Search results for: 'signaling pathways angiogenesis'
-
 L1047 DiscoveryProbe™ Angiogenesis LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 84 small molecule compounds for angiogenesis research.
L1047 DiscoveryProbe™ Angiogenesis LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 84 small molecule compounds for angiogenesis research. -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
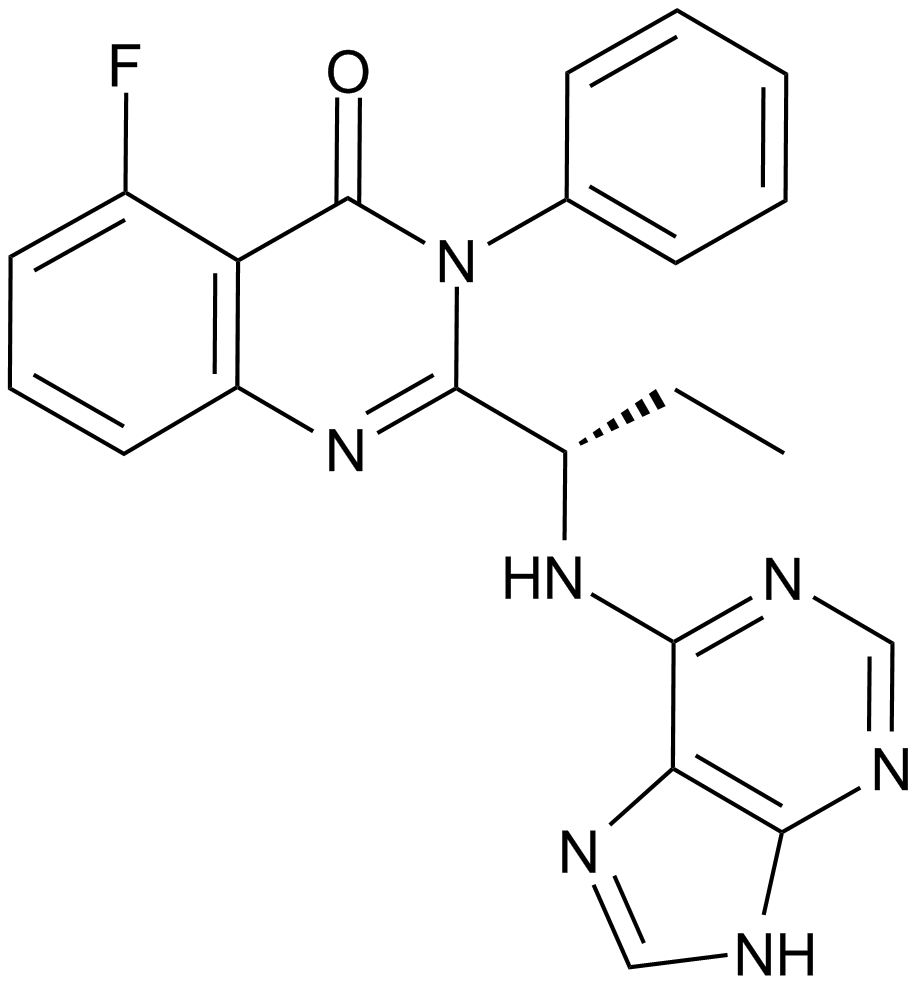 A3005 CAL-101 (Idelalisib, GS-1101)8 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: PI3K inhibitor
A3005 CAL-101 (Idelalisib, GS-1101)8 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: PI3K inhibitor -
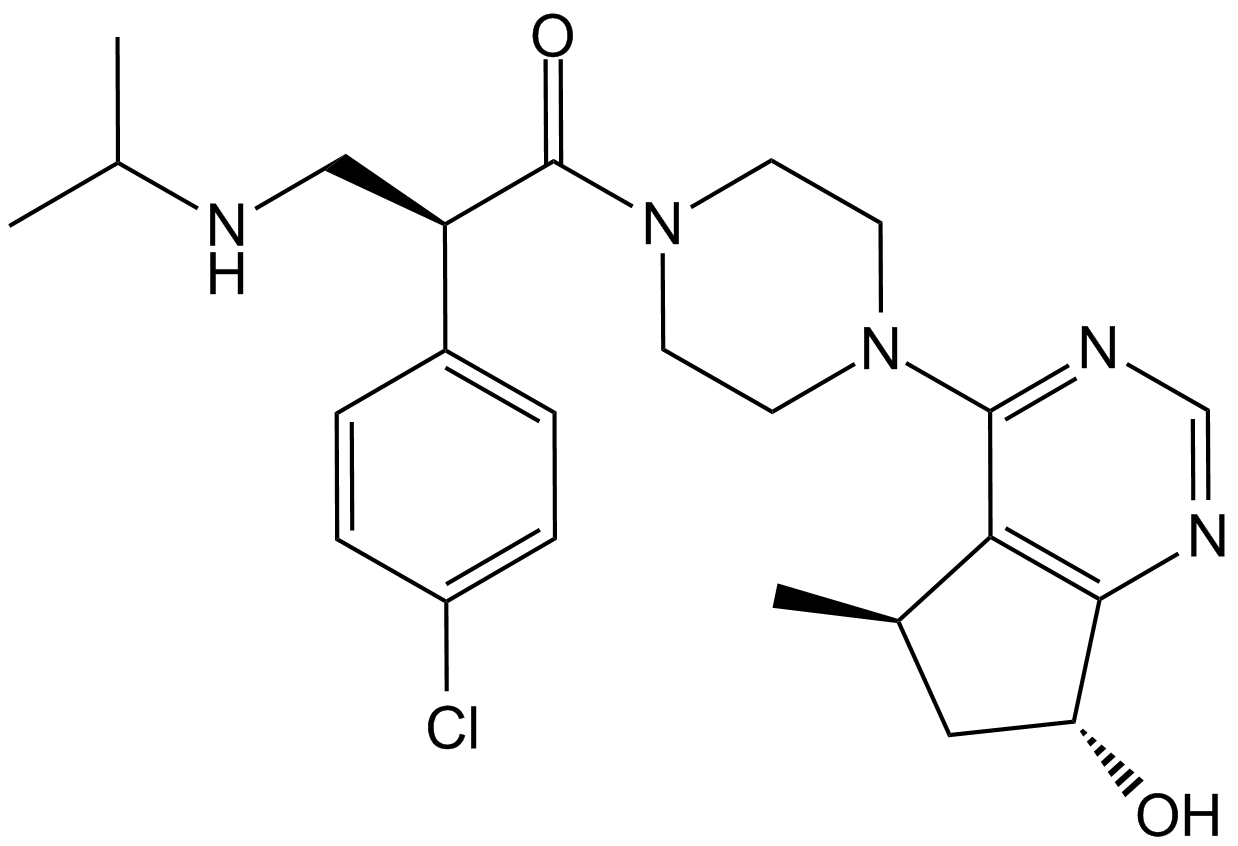 A3006 GDC-0068 (RG7440)2 CitationTarget: AktSummary: Pan-AKT inhibitor,highly selective
A3006 GDC-0068 (RG7440)2 CitationTarget: AktSummary: Pan-AKT inhibitor,highly selective -
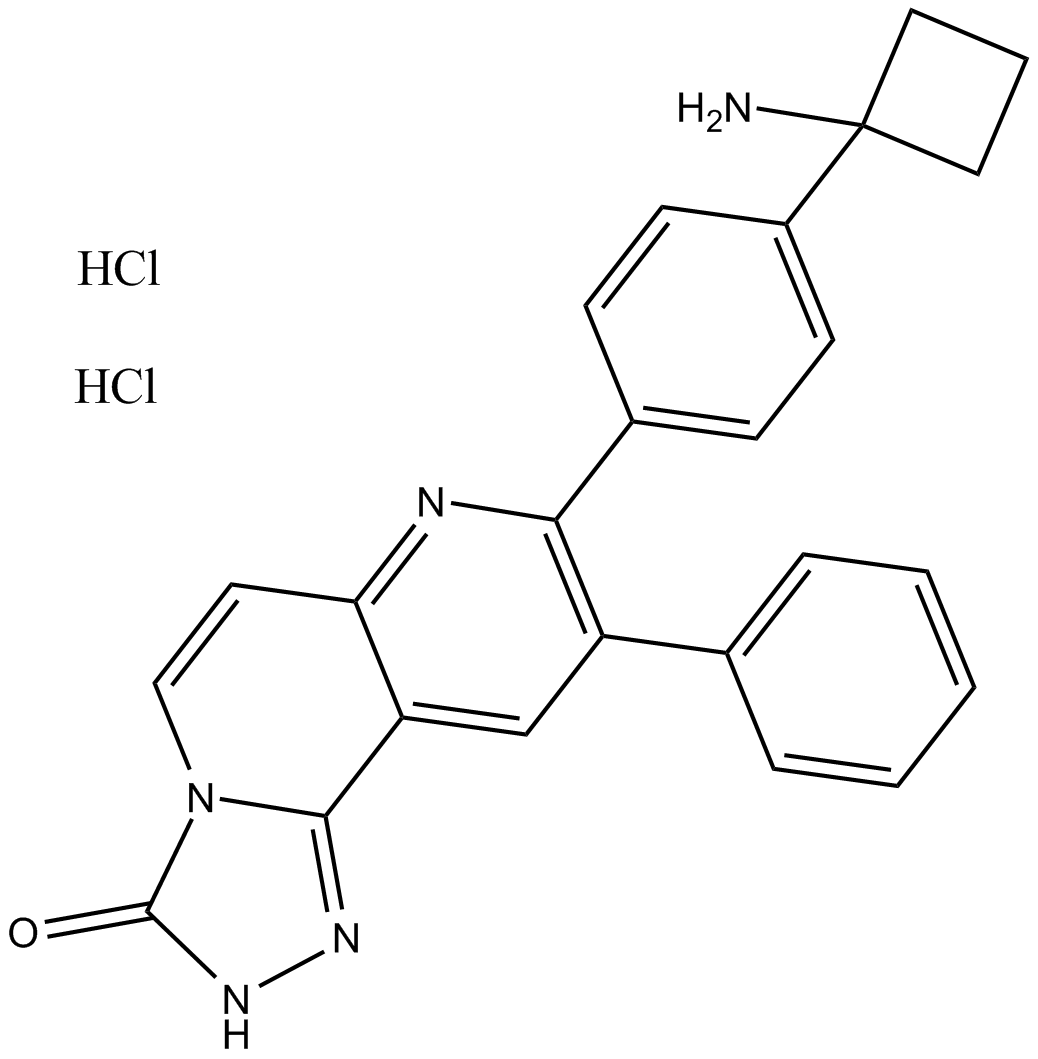 A3010 MK-2206 dihydrochloride51 CitationTarget: AktSummary: Akt1/2/3 inhibitor
A3010 MK-2206 dihydrochloride51 CitationTarget: AktSummary: Akt1/2/3 inhibitor -
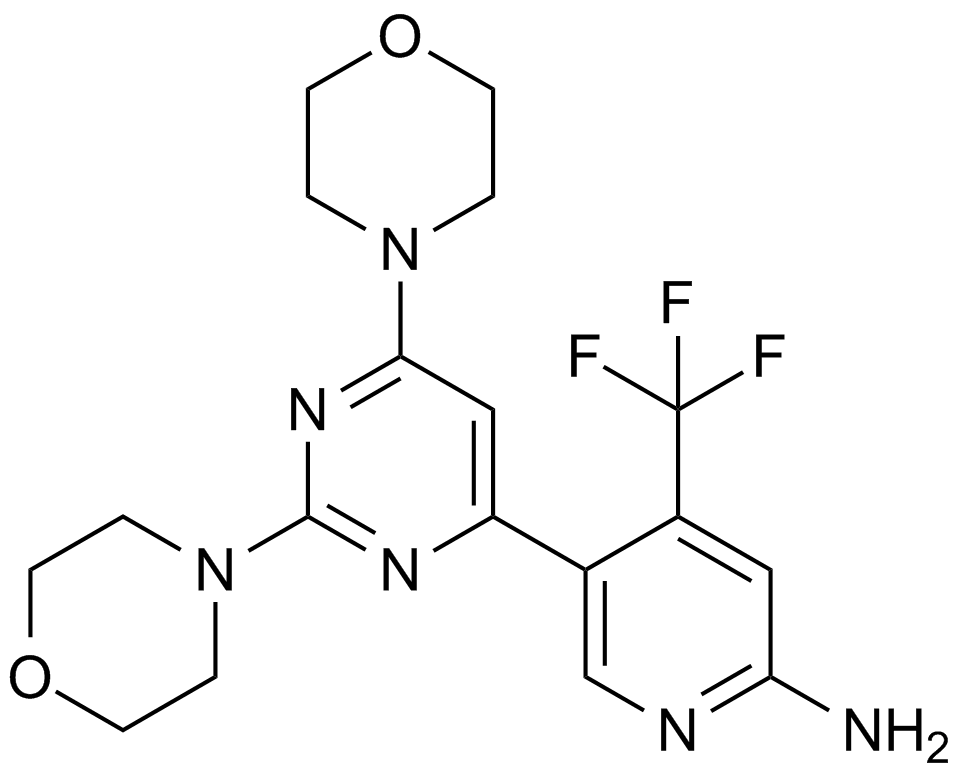 A3015 BKM1203 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Inhibitor of pan-Class I PI3K
A3015 BKM1203 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Inhibitor of pan-Class I PI3K -
 A3135 A-443654Summary: Akt inhibitor,potent and selective
A3135 A-443654Summary: Akt inhibitor,potent and selective


