Teriflunomide
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 270.21 |
| Cas No. | 108605-62-5 |
| Formula | C12H9F3N2O2 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥13.5 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥2.54 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming and ultrasonic |
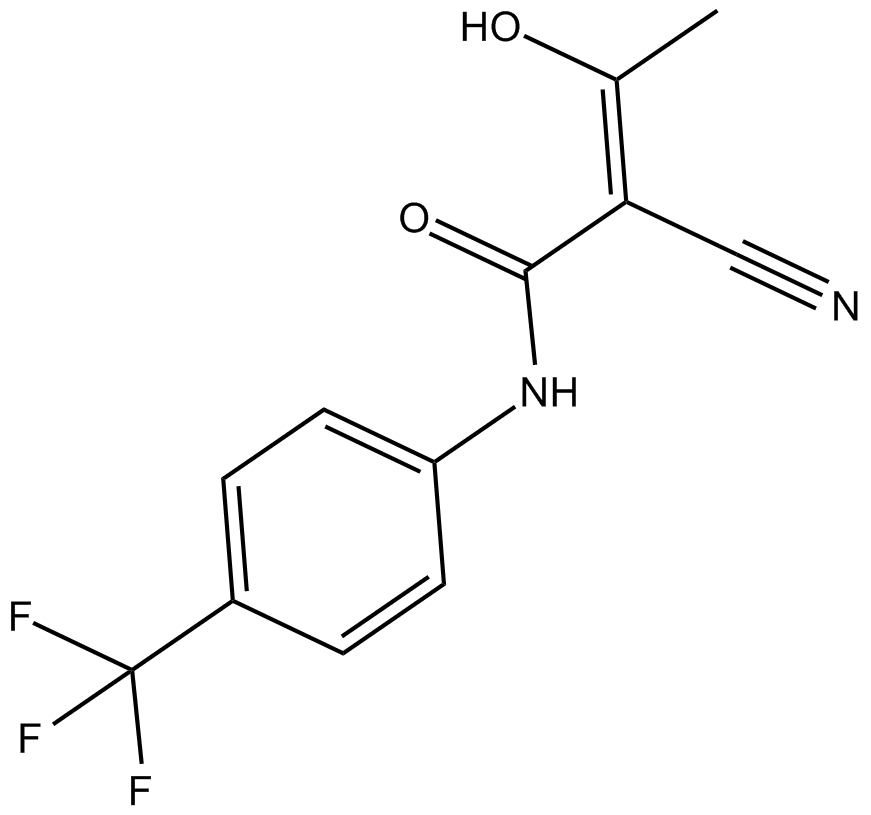
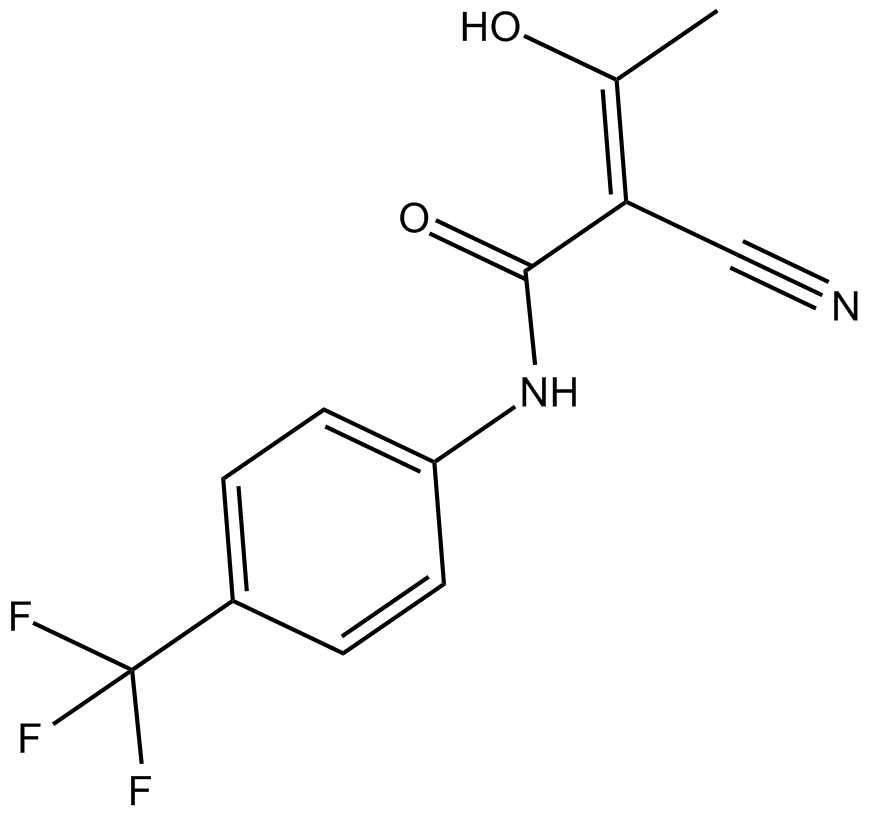
| Chemical Name | (Z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]but-2-enamide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(O)=C(C(Nc1ccc(C(F)(F)F)cc1)=O)C#N |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Human synoviocytes |
|
Reaction Conditions |
10-7 ~ 10-4 M teriflunomide for 50 h incubation |
|
Applications |
Teriflunomide inhibited the production of prostaglandin E2 in TNF-α- or IL-1α-stimulated isolated human synoviocytes (IC50s = 7 and 3 μM, respectively). At higher concentrations (> 10 μM), teriflunomide also reduced the production of matrix metalloproteinase 1 and IL-6 due to the known inhibitory effect of teriflunomide on pyrimidine synthesis, which could be reversed by the addition of uridine. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Male Dark Agouti (DA) rat, 6-week old |
|
Dosage form |
3 and 10 mg/kg Once daily by oral route |
|
Applications |
Teriflunomide (3 and 10 mg/kg) delayed disease onset and decreased neurological deficits in a rat model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced by complete Freund’s adjuvant and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Burger D, Begué-Pastor N, Benavent S, et al. The active metabolite of leflunomide, A77 1726, inhibits the production of prostaglandin E(2), matrix metalloproteinase 1 and interleukin 6 in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2003, 42(1): 89-96. 2. McMonagle-Strucko K. Teriflunomide reduces behavioral, electrophysiological, and histopathological deficits in the Dark Agouti rat model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Neurology, 2009, 256(1): 89-103. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure