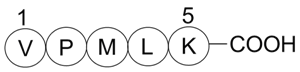
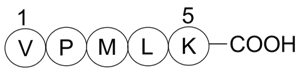
Bax inhibitor peptide V5
Bax inhibitor peptide V5 (BIP V5) is a peptide inhibitor of Bax translocation to mitochondria [1].
Bax is a pro-apoptotic member of Bcl-2 family proteins and plays an important role in mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Bax stays in the cytosol and transfers into mitochondria after apoptotic stimuli [1].
BIP V5 is a membrane-permeable peptide inhibitor of Bax translocation to mitochondria. In HeLa cells, BIP V5 protected cells from UVC- and STS-induced apoptosis. In U87-MG glioma cells, MCF-7 breast cancer cells and LNCaP prostate cancer cells, BIP V5 also inhibited apoptosis induced by anti-cancer drugs cisplatin, etoposide and doxorubicin. While BIP V5 did not suppress UVC- or STS-induced apoptosis in Bax-deficient cells (DU145), which suggested BIP V5 only suppressed Bax-mediated apoptosis. Also, BIP (V5) inhibited Bax translocation to mitochondria stimulated by UVC irradiation and STS treatment. The caspase activation and the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria triggered by apoptotic stimuli were also significantly inhibited by BIP V5. BIP V5 inhibited the interaction of Ku70 and endogenous Bax in a dose-dependent way [1].
In a mouse model, BIP V5 increased expression of anti-apoptotic proteins XIAP and Bcl-2 by more than 11- and 3-fold and reduced expression of apoptosis-inducing proteins Bax, Bad, and nuclear factor-κ B-p65 by 10, 30, and nearly 50%, respectively. Also, BIP V5 increased glucose-responsive insulin secretion [2].
References:
[1]. Sawada M, Hayes P, Matsuyama S. Cytoprotective membrane-permeable peptides designed from the Bax-binding domain of Ku70. Nat Cell Biol, 2003, 5(4): 352-357.
[2]. Rivas-Carrillo JD, Soto-Gutierrez A, Navarro-Alvarez N, et al. Cell-permeable pentapeptide V5 inhibits apoptosis and enhances insulin secretion, allowing experimental single-donor islet transplantation in mice. Diabetes, 2007, 56(5): 1259-1267.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 586.79 |
| Cas No. | 579492-81-2 |
| Formula | C27H50N6O6S |
| Solubility | ≥29.35 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥91.4 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | (S)-6-amino-2-((Z)-((S)-2-((Z)-((S)-2-((Z)-(((S)-1-((S)-2-amino-3-methylbutanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)(hydroxy)methylene)amino)-1-hydroxy-4-(methylthio)butylidene)amino)-1-hydroxy-4-methylpentylidene)amino)hexanoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C[C@@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@]1([H])CCCN1C([C@](N)([H])C(C)C)=O)([H])CCSC)([H])/C(O)=N/[C@@](C(O)=O)([H])CCCCN)C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1,2]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Mouse islet isolation |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >24.1mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
0-100 μM, 24 h |
|
Applications |
Bax inhibitor peptide V5 (0-50 μM) reduced cell death in STF-cMyc cells but not in SW620 or NCI-H23 cells. BIP V5 does not result in any significant effect on cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. In mouse islet isolation, BIP V5 (100 μM) treatment upregulated expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and XIAP by more than 3- and 11-fold and downregulated expression of apoptosis-inducing proteins Bax, Bad, and nuclear factor-κB-p65 by 10, 30, and nearly 50%, respectively. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
Streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice |
|
Dosage form |
100 μmol/l |
|
Application |
Following transplantation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, 150 BIP V5-treated islet equivalents functioned as well as 450 control untreated islet equivalents in normalizing blood glucose. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Jo M J, Paek A R, Choi J S, et al. Regulation of cancer cell death by a novel compound, C604, in a c-Myc-overexpressing cellular environment[J]. European journal of pharmacology, 2015, 769: 257-265. [2]. Sawada M, Hayes P, Matsuyama S. Cytoprotective membrane-permeable peptides designed from the Bax-binding domain of Ku70. Nat Cell Biol, 2003, 5(4): 352-357. [2].Rivas-Carrillo JD, Soto-Gutierrez A, Navarro-Alvarez N, et al. Cell-permeable pentapeptide V5 inhibits apoptosis and enhances insulin secretion, allowing experimental single-donor islet transplantation in mice. Diabetes, 2007, 56(5): 1259-1267. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure