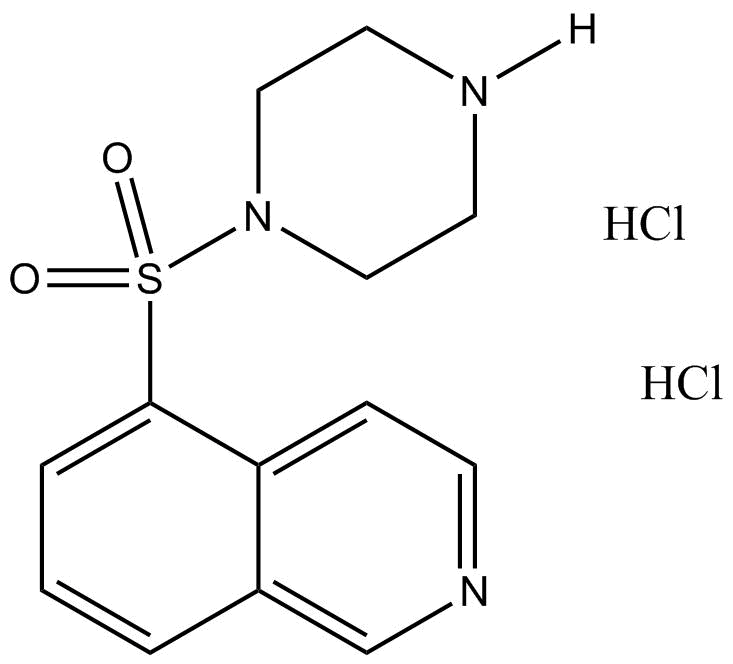
HA-100 (hydrochloride)
HA-100 is a dechlorinated analogue of 1-(8-chloro-5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)piperazine (HA-156). HA-100 is an inhibitor of protein kinases (PKs) including PKA, PKC, and PKG [1].
Protein kinases are enzymes that can phosphorylate other proteins. Phosphorylation of proteins usually results in a functional change of the target protein (substrate) by changing enzyme activity, cellular location, or association with other proteins. Protein kinases operate in a large number of distinct signaling pathways, especially those involved in signal transduction. Protein kinases have also existed in bacteria and plant [2].
HA-100 inhibited the activity of PKA, PKC, and PKG with the IC50 values of 8, 12, and 4 μM, respectively. It showed less activity in blocking the activity of myosin light chain kinase with the IC50 of 240 μM [1]. HA-100 markedly decreased the affinity for MLC-kinase. HA-100 did not inhibit myosin light chain phosphorylation in platelets exposed to collagen significantly [1].
Reference:
[1] Hagiwara M, Inagaki M, Watanabe M, et al. Selective modulation of calcium-dependent myosin phosphorylation by novel protein kinase inhibitors, isoquinolinesulfonamide derivatives[J]. Molecular pharmacology, 1987, 32(1): 7-12.
[2] Krebs E G. Protein kinases[J]. Current topics in cellular regulation, 1972, 5: 99-133.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 350.3 |
| Cas No. | 210297-47-5 |
| Formula | C13H15N3O2S·2HCl |
| Synonyms | C-1 |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥131.8 mg/mL in H2O; ≥19.17 mg/mL in DMSO with ultrasonic |
| Chemical Name | 5-(1-piperazinylsulfonyl)-isoquinoline, dihydrochloride |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=S(c1cccc2c1ccnc2)(N1CCNCC1)=O.Cl.Cl |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure