibitor PP 2 -
 B7407 Insulin (human) recombinant expressed in yeastTarget: Insulin ReceptorsSummary: Endogenous insulin receptor agonist
B7407 Insulin (human) recombinant expressed in yeastTarget: Insulin ReceptorsSummary: Endogenous insulin receptor agonist -
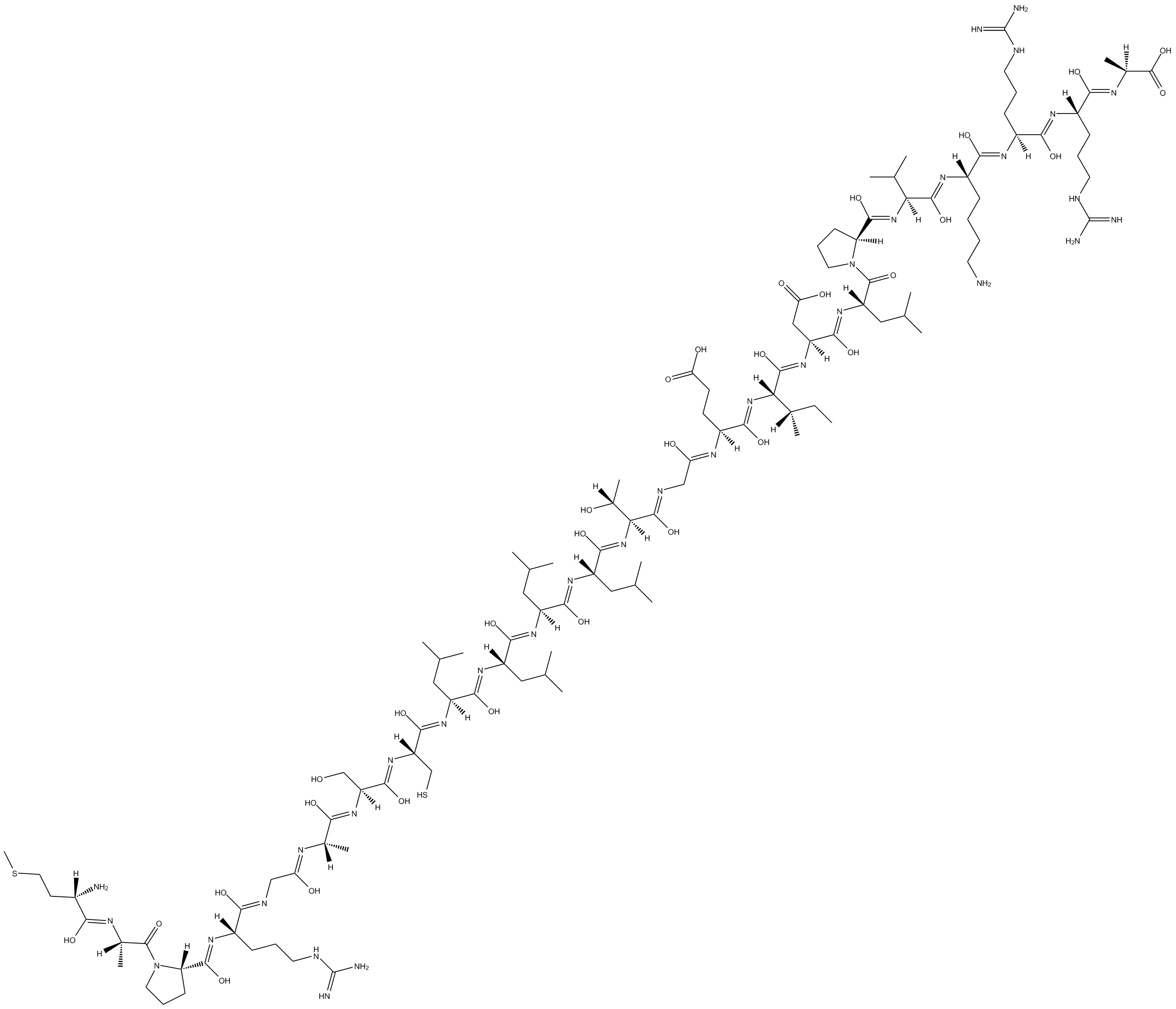 B7764 HNGF6ASummary: increases glucose stimulated insulin secretion and glucose metabolism
B7764 HNGF6ASummary: increases glucose stimulated insulin secretion and glucose metabolism -
 B5257 NTR 368Summary: cytoplasmic peptide of the neurotrophin receptor p75NTR
B5257 NTR 368Summary: cytoplasmic peptide of the neurotrophin receptor p75NTR -
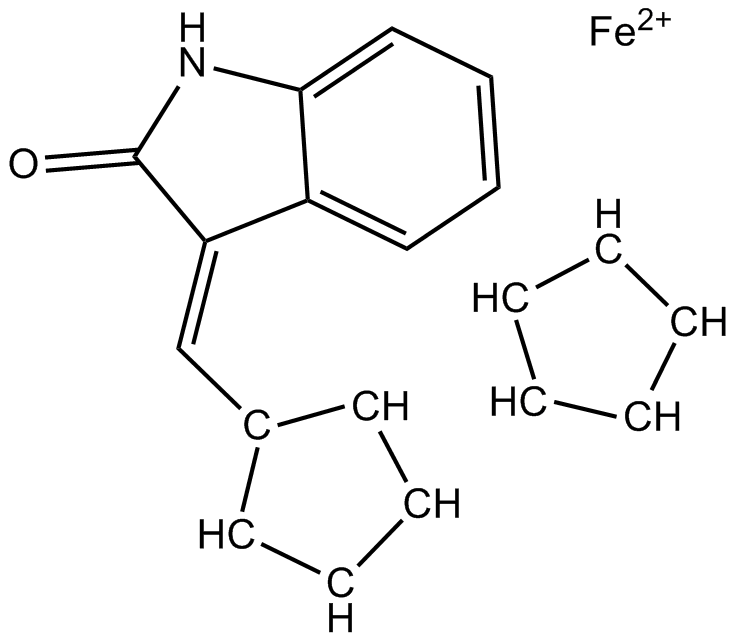 B5490 (E)-FeCP-oxindoleSummary: VEGFR-2 inhibitor
B5490 (E)-FeCP-oxindoleSummary: VEGFR-2 inhibitor -
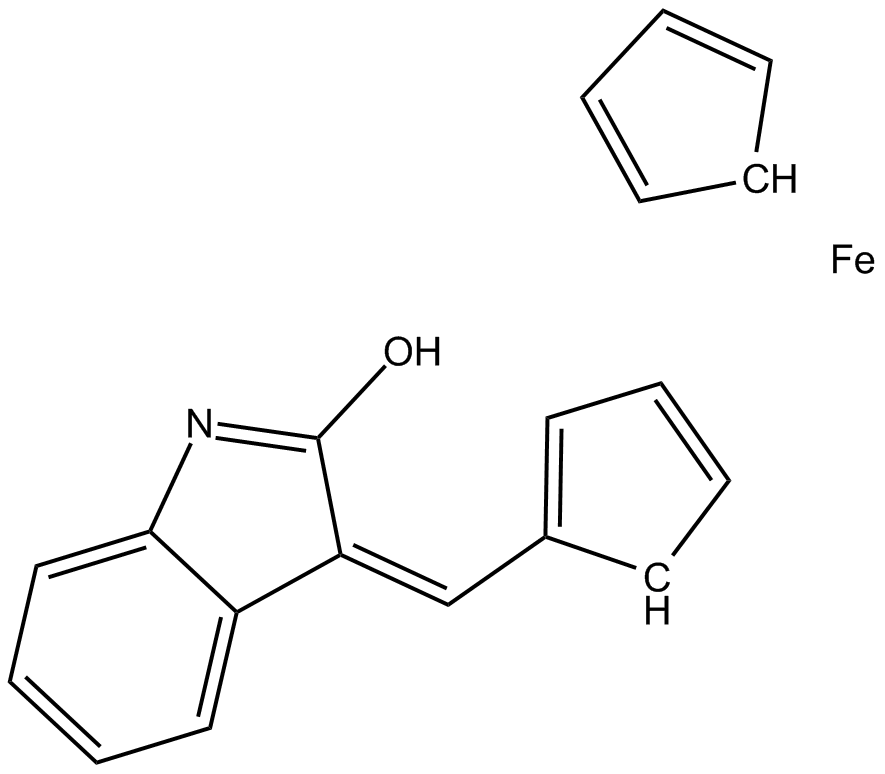 B5491 (Z)-FeCP-oxindoleSummary: VEGFR-2 inhibitor
B5491 (Z)-FeCP-oxindoleSummary: VEGFR-2 inhibitor -
 B5792 BMS 599626 dihydrochlorideSummary: EGFR and ErbB2 inhibitor,potent and selective
B5792 BMS 599626 dihydrochlorideSummary: EGFR and ErbB2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
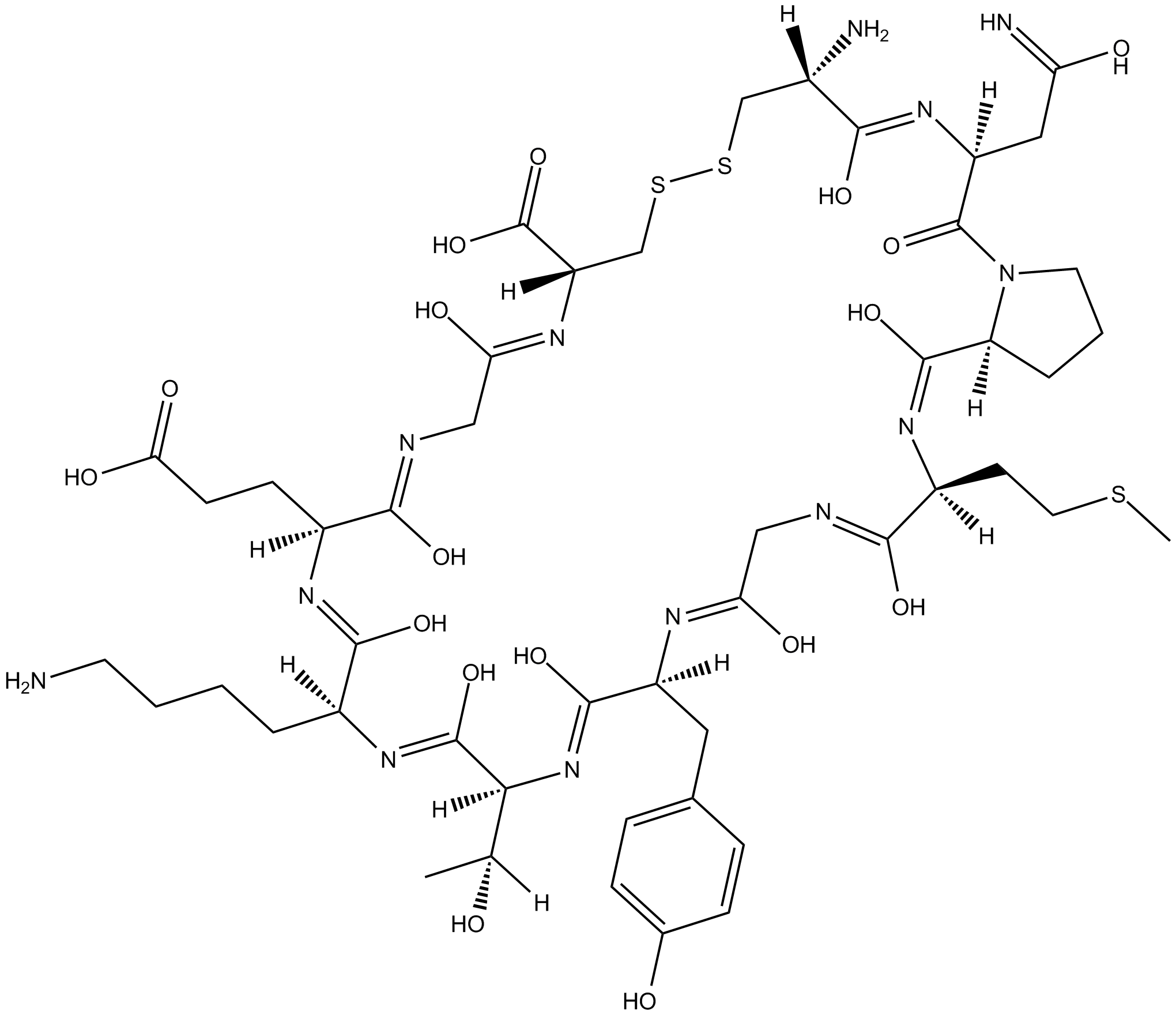 B5801 Cyclotraxin BSummary: TrkB receptor antagonist
B5801 Cyclotraxin BSummary: TrkB receptor antagonist -
 A8197 Compound 561 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: REGFR inhibitor
A8197 Compound 561 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: REGFR inhibitor


